操作系统实现-进入内核
博客网址:www.shicoder.top
微信:18223081347
欢迎加群聊天 :452380935
这一次我们正式进入内核,编写相关的内核代码,也就是kernel代码
数据类型定义
因为我们在内核中会使用一些数据,因此先提前定义一些数据类型
#define EOF -1
#define NULL ((void *)0) // 空指针
#define EOS '\0' // 字符串结尾
#define bool _Bool
#define true 1
#define false 0
#define _packed __attribute__((packed)) // 用于定义特殊的结构体 不对齐
typedef unsigned int size_t;
typedef char int8;
typedef short int16;
typedef int int32;
typedef long long int64;
typedef unsigned char u8;
typedef unsigned short u16;
typedef unsigned int u32;
typedef unsigned long long u64;
typedef u32 time_t;
typedef u32 idx_t;
输入输出
我们知道,在操作系统启动的时候,刚开始都是黑乎乎的界面,然后光标闪烁等,那么这个是怎么实现的呢,一般这种都是通过向一些寄存器写入一些值和和获取一些值实现,因此就需要用一些输入输出函数
首先是四个函数
extern u8 inb(u16 port); // 输入1个字节 从port端口中读一个字节
extern u16 inw(u16 port); // 输入2个字节 从port端口中读2个字节
extern void outb(u16 port,u8 value); // 输出1个字节 将value值输入到port端口中
extern void outw(u16 port,u16 value); // 输出2个字节 将value值输入到port端口中
我们采用汇编实现
global inb ; 将inb导出
inb:
; 栈帧保存
push ebp
mov ebp, esp
xor eax, eax ;清空
mov edx, [ebp + 8] ;port [ebp + 8]就是传入进来的port
in al, dx ;将dx所指向的端口,读取一个字放在al,也就是从port端口读一个字节
jmp $+2 ;延迟
jmp $+2 ;延迟
jmp $+2 ;延迟
leave ; 恢复栈帧
ret
global outb ; 将outb导出
outb:
; 栈帧保存
push ebp
mov ebp, esp
mov edx, [ebp + 8] ;port [ebp + 8]就是传入进来的port
mov eax, [ebp + 12] ; value 参数入栈是从右往左 所以value地址更高
out dx, al ;将al的8比特输出到dx的端口号
jmp $+2 ;延迟
jmp $+2 ;延迟
jmp $+2 ;延迟
leave ; 恢复栈帧
ret
global inw ; 将inw导出
inw:
; 栈帧保存
push ebp
mov ebp, esp
xor eax, eax ;清空
mov edx, [ebp + 8] ;port [ebp + 8]就是传入进来的port
in ax, dx ;将dx所指向的端口,读取2个字放在ax
jmp $+2 ;延迟
jmp $+2 ;延迟
jmp $+2 ;延迟
leave ; 恢复栈帧
ret
global outw ; 将outw导出
outw:
; 栈帧保存
push ebp
mov ebp, esp
mov edx, [ebp + 8] ;port [ebp + 8]就是传入进来的port
mov eax, [ebp + 12] ; value 参数入栈是从右往左 所以value地址更高
out dx, ax ;将ax的2个字输出到dx的端口号
jmp $+2 ;延迟
jmp $+2 ;延迟
jmp $+2 ;延迟
leave ; 恢复栈帧
ret
我们在kernel中测试下获取光标的位置,相关的寄存器有以下几个
- CRT 地址寄存器 0x3D4
- CRT 数据寄存器 0x3D5
- CRT 光标位置 - 高位 0xE
- CRT 光标位置 - 低位 0xF
比如我们把光标高位位置给地址寄存器,那么就可以通过数据寄存器得到和设置光标位置的高位值
// - CRT 地址寄存器 0x3D4
// - CRT 数据寄存器 0x3D5
// - CRT 光标位置 - 高位 0xE
// - CRT 光标位置 - 低位 0xF
#define CRT_ADDR_REG 0x3d4
#define CRT_DATA_REG 0x3d5
#define CRT_CURSOR_H 0xe
#define CRT_CURSOR_L 0xf
void kernel_init()
{
outb(CRT_ADDR_REG,CRT_CURSOR_H);
u16 pos = inb(CRT_DATA_REG) << 8;
outb(CRT_ADDR_REG,CRT_CURSOR_L);
pos |= inb(CRT_DATA_REG); // 到这里,pos值为240,通过qemu也可以看到,光标在第4行,每行80字符
u8 data = inb(CRT_DATA_REG);
// 比如想把光标位置改为160
outb(CRT_ADDR_REG,CRT_CURSOR_H);
outb(CRT_DATA_REG,0);
outb(CRT_ADDR_REG,CRT_CURSOR_L);
outb(CRT_DATA_REG,160); // 到这里,就可以看到光标在第3行开始处
}
字符串函数实现
我们在C语言中,使用过很多字符串函数,比如
char *strcpy(char *dest, const char *src);
char *strcat(char *dest, const char *src);
size_t strlen(const char *str);
int strcmp(const char *lhs, const char *rhs);
char *strchr(const char *str, int ch);
