【数据结构与算法Python版学习笔记】树——利用二叉堆实现优先级队列
概念
- 队列有一个重要的变体,叫作优先级队列。
- 和队列一样,优先级队列从头部移除元素,不过元素的逻辑顺序是由优先级决定的。
- 优先级最高的元素在最前,优先级最低的元素在最后。
- 实现优先级队列的经典方法是使用叫作
二叉堆(Binary Heap)的数据结构。- 二叉堆的入队操作和出队操作均可达到O(log n)。
- 其逻辑结构上像二叉树, 却是用非嵌套的列表来实现的
- 二叉堆有两个常见的变体:
- 最小堆(最小的元素一直在队首)
- 最大堆(最大的元素一直在队首)
二叉堆的操作
-
BinaryHeap()新建一个空的二叉堆。 -
insert(k)往堆中加入一个新元素。 -
findMin()返回最小的元素,元素留在堆中。 -
delMin()返回最小的元素,并将该元素从堆中移除。 -
isEmpty()在堆为空时返回True,否则返回False。 -
size()返回堆中元素的个数。 -
buildHeap(list)根据一个列表创建堆。
用非嵌套列表实现二叉堆
结构属性
- 为了使堆操作能保持在对数水平上, 就必须采用二叉树结构;
- 同样, 如果要使操作始终保持在对数数量级上, 就必须始终保持二叉树的“平衡”
- 树根左右子树拥有相同数量的节点
- 我们采用“
完全二叉树”的结构来近似实现“平衡”
完全二叉树,叶节点最多只出现在最底层和次底层,而且最底层的叶节点都连续集中在最左边,每个内部节点都有两个子节点, 最多可有1个节点例外- 下标为p
- 左子节点下标为2p
- 右子节点为2p+1
- 父节点下标为p//2
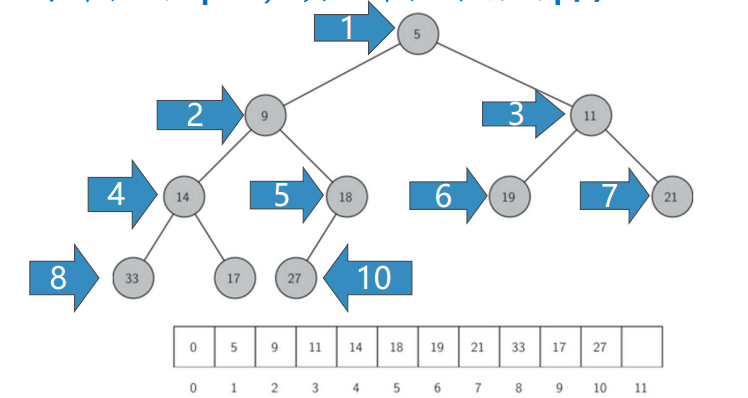
堆次序 Heap Order
- 任何一个节点x, 其父节点p中的key均小于x中的key
这样,符合“堆”性质的二叉树,其中任何一条路径,均是一个已排序数列, 根节点的key最小
二叉堆操作的实现
二叉堆初始化
- 采用一个列表来保存堆数据,其中表首下标为0的项无用,但为了后面代码可以用到简单的整数乘除法,仍保留它。
class BinHeap:
def __init__(self):
self.heapList=[0]
self.currentSize=0
insert(key)方法
- 新key加在列表末尾,显然无法保持“堆”次序虽然对其它路径的次序没有影响,但对于其到根的路径可能破坏次序
- 需要将新key沿着路径来“上浮”到其正确位置
- 注意:新key的“上浮”不会影响其它路径节点的“堆”次序
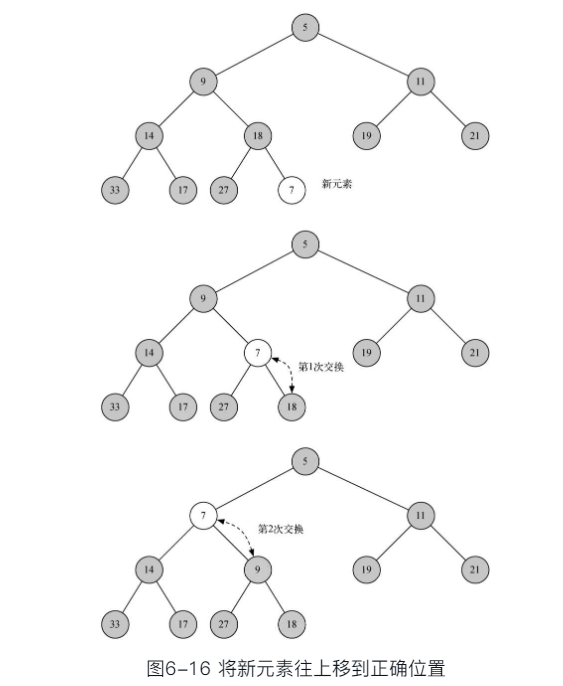
# 上浮
def percUp(self, i):
while i//2 > 0:
if self.heapList[i] < self.heapList[i//2]:
self.heapList[i], self.heapList[i //
2] = self.heapList[i//2], self.heapList[i]
i = i//2
def insert(self, k):
self.heapList.append(k)
self.currentSize += 1
self.percUp(self.currentSize)
delMin()方法
- 移走整个堆中最小的key:根节点heapList[1]
- 为了保持“完全二叉树”的性质,只用最后一个节点来代替根节点.
