JsonPath的使用
简介
JSONPath是一种用于选择JSON文档部分的查询语言。类似于XPath在xml文档中的定位,JsonPath表达式通常用来路径检索或设置Json。
JSONPath在线解析:http://jsonpath.com/
JSONPath语法
操作符
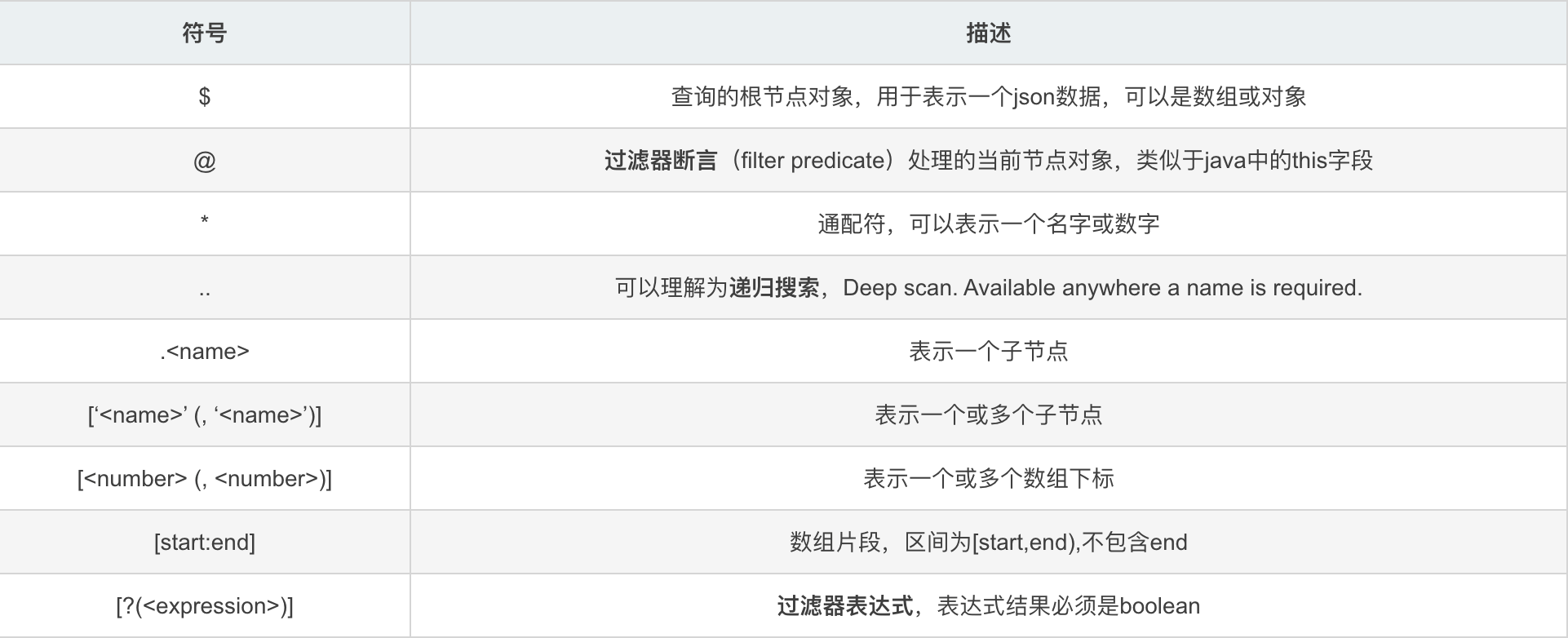
函数
可以在JsonPath表达式执行后进行调用,其输入值为表达式的结果。
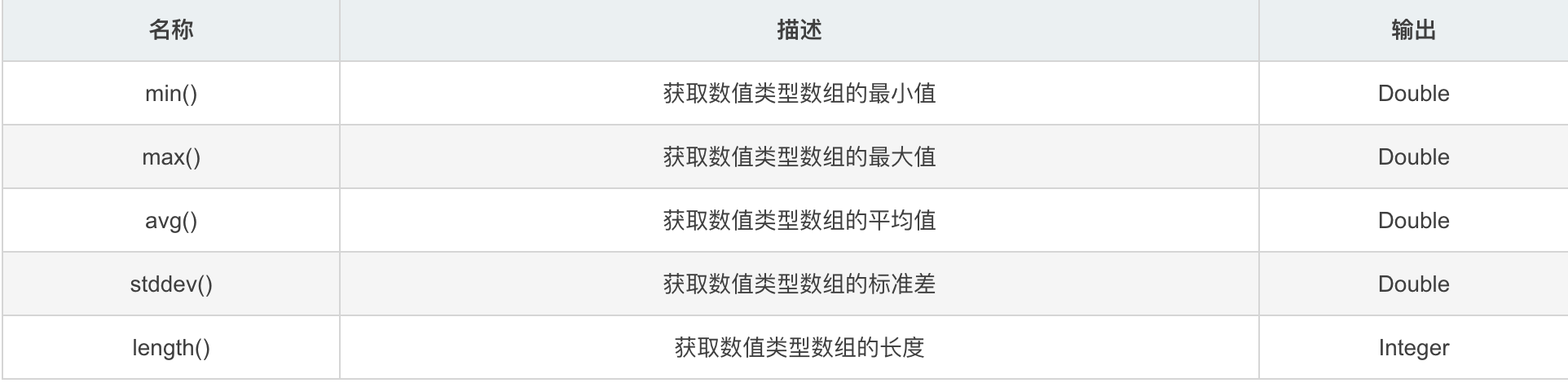
过滤器
过滤器是用于过滤数组的逻辑表达式,一个通常的表达式形如:[?(@.age > 18)],可以通过逻辑表达式&&或||组合多个过滤器表达式,例如[?(@.price < 10 && @.category == ‘fiction’)],字符串必须用单引号或双引号包围,例如[?(@.color == 'blue')] or [?(@.color == "blue")]。
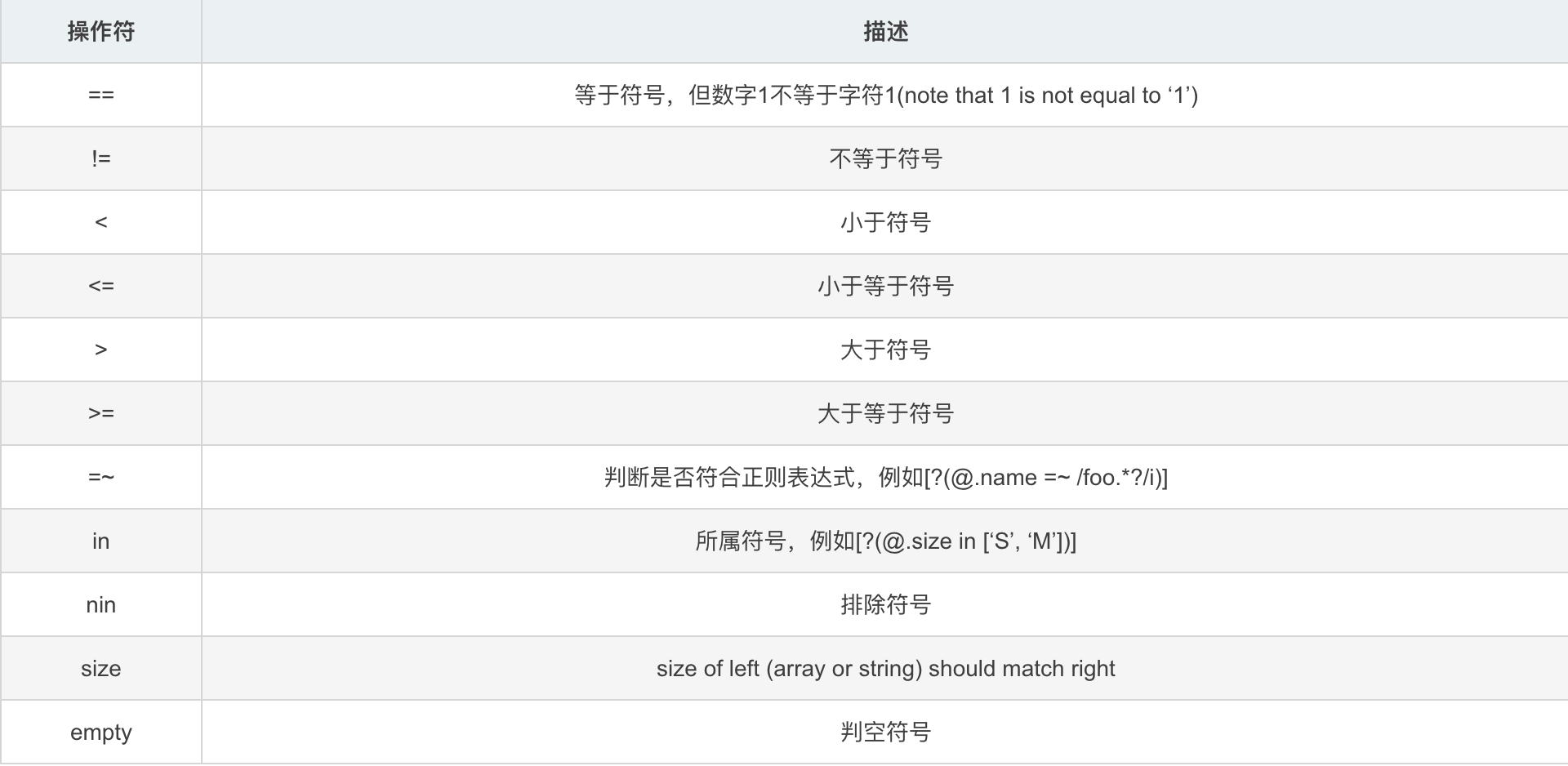
XPATH 和 JSONPath获取元素的方法比较和示例
[]在xpath表达式总是从前面的路径来操作数组,索引是从1开始。
使用JOSNPath的[]操作符操作一个对象或者数组,索引是从0开始。
{ "store": {
"book": [
{ "category": "reference",
"author": "Nigel Rees",
"title": "Sayings of the Century",
"price": 8.95
},
{ "category": "fiction",
"author": "Evelyn Waugh",
"title": "Sword of Honour",
"price": 12.99
},
{ "category": "fiction",
"author": "Herman Melville",
"title": "Moby Dick",
"isbn": "0-553-21311-3",
"price": 8.99
},
{ "category": "fiction",
"author": "J. R. R. Tolkien",
"title": "The Lord of the Rings",
"isbn": "0-395-19395-8",
"price": 22.99
}
],
"bicycle": {
"color": "red",
"price": 19.95
}
}
}
| XPath | JSONPath | Result |
|---|---|---|
| /store/book/author | $.store.book[*].author | 书点所有书的作者 |
| //author | $..author | 所有作者 |
| /store/* | $.store.* | store的所有元素。所有的bookst和bicycle |
| /store//price | $.store..price | store里面所有东西的price |
| //book[3] | $..book[2] | 第三个书 |
| //book[last()] | $..book[(@.length-1)] $..book[-1:] | 最后一本书 |
| //book[position()< 3] | $..book[0,1] $..book[:2] | 前两本书 |
