第10课 - struct和union分析
第10课 - struct和union分析

1. 空结构体
在C语言中,结构体表示一系列变量的的集合,那编译器如何处理空结构体呢?
一类编译器认为,既然你是空结构体,内部没有成员变量那结构体大小就为0,但是可以正常编译;另一类编译器认为,空结构体有悖于结构体设计的初衷,既然结构体是变量的集合但空结构体中却没有成员变量,所以编译直接报错。
使用不同的编译器编译下面的代码:
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 3 // 空结构体 4 struct Test{ 5 6 }; 7 8 int main() 9 { 10 struct Test t1; 11 struct Test t2; 12 13 printf("sizeof(struct Test) = %zu\n", sizeof(struct Test)); 14 15 printf("sizeof(t1) = %zu, &t1 = %p\n", sizeof(t1), &t1); 16 printf("sizeof(t2) = %zu, &t2 = %p\n", sizeof(t2), &t2); 17 18 return 0; 19 }
gcc编译器 ==> 编译通过,且空结构体的大小为0。
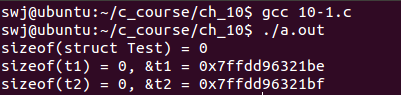
VS2010编译器 ==> 编译报错

BCC编译器 ==> 编译报错
2. 柔性数组
(1)柔性数组即数组大小待定的数组,如:int SoftArray[ ];
(2)C语言中可以由结构体产生柔性数组 // 柔性数组仅存在于结构体中
(3)C语言中结构体的最后一个元素可以是柔性数组 // 柔性数组必须为结构体的最后一个元素,否则编译报错:10-2.c:5:9: error: flexible array member not at end of struct
柔性数组:
1 struct SoftArray { 2 int len; 3 int array[]; // 结构体最后一个元素为柔性数组 4 };
第一次碰到柔性数组,不禁有两个疑问:① 柔性数组大小为多少,它表示什么?② 为什么需要柔性数组,它的用法是什么?
第一个疑问我们写代码测试一下便知道了
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 3 struct SoftArray { 4 int len; 5 int array[]; // 结构体最后一个元素为柔性数组 6 }; 7 8 int main() 9 { 10 struct SoftArray sa; 11 12 printf("sizeof(struct SoftArray) = %zu\n", sizeof(struct SoftArray)); 13 printf("&sa.len = %p, sa.array = %p\n", &sa.len, sa.array); 14 15 return 0; 16 }
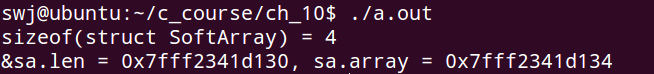
执行结果如下,可见 array 是不占用内存空间的,通过打印 len 和 array 的地址可以看出来,array 是一个标识符,标识结构体尾字节的下一个字节的地址。
第二个疑问通过唐老师的讲解,了解到柔性数组的用法
柔性数组的一般用法如下,通过柔性数组可以得到一个动态大小的数组。
1 struct SoftArray* sa = NULL; 2 sa = (struct SoftArray*)malloc(sizeof(struct SoftArray)+sizoef(int)*5); 3 sa->len = 5;
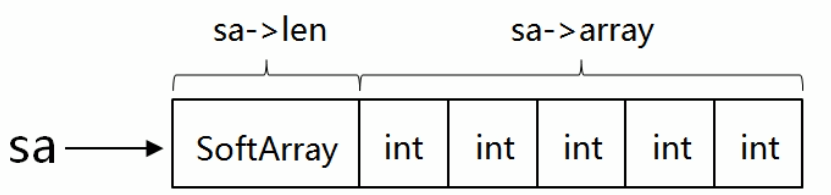
结构体的内存布局如下:
【柔性数组使用分析】
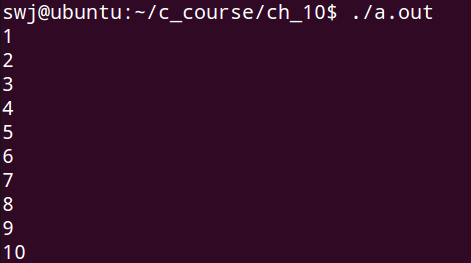
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <malloc.h> 3 4 struct SoftArray 5 { 6 int len; 7 int array[]; 8 }; 9 10 struct SoftArray* create_soft_array(int size) 11 { 12 struct SoftArray* ret = NULL; 13 14 if( size > 0 ) 15 { 16 ret = (struct SoftArray*)malloc(sizeof(struct SoftArray) + sizeof(int) * size); 17 18 ret->len = size; 19 } 20 21 return ret; 22 } 23 24 void delete_soft_array(struct SoftArray* sa) 25 { 26 free(sa); 27 } 28 29 void func(struct SoftArray* sa) 30 { 31 int i = 0; 32 33 if( NULL != sa ) 34 { 35 for(i=0; i<sa->len; i++) 36 { 37 sa->array[i] = i + 1; 38 } 39 } 40 } 41 42 int main() 43 { 44 int i = 0; 45 struct SoftArray* sa = create_soft_array(10); 46 47 func(sa); 48 49 for(i=0; i<sa->len; i++) 50 { 51 printf("%d\n", sa->array[i]); 52 } 53 54 delete_soft_array(sa); 55 56 return 0; 57 }
程序输出结果:
3. 共用体(union)
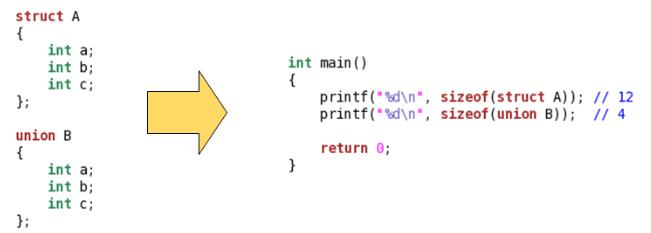
(1)C语言中的union在语法上与struct相似
(2)union只分配最大成员的空间,所有成员共享这个空间
(3)union的使用受系统大小端的影响
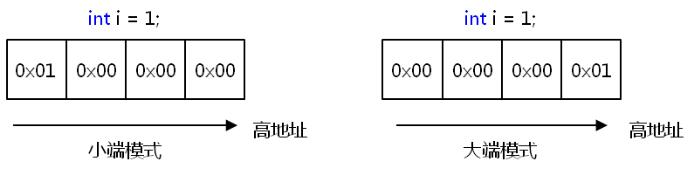
【判断系统的大小端】
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 3 int system_mode() 4 { 5 union SM 6 { 7 int i; 8 char c; 9 }; 10 11 union SM sm; 12 sm.i = 1; 13 return sm.c; 14 } 15 16 int main() 17 { 18 // 返回1时为小端,0为大端模式 19 printf("System Mode: %d\n", system_mode()); 20 return 0; 21 }