- 将新的根节点沿着一条路径“下沉”,直到比两个子节点都小
- “下沉”路径的选择:如果比子节点大,那么选择较小的子节点交换下沉
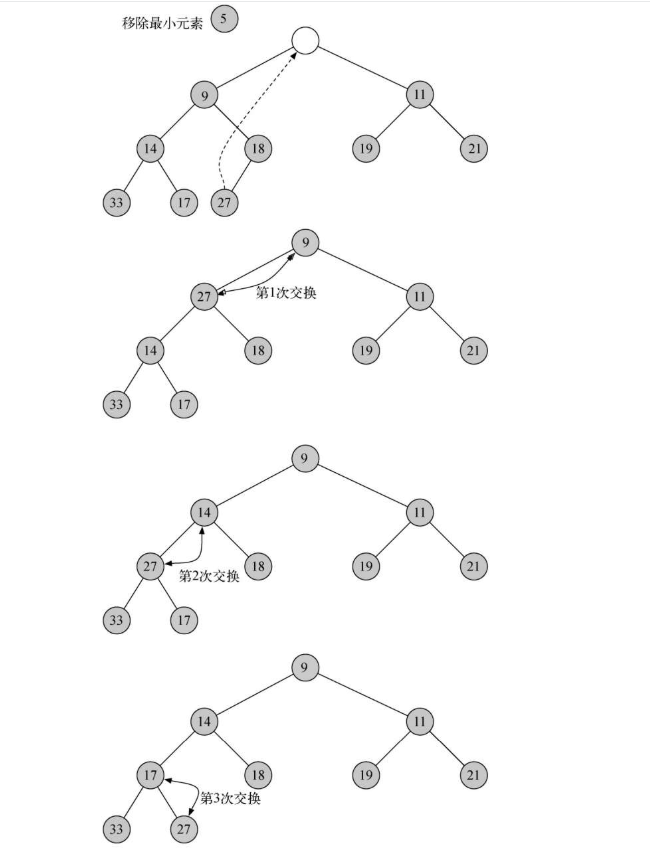
def percDown(self, i):
while(i*2) <= self.currentSize:
mc = self.minChild(i)
if self.heapList[i] > self.heapList(mc):
self.heapList[i], self.heapList[mc] = self.heapList[mc], self.heapList[i]
i = mc
def minChild(self, i):
if i*2+1 > self.currentSize:
return i*2
else:
if self.heapList[i*2] < self.heapList[i*2+1]:
return i*2
else:
return i*2+1
def delMin(self):
retval = self.heapList[1]
self.heapList[1] = self.heapList[self.currentSize]
self.currentSize -= 1
self.heapList.pop()
self.percDown(1)
return retval
buildHeap(lst)方法:从无序表生成“堆”
- 用insert(key)方法,将无序表中的数据项逐个insert到堆中,但这么做的总代价是O(nlog n)
- 其实,用“下沉”法,能够将总代价控制在O(n)
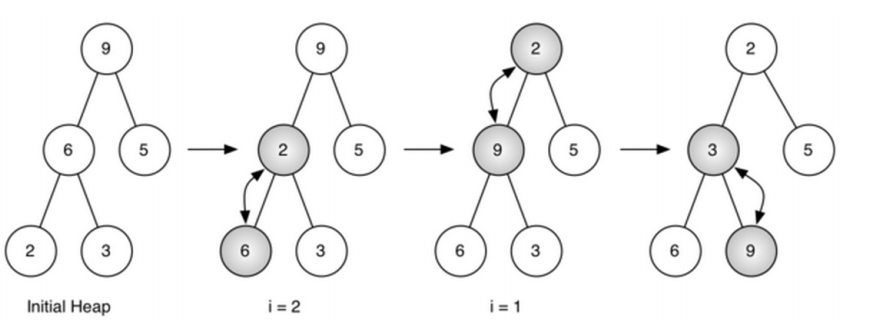
def buildHeap(self, alist):
i = len(alist)//2
self.currentSize = len(alist)
self.heapList = [0]+alist[:]
print(len(self.heapList), i)
while(i > 0):
print(self.heapList, i)
self.percDown(i)
i -= 1
print(self.heapList, i)
堆排序
- “堆排序”算法: O(nlog n)
二叉堆列表实现完整代码
class BinHeap:
def __init__(self):
self.heapList = [0]
self.currentSize = 0
# 上浮
def percUp(self, i):
while i//2 > 0:
if self.heapList[i] < self.heapList[i//2]:
self.heapList[i], self.heapList[i //
2] = self.heapList[i//2], self.heapList[i]
i = i//2
def insert(self, k):
self.heapList.append(k)
self.currentSize += 1
self.percUp(self.currentSize)
def percDown(self, i):
while(i*2) <= self.currentSize:
mc = self.minChild(i)
if self.heapList[i] > self.heapList(mc):
self.heapList[i], self.heapList[mc] = self.heapList[mc], self.heapList[i]
i = mc
def minChild(self, i):
if i*2+1 > self.currentSize:
return i*2
else:
if self.heapList[i*2] < self.heapList[i*2+1]:
return i*2
else:
return i*2+1
def delMin(self):
retval = self.heapList[1]
self.heapList[1] = self.heapList[self.currentSize]
self.currentSize -= 1
self.heapList.pop()
self.percDown(1)
return retval
def buildHeap(self, alist):
i = len(alist)//2
self.currentSize = len(alist)
self.heapList = [0]+alist[:]
print(len(self.heapList), i)
while(i > 0):
print(self.heapList, i)
self.percDown(i)
i -= 1
print(self.heapList, i)
作者:砥才人
出处:https://www.cnblogs.com/shiroe
本系列文章为笔者整理原创,只发表在博客园上,欢迎分享本文链接,如需转载,请注明出处!