char *strrchr(const char *str, int ch);
int memcmp(const void *lhs, const void *rhs, size_t count);
void *memset(void *dest, int ch, size_t count);
void *memcpy(void *dest, const void *src, size_t count);
void *memchr(const void *ptr, int ch, size_t count);
下面是其实现的代码
char *strcpy(char *dest, const char *src)
{
char *ptr = dest;
while (true)
{
*ptr++ = *src;
if (*src++ == EOS)
return dest;
}
}
char *strcat(char *dest, const char *src)
{
char *ptr = dest;
while (*ptr != EOS)
{
ptr++;
}
while (true)
{
*ptr++ = *src;
if (*src++ == EOS)
{
return dest;
}
}
}
size_t strlen(const char *str)
{
char *ptr = (char *)str;
while (*ptr != EOS)
{
ptr++;
}
return ptr - str;
}
int strcmp(const char *lhs, const char *rhs)
{
while (*lhs == *rhs && *lhs != EOS && *rhs != EOS)
{
lhs++;
rhs++;
}
return *lhs < *rhs ? -1 : *lhs > *rhs;
}
char *strchr(const char *str, int ch)
{
char *ptr = (char *)str;
while (true)
{
if (*ptr == ch)
{
return ptr;
}
if (*ptr++ == EOS)
{
return NULL;
}
}
}
char *strrchr(const char *str, int ch)
{
char *last = NULL;
char *ptr = (char *)str;
while (true)
{
if (*ptr == ch)
{
last = ptr;
}
if (*ptr++ == EOS)
{
return last;
}
}
}
int memcmp(const void *lhs, const void *rhs, size_t count)
{
char *lptr = (char *)lhs;
char *rptr = (char *)rhs;
while (*lptr == *rptr && count-- > 0)
{
lptr++;
rptr++;
}
return *lptr < *rptr ? -1 : *lptr > *rptr;
}
void *memset(void *dest, int ch, size_t count)
{
char *ptr = dest;
while (count--)
{
*ptr++ = ch;
}
return dest;
}
void *memcpy(void *dest, const void *src, size_t count)
{
char *ptr = dest;
while (count--)
{
*ptr++ = *((char *)(src++));
}
return dest;
}
void *memchr(const void *str, int ch, size_t count)
{
char *ptr = (char *)str;
while (count--)
{
if (*ptr == ch)
{
return (void *)ptr;
}
ptr++;
}
}
基础显卡驱动
我们知道比如在显示器显示hello,world\n,那么显示器就会先输出一句hello,world,然后换行,这一次就是实现这个操作,其实可以想下,换行,不就是设置一下光标位置嘛,那不就是第二个部分输入输出的样例吗,下面来实现吧,同时注意有以下寄存器
- CRT 地址寄存器 0x3D4
- CRT 数据寄存器 0x3D5
- CRT 光标位置 - 高位 0xE
- CRT 光标位置 - 低位 0xF
- CRT 显示开始位置 - 高位 0xC
- CRT 显示开始位置 - 低位 0xD
| 控制字符 | 八进制 | 十六进制 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|---|
| NUL | 0 | 0x00 | 在输入时忽略,不保存在输入缓冲中 |
| ENQ | 5 | 0x05 | 传送应答消息 |
| BEL | 7 | 0x07 | 从键盘发声响 |
| BS | 10 | 0x08 | 将光标移向左边一个字符位置处;若光标已经处在左边沿,则无动作 |
| HT | 11 | 0x09 | 将光标移到下一个制表位;若右侧已经没有制表位,则移到右边缘处 |
| LF | 12 | 0x0A | 此代码导致一个回车或换行操作 |
| VT | 13 | 0x0B | 作用如LF |
| FF | 14 | 0x0C | 作用如LF |
| CR | 15 | 0x0D | 将光标移到当前行的左边缘处 |
| SO | 16 | 0x0E | 使用由 SCS 控制序列设计的 G1 字符集 |
| SI | 17 | 0x0F | 选择 G0 字符集,由 ESC 序列选择 |
| XON | 21 | 0x11 | 使终端重新进行传输 |
| XOFF | 23 | 0x13 | 使中断除发送 XOFF 和 XON 以外,停止发送其它所有代码 |
| CAN | 30 | 0x18 | 如果在控制序列期间发送,则序列不会执行而立刻终止,同时会显示出错字符 |
| SUB | 32 | 0x1A | 作用同 CAN |
| ESC | 33 | 0x1B | 产生一个控制序列 |
| DEL | 177 | 0x7F | 在输入时忽略 不保存在输入缓冲中 |
#define CRT_ADDR_REG 0x3D4 // CRT(6845)索引寄存器
