Caffe源码理解3:Layer基类与template method设计模式
博客:blog.shinelee.me | 博客园 | CSDN
写在前面
层的概念在深度神经网络中占据核心位置,给定输入,数据在层间运算流动,最终输出结果。层定义了对数据如何操作,根据操作的不同,可以对层进行划分(具体参见Caffe Layers):
- Data Layers:跟据文件类型和格式读取和处理数据,给网络输入
- Vision Layers:输入特征图输出也是特征图,像卷积、池化等
- Activation Layers:定义了逐元素的操作,输入输出shape相同,像ReLU、sigmoid等,
- Loss Layers:比较网络最终输出与目标的偏差,以缩小偏差为目的来驱动网络向目标学习,像Softmax with Loss等
- Common Layers:全连接层、dropout等
- Normalization Layers:归一化层,像LRN、MVN、BN等
- Utility Layers:特殊功能的层,像split、slice、concat等
注意,在Caffe中激活是单独的层,损失也是单独的层。所有这些层,都从一个共同的基类Layer继承而来,Layer定义了这些类共有的行为和数据部分,这篇文章的重点就是介绍这个基类。
Layer采用了template method设计模式,因此先介绍template method。
template method设计模式
template method设计模式,即在父类中定义好流程的框架,而流程中的某些步骤在子类中具体实现。下面以打开文件为例(例子来自侯捷老师),所有客户端软件打开文件的流程都是类似的,如下图所示,这个流程可以事先定义好,写在SDK里,但是,将来这个SDK要被用来打开什么类型的文件是SDK的设计者无法完全预测的,因此具体某个类型的文件该如何读取应由SDK的使用者来编写。
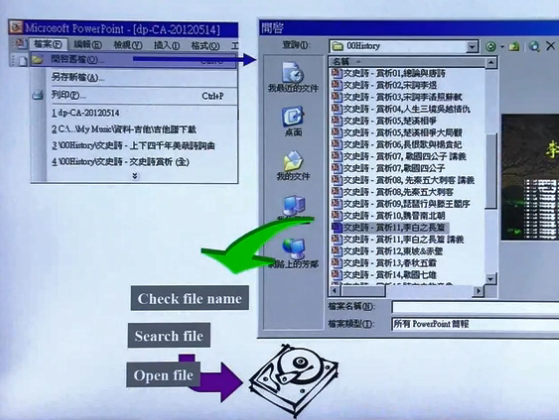
那么,SDK设计者定义的流程如何在执行到文件读取步骤时使用“将来”SDK使用者编写的程序?这就需要SDK的设计者将这个步骤设计为虚函数(关于虚函数可以查看cppreference.com),将来SDK的使用者继承这个类同时重写对应的虚函数,这种实现方法就是template method设计模式,其调用顺序如下图所示。
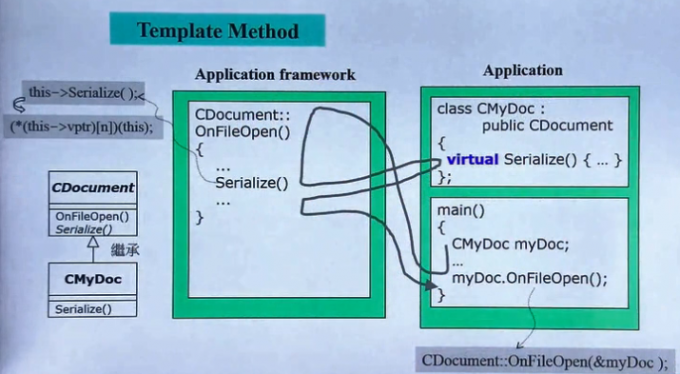
caffe中的基类Layer在设计时就采用了这种思想。
Layer 基类
Layer成员变量
先看一下Layer的成员变量,具体参看注释。
LayerParameter layer_param_; // 将protobuf中定义的该层的超参数等对象化存储
Phase phase_; // TRAIN or TEST,指示该层参与训练还是测试
vector<shared_ptr<Blob<Dtype> > > blobs_; // 存储可学习参数(权重)param blob
vector<bool> param_propagate_down_; // 指示每个param blob是否需要计算diff
vector<Dtype> loss_; // 存储top blob在损失函数中的权重loss_weight(与top blob数量相同),在反向传播时会作用在梯度上
// 对于损失层loss_weight默认为1(见LossLayer的LayerSetUp),其他层默认对损失函数没有直接贡献
层所拥有的是它的可学习参数部分,输入输出都不属于层,因此输入输出blob并不是层的成员变量,而只出现在接口上,层关注的是对数据的操作方式本身,这是设计时的考量。
构造与析构
构造与析构,Layer的子类不需要实现自己的构造函数,所有的set up操作应该在后面的SetUp函数中完成,构造函数中仅将纳入LayerParameter、设置pahse_以及写入初始网络权重(如果在protobuf文件中指定了的话)。
explicit Layer(const LayerParameter& param)
: layer_param_(param) {
// Set phase and copy blobs (if there are any).
