python基础-类的起源
Python中一切事物都是对象。
class Foo(object): def __init__(self,name): self.name = name f = Foo("alex")
f对象是FOO类的一个实例,Foo类对象是type类的一个实例。
print(type(f))
print(type(foo))
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*- __author__ = 'shisanjun' class Foo(object): def func(self): print("hello world") f=Foo() print(type(f)) print(type(Foo)) """ <class '__main__.Foo'> <class 'type'> """ def func(self): print("特别定义") f1=type("Foo1",(object,),{"func":func}) print(type(f1))
类默认是由 type 类实例化产生,type类中如何实现的创建类?类又是如何创建对象?
答:类中有一个属性 __metaclass__,其用来表示该类由 谁 来实例化创建,所以,我们可以为 __metaclass__ 设置一个type类的派生类,从而查看 类 创建的过程。
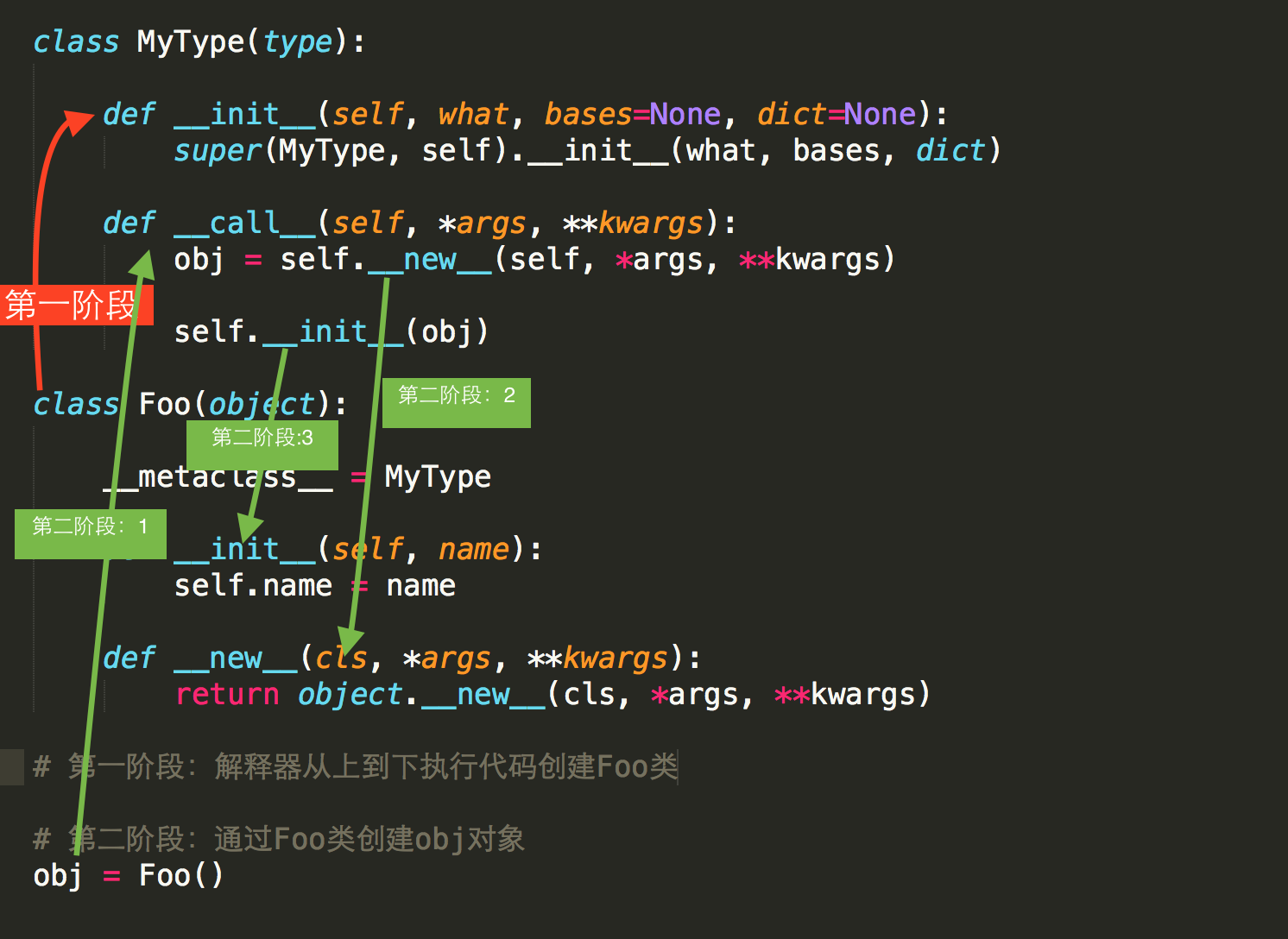
类的生成 调用 顺序依次是 __new__ --> __init__ --> __call__
class MyType(type): def __init__(self,*args,**kwargs): print("Mytype __init__",*args,**kwargs) def __call__(self, *args, **kwargs): print("Mytype __call__", *args, **kwargs) obj = self.__new__(self) print("obj ",obj,*args, **kwargs) print(self) self.__init__(obj,*args, **kwargs) return obj def __new__(cls, *args, **kwargs): print("Mytype __new__",*args,**kwargs) return type.__new__(cls, *args, **kwargs) print('here...') class Foo(object,metaclass=MyType): def __init__(self,name): self.name = name print("Foo __init__") def __new__(cls, *args, **kwargs): print("Foo __new__",cls, *args, **kwargs) return object.__new__(cls) f = Foo("Alex") print("f",f) print("fname",f.name) 自定义元类