#define CRT_DATA_REG 0x3D5 // CRT(6845)数据寄存器
#define CRT_START_ADDR_H 0xC // 显示内存起始位置 - 高位
#define CRT_START_ADDR_L 0xD // 显示内存起始位置 - 低位
#define CRT_CURSOR_H 0xE // 光标位置 - 高位
#define CRT_CURSOR_L 0xF // 光标位置 - 低位
#define MEM_BASE 0xB8000 // 显卡内存起始位置
#define MEM_SIZE 0x4000 // 显卡内存大小
#define MEM_END (MEM_BASE + MEM_SIZE) // 显卡内存结束位置
#define WIDTH 80 // 屏幕文本列数
#define HEIGHT 25 // 屏幕文本行数
#define ROW_SIZE (WIDTH * 2) // 每行字节数 一个字符由2个字节控制 ,一个是ascii,一个是样式
#define SCR_SIZE (ROW_SIZE * HEIGHT) // 屏幕字节数
#define ASCII_NUL 0x00
#define ASCII_ENQ 0x05
#define ASCII_BEL 0x07 // \a
#define ASCII_BS 0x08 // \b
#define ASCII_HT 0x09 // \t
#define ASCII_LF 0x0A // \n
#define ASCII_VT 0x0B // \v
#define ASCII_FF 0x0C // \f
#define ASCII_CR 0x0D // \r
#define ASCII_DEL 0x7F
static u32 screen; // 记录当前显示器开始的内存位置
static u32 pos; // 记录当前光标内存位置
static u32 x, y; // 当前光标坐标
// 删除后,会在那里显示一个类似橡皮擦的样式光标
static u8 attr = 7; // 字符样式
static u16 erase = 0x0720; // 空格 07是字符,20是样式
// 获得当前显示器的位置
static void get_screen()
{
outb(CRT_ADDR_REG, CRT_START_ADDR_H); // 显示内存起始位置高地址
screen = inb(CRT_DATA_REG) << 8; // 显示内存起始位置值的高8位
outb(CRT_ADDR_REG, CRT_START_ADDR_L); // 显示内存起始位置低地址
screen |= inb(CRT_DATA_REG); // 显示内存起始位置值的低8位
screen <<= 1; // screen *= 2 屏幕上每个位置是由2个字进行描述
screen += MEM_BASE; // 真正的位置
}
// 设置显示器位置
static void set_screen()
{
outb(CRT_ADDR_REG, CRT_START_ADDR_H); // 显示内存起始位置高地址
outb(CRT_DATA_REG, ((screen - MEM_BASE) >> 9) & 0xff); // 因为screen获得时候,是左移1位,然后再移8位是高地址
outb(CRT_ADDR_REG, CRT_START_ADDR_L); // 显示内存起始位置低地址
outb(CRT_DATA_REG, ((screen - MEM_BASE) >> 1) & 0xff); // 因为screen获得时候,是左移1位
}
// 获得当前光标位置
static void get_cursor()
{
outb(CRT_ADDR_REG, CRT_CURSOR_H); // 光标内存起始位置高地址
pos = inb(CRT_DATA_REG) << 8; // 光标内存起始位置值的高8位
outb(CRT_ADDR_REG, CRT_CURSOR_L); // 光标内存起始位置低地址
pos |= inb(CRT_DATA_REG); // 光标内存起始位置值的低8位
pos <<= 1;
pos += MEM_BASE;
// 获得光标的坐标
get_screen();
u32 delta = (pos - screen) >> 1;
x = delta % WIDTH;
y = delta / WIDTH;
}
// 设置当前光标位置
static void set_cursor()
{
outb(CRT_ADDR_REG, CRT_CURSOR_H); // 光标内存起始位置高地址
outb(CRT_DATA_REG, ((pos - MEM_BASE) >> 9) & 0xff);
outb(CRT_ADDR_REG, CRT_CURSOR_L); // 光标内存起始位置低地址
outb(CRT_DATA_REG, ((pos - MEM_BASE) >> 1) & 0xff);
}
void console_clear()
{
screen = MEM_BASE;
pos = MEM_BASE;
x = y = 0;
set_cursor();
set_screen();
// 清空 让屏幕全为空格
u16 *ptr = (u16 *)MEM_BASE;
while (ptr < (u16 *)MEM_END)
{
*ptr++ = erase;
}
}
void console_init()
{
// 相当于screen为第二行开始的地方,意思就是我们只能从显示器第二行开始看,第一行就看不到了
// screen = 80 * 2 + MEM_BASE;
// set_screen();
// get_screen();
// 比如设置光标为124, 第一行的后半截,124/2=62
// pos = 124 + MEM_BASE;
// set_cursor();
console_clear();
}
// 超过屏幕显示大小,向上滚屏,也就是把最上面一行去掉
static void scroll_up()
{
if (screen + SCR_SIZE + ROW_SIZE < MEM_END)
{
u32 *ptr = (u32 *)(screen + SCR_SIZE);
for (size_t i = 0