phase_ = param.phase();
if (layer_param_.blobs_size() > 0) {
blobs_.resize(layer_param_.blobs_size());
for (int i = 0; i < layer_param_.blobs_size(); ++i) {
blobs_[i].reset(new Blob<Dtype>());
blobs_[i]->FromProto(layer_param_.blobs(i));
}
}
}
virtual ~Layer() {}
SetUp成员函数
SetUp是本文最为关注的成员函数,顾名思义,其负责完成层的基础搭建工作。在Net初始化时会顺序调用每个层的SetUp函数来搭建网络,见Net::Init,Net::Init利用多态+template method在一个循环中完成所有层的搭建。
// in Net::Init
for (int layer_id = 0; layer_id < param.layer_size(); ++layer_id) {
// ……
// After this layer is connected, set it up.
layers_[layer_id]->SetUp(bottom_vecs_[layer_id], top_vecs_[layer_id]);
// ……
}
// in net.hpp
/// @brief Individual layers in the net
vector<shared_ptr<Layer<Dtype> > > layers_;
SetUp在设计时就采用了template method设计思想,基类Layer为所有派生类的SetUp定义好了流程框架,先检查bottom和top的blob数量是否正确,然后调用LayerSetUp为完成层“个性化”的搭建工作(如卷积层会设置pad、stride等参数),再根据层自己定义的操作以及bottom的shape去计算top的shape,最后根据loss_weight设置top blob在损失函数中的权重。其中,Reshape为纯虚函数,子类必须自己实现,CheckBlobCounts和LayerSetUp为虚函数,提供了默认实现,子类也可以定义自己的实现。一般,SetUp的执行顺序为:
- 进入父类的
SetUp函数 - 执行父类的
CheckBlobCounts,在这个函数中会执行子类的ExactNumBottomBlobs等函数 - 执行子类的
LayerSetUp - 执行子类的
Reshape - 执行父类的
SetLossWeights - 退出父类的
SetUp函数
void SetUp(const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& bottom,
const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& top) {
CheckBlobCounts(bottom, top);
LayerSetUp(bottom, top);
Reshape(bottom, top);
SetLossWeights(top);
}
virtual void CheckBlobCounts(const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& bottom,
const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& top) {
// 实现具体省略
/* check that the number of bottom and top Blobs provided as input
match the expected numbers specified
by the {ExactNum,Min,Max}{Bottom,Top}Blobs() functions
*/
}
/* This method should do one-time layer specific setup. This includes reading
* and processing relevent parameters from the <code>layer_param_</code>.
* Setting up the shapes of top blobs and internal buffers should be done in
* <code>Reshape</code>, which will be called before the forward pass to
* adjust the top blob sizes.
*/
virtual void LayerSetUp(const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& bottom,
const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& top) {}
/* This method should reshape top blobs as needed according to the shapes
* of the bottom (input) blobs, as well as reshaping any internal buffers
* and making any other necessary adjustments so that the layer can
* accommodate the bottom blobs.
*/
virtual void Reshape(const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& bottom,
const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& top) = 0;
/**
* Called by SetUp to initialize the weights associated with any top blobs in
* the loss function. Store non-zero loss weights in the diff blob.
*/
inline void SetLossWeights(const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& top) {
const int num_loss_weights = layer_param_.loss_weight_size();
if (num_loss_weights) {
CHECK_EQ(top.size(), num_loss_weights) << "loss_weight must be "
"unspecified or specified once per top blob.";
for (int top_id = 0; top_id < top.size(); ++top_id) {
const Dtype loss_weight = layer_param_.loss_weight(top_id);
if (loss_weight == Dtype(0)) { continue; }
this->set_loss(top_id, loss_weight);
const int count = top[top_id]->count();
Dtype* loss_multiplier = top[top_id]->mutable_cpu_diff();
caffe_set(count, loss_weight, loss_multiplier);
}
}
}
Layer在设计之初无法料想到今天会有如此多各种各样的层,但是这些层只需要继承基类Layer,同时定义好各自个性化的LayerSetUp和Reshape等函数,就可以将自己纳入到SetUp的搭建流程,并通过Net::Init进一步纳入整个网络的搭建中。
前向传播与反向传播
Layer为所有层定义了前向传播与反向传播的通用接口Forward和Backward,实际上,Forward和Backward是Forward_cpu、Forward_gpu和Backward_cpu、Backward_gpu的包装器,子类需要定义自己的Forward_cpu、Forward_gpu和Backward_cpu、Backward_gpu,比如,卷积层前向传播要通过卷积操作,池化层前向传播时要通过池化操作,而不需要重写Forward和Backward。此外,如果子类不定义自己的gpu函数,默认的gpu函数实际调用的是cpu函数,如下面代码所示,所以如果要使用GPU,必须要自己实现Forward_gpu和Backward_gpu。
public:
inline Dtype Forward(const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& bottom,
const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& top);
inline void Backward(const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& top,
const vector<bool>& propagate_down,
const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& bottom);
protected:
virtual void Forward_cpu(const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& bottom,
const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& top) = 0;
