redis 原理 安装
原理-->安装-->小案例
一、原理介绍
(1)什么是?
redis 就是一个数据库,底层使用C语言编写的 , 存储数据在内存中被广泛应用于缓存方向
(2)业务流程
获取数据先从redis 获取,如果获得数据直接返回,就不访问数据库了
如果得不到数据,可以直接从数据库中查询 , 查询后放入到redis中一份 , 下一次再访问的时候从redis中查询到
(3)支持的数据类型
String
List
Set 求交集、并集
zSet
hash
(4)能否将数据持久化,如何实现?
1)RDB持久化原理:(分时持久化)
通过bgsave命令触发,然后父进程执行fork操作创建子进程,子进程创建RDB文件,根据父进程内存生成临时快照文件,完成后对原有文件进行原子替换(定时一次性将所有数据进行快照生成一份副本存储在硬盘中)
优点:是一个紧凑压缩的二进制文件,Redis加载RDB恢复数据远远快于AOF的方式。
缺点:由于每次生成RDB开销较大,非实时持久化,
2)AOF持久化原理:(实时持久化)
开启后,Redis每执行一个修改数据的命令,都会把这个命令添加到AOF文件中。
优点 : 每次CRUD 数据都会持久化到硬盘上 数据可靠安全 不会丢失
缺点:所以AOF文件体积逐渐变大,需要定期执行重写操作来降低文件体积,加载慢
(5)与同类技术mongodb 区别
也是一个nosql数据库 但是二者不能放在一起对比 因为完全没有可比性 使用场景完全不同
redis 一般用于分布式缓存使用
mongodb 主要用于硬盘存储 存储大型的文本数据 mongodb 比redis数据类型更加丰富
二、linux安装
1) cd /root

2) 进入对应文件夹创建redis文件夹
cd /usr/local
mkdir redis
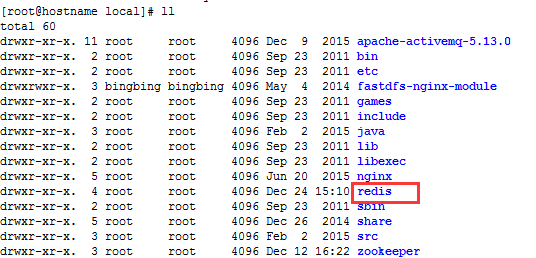
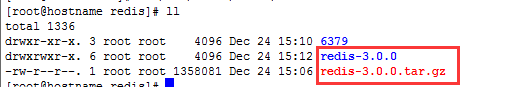
3) 将root下得压缩包复制到当前文件夹,并解压
#cp /root/redis/redis-3.0.0.tar.gz ./
#tar -zxvf redis-3.0.0.tar.gz -C ./
4) 进入redis-3.0.0编译
[root@hostname redis-3.0.0]# make
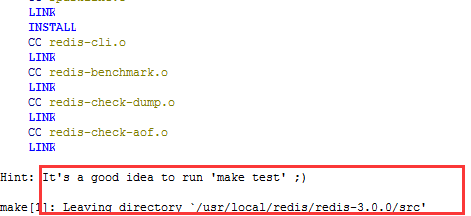
如果不能使用需要在linux中安装c
[root@hostname redis-3.0.0]# yum install gcc
5)
[root@hostname redis-3.0.0]# make install PREFIX='/usr/local/redis/6379'

[root@hostname redis-3.0.0]# cd /usr/local/redis/6379

[root@hostname 6379]# cd bin [root@hostname bin]# ll
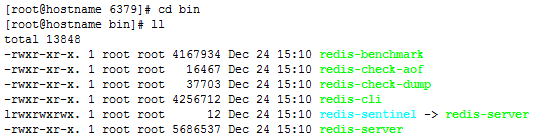
[root@hostname bin]# ./redis-server

以上为前端启动,但由于总是前端启动不方便
接下来设置后端启动
[root@hostname bin]# cd /usr/local/redis/redis-3.0.0 [root@hostname redis-3.0.0]# ll
[root@hostname redis-3.0.0]# cp redis.conf /usr/local/redis/6379/bin/ [root@hostname redis-3.0.0]# cd /usr/local/redis/6379/bin/ [root@hostname redis-3.0.0]# vim redis.conf
将daemonize no 改为 daemonize yes