| //book[isbn] | $..book[?(@.isbn)] | 过滤出所有的包含isbn的书 |
| //book[price<10] | $..book[?(@.price<10)] | 过滤出价格低于10的书。 |
| //* | $..* | 所有元素 |
JSONPath 表达式的使用
一、JSONPath使用需要的包
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/com.jayway.jsonpath/json-path -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.jayway.jsonpath</groupId>
<artifactId>json-path</artifactId>
<version>2.4.0</version>
</dependency>
二、使用说明
1、JSONPath是xpath在json的应用
2、JSONPath 是参照xpath表达式来解析xml文档的方式,json数据结构通常是匿名的并且不一定需要有根元素。
3、JSONPath 用一个抽象的名字$来表示最外层对象
4、JSONPath 允许使用通配符 * 表示所以的子元素名和数组索引
三、JSONPath表达式语法
JSONPath 表达式可以使用.符号解析json:
$.store.book[0].title
或者使用[]符号
$['store']['book'][0]['title']
四、测试实例
Json文件内容如下:
{ "store": {
"book": [
{ "category": "reference",
"author": "Nigel Rees",
"title": "Sayings of the Century",
"price": 8.95
},
{ "category": "fiction",
"author": "Evelyn Waugh",
"title": "Sword of Honour",
"price": 12.99,
"isbn": "0-553-21311-3"
}
],
"bicycle": {
"color": "red",
"price": 19.95
}
}
}
首先,读取json文件,使用commons.io的 FileUtils的readFileToString方法:
String path =System.getProperty("user.dir")+File.separator+"testdata"+File.separator+"test.json";
String jsonString = FileUtils.readFileToString(new File(path),"utf-8");
ReadContext context = JsonPath.parse(json);
其次,输出book[1]的author值。有两种方法:
方法一:
JsonPath.read(json,"$.store.book[1].author");
或
context.read("$.store.book[1].author");
输出:Evelyn Waugh
方法二:
JsonPath.read(json,"$['store']['book'][1]['author']");
context.read("$['store']['book'][1]['author']");