virtual void Forward_gpu(const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& bottom,
const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& top) {
// LOG(WARNING) << "Using CPU code as backup.";
return Forward_cpu(bottom, top);
}
virtual void Backward_cpu(const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& top,
const vector<bool>& propagate_down,
const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& bottom) = 0;
virtual void Backward_gpu(const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& top,
const vector<bool>& propagate_down,
const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& bottom) {
// LOG(WARNING) << "Using CPU code as backup.";
Backward_cpu(top, propagate_down, bottom);
}
在下面代码中,注意Forward中的loss_weight的来源以及损失的计算。
template <typename Dtype>
inline Dtype Layer<Dtype>::Forward(const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& bottom,
const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& top) {
Dtype loss = 0;
Reshape(bottom, top);
switch (Caffe::mode()) {
case Caffe::CPU:
Forward_cpu(bottom, top);
for (int top_id = 0; top_id < top.size(); ++top_id) {
if (!this->loss(top_id)) { continue; }
const int count = top[top_id]->count();
const Dtype* data = top[top_id]->cpu_data();
const Dtype* loss_weights = top[top_id]->cpu_diff(); // 在损失函数中的权重
loss += caffe_cpu_dot(count, data, loss_weights);
}
break;
case Caffe::GPU:
Forward_gpu(bottom, top);
#ifndef CPU_ONLY
for (int top_id = 0; top_id < top.size(); ++top_id) {
if (!this->loss(top_id)) { continue; }
const int count = top[top_id]->count();
const Dtype* data = top[top_id]->gpu_data();
const Dtype* loss_weights = top[top_id]->gpu_diff();
Dtype blob_loss = 0;
caffe_gpu_dot(count, data, loss_weights, &blob_loss);
loss += blob_loss;
}
#endif
break;
default:
LOG(FATAL) << "Unknown caffe mode.";
}
return loss;
}
template <typename Dtype>
inline void Layer<Dtype>::Backward(const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& top,
const vector<bool>& propagate_down,
const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& bottom) {
switch (Caffe::mode()) {
case Caffe::CPU:
Backward_cpu(top, propagate_down, bottom);
break;
case Caffe::GPU:
Backward_gpu(top, propagate_down, bottom);
break;
default:
LOG(FATAL) << "Unknown caffe mode.";
}
}
其他成员函数
首先是成员变量的set和get函数:
virtual inline const char* type() const { return ""; } // return the layer type
inline void SetPhase(Phase p) { phase_ = p;}
vector<shared_ptr<Blob<Dtype> > >& blobs() { return blobs_;}
vector<Blob<Dtype>*> GetBlobs();
void SetBlobs(const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& weights);
inline Dtype loss(const int top_index) const;
inline void set_loss(const int top_index, const Dtype value);
const LayerParameter& layer_param() const { return layer_param_; }
inline bool param_propagate_down(const int param_id);
inline void set_param_propagate_down(const int param_id, const bool value);
ToProto将该层的参数设置以及学习到的权重序列化输出。
// Serialize LayerParameter to protocol buffer
template <typename Dtype>
void Layer<Dtype>::ToProto(LayerParameter* param, bool write_diff) {
param->Clear();
param->CopyFrom(layer_param_);
param->clear_blobs();
for (int i = 0; i < blobs_.size(); ++i) {
blobs_[i]->ToProto(param->add_blobs(), write_diff);
}
}
下面为供CheckBlobCounts使用的函数,根据层的需要自行定义,默认状态对top和bottom的blob数量不做要求。可见,其实CheckBlobCounts也采用了template method设计思想,只是这个函数没那么重要,按下不表。
virtual inline int ExactNumBottomBlobs() const { return -1; }
virtual inline int MinBottomBlobs() const { return -1; }
virtual inline int MaxBottomBlobs() const { return -1; }
virtual inline int MaxBottomBlobs() const { return -1; }
virtual inline int ExactNumTopBlobs() const { return -1; }
virtual inline int MinTopBlobs() const { return -1; }
virtual inline int MaxTopBlobs() const { return -1; }
virtual inline bool EqualNumBottomTopBlobs() const { return false; }
其他成员函数
/* If this method returns true, Net::Init will create enough "anonymous" top
* blobs to fulfill the requirement specified by ExactNumTopBlobs() or
* MinTopBlobs().
*/
virtual inline bool AutoTopBlobs() const { return false; }
/* If AllowForceBackward(i) == false, we will ignore the force_backward
* setting and backpropagate to blob i only if it needs gradient information
* (as is done when force_backward == false).
*/
virtual inline bool AllowForceBackward(const int bottom_index) const {
return true;
}
以上。


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号