启动
[root@hostname redis-3.0.0]# cd /usr/local/redis/6379/bin/ [root@hostname bin]# ./redis-server redis.conf [root@hostname bin]# ps -ef|grep redis


安装完成 !
三、部署到项目中(以轮播图为例)
创建一个新的常量接口(命名为不是一定的)
public interface Contents {
public final static String CONTENT_REDIS_KEY="contentList";
}
只需在service的实现类中进行修改
每次新增修改删除后都需要对redis中的数据删
@Service
@Transactional public class ContentServiceImpl implements ContentService { @Autowired private ContentDao contentDao; @Autowired private RedisTemplate redisTemplate; @Override public List<Content> findAll() { return contentDao.selectByExample(null); } @Override public void add(Content content) { //1 将新广告添加到数据库中 contentDao.insertSelective(content); //2根据分类 到redis中删除对应的分类广告集合数据 redisTemplate.boundHashOps(Contents.CONTENT_REDIS_KEY).delete(content.getCategoryId()); } @Override public Content findOne(Long id) { return contentDao.selectByPrimaryKey(id); } @Override public void update(Content content) { //1 根据广告ID 到数据库中 查询广告对象 Content oldContent = contentDao.selectByPrimaryKey(content.getId()); //2根据广告对象中的分类id 删除redis中对应的广告集合数据 redisTemplate.boundHashOps(Contents.CONTENT_REDIS_KEY).delete(oldContent.getCategoryId()); //3根据广告对象中的分类最新id 删除redis中对应的广告集合数据 redisTemplate.boundHashOps(Contents.CONTENT_REDIS_KEY).delete(content.getCategoryId()); //4 将新的广告对象更新到数据库中 contentDao.updateByPrimaryKeySelective(content); } @Override public void delete(Long[] ids) { if(ids!=null){ for(Long id:ids){ // 1 根据广告ID 到数据库中 查询广告对象 Content content = contentDao.selectByPrimaryKey(id); //2 根据广告对象中的分类id 删除redis中对应的广告集合数据 redisTemplate.boundHashOps(Contents.CONTENT_REDIS_KEY).delete(content.getCategoryId()); //3 根据广告id 删除数据库中的广告数据 contentDao.deleteByPrimaryKey(id); } } } @Override public PageResult findPage(Content content, int page, int rows) { PageHelper.startPage(page,rows); ContentQuery query = new ContentQuery(); ContentQuery.Criteria criteria = query.createCriteria(); if(content!=null){ if(content.getTitle()!=null&&!"".equals(content.getTitle())){ criteria.andTitleLike("%"+content.getTitle()+"%"); } } contentList = contentDao.selectByExample(query); return new PageResult(contentList.getTotal(),contentList.getResult()); } //首页 轮播图 @Override public List<Content> findByCategoryId(Long categoryId) { ContentQuery query = new ContentQuery(); ContentQuery.Criteria criteria = query.createCriteria(); criteria.andCategoryIdEqualTo(categoryId); return contentDao.selectByExample(query); } //首页 轮播图 通过redis @Override public List<Content> findByCategoryIdFromRedis(Long categoryId) { //1根据分类id到redis 中获取数据 contentList = redisTemplate.boundHashOps(Contents.CONTENT_REDIS_KEY).get(categoryId); //2 如果redis中没有数据 到数据库中取数据 if(contentList==null){ contentList = findByCategoryId(categoryId); //3 如果从数据库中取到数据 则放入redis中一份 redisTemplate.boundHashOps(Contents.CONTENT_REDIS_KEY).put(categoryId,contentList); } return contentList; } }
四、注意
@Test
public void testPut(){
redisTemplate.boundHashOps("listHash").put("001","zzz");
redisTemplate.boundHashOps("listHash").put("002","yyy");
redisTemplate.boundHashOps("listHash").put("003","lll");
redisTemplate.boundHashOps("listHash").put("004","bbb");
}
@Test
public void testGetAll(){
Map<String,String> entries = redisTemplate.boundHashOps("listHash").entries();
//map 为hash类型的时候 不能遍历 需要转为set类型
Set<Map.Entry<String, String>> entrySet = entries.entrySet();
for(Map.Entry<String, String> map:entrySet ){
System.out.println("==key值=="+map.getKey()+"====");
System.out.println("==value值=="+map.getValue()+"====");
}
}