输出:Evelyn Waugh
//输出book[*]中category == 'reference'的book
List<Object> categorys = context.read("$.store.book[?(@.category == 'reference')]");
for(Object st: categorys){
System.out.println(st.toString());
}
输出: {category=reference, author=Nigel Rees, title=Sayings of the Century, price=8.95}
//输出book[*]中price>10的book
List<Object> prices = context.read("$.store.book[?(@.price>10)]");
for(Object p:prices){
System.out.println(p.toString());
}
输出:{category=fiction, author=Evelyn Waugh, title=Sword of Honour, price=12.99, isbn=0-553-21311-3}
//bicycle[*]中含有color元素的bicycle
List<Object> color = context.read("$.store.bicycle[?(@.color)]");
for(Object is :color){
System.out.println(is.toString());
}```
输出://{color=red, price=19.95}
//输出该json中所有price的值
List<Object> pp = context.read("$..price");
for(Object p :pp){
System.out.println(p.toString());
}
输出: 8.95 12.99 19.95
List<String> authors = context.read("$.store.book[*].author");
for (String str : authors) {
System.out.println(str);
}
输出:Nigel Rees Evelyn Waugh
参考文章:
https://blog.csdn.net/myself8202/article/details/80724968
https://goessner.net/articles/JsonPath/index.html#e2





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· Linux系列:如何用heaptrack跟踪.NET程序的非托管内存泄露
· 开发者必知的日志记录最佳实践
· SQL Server 2025 AI相关能力初探
· Linux系列:如何用 C#调用 C方法造成内存泄露
· AI与.NET技术实操系列(二):开始使用ML.NET
· 无需6万激活码!GitHub神秘组织3小时极速复刻Manus,手把手教你使用OpenManus搭建本
· C#/.NET/.NET Core优秀项目和框架2025年2月简报
· Manus爆火,是硬核还是营销?
· 一文读懂知识蒸馏
· 终于写完轮子一部分:tcp代理 了,记录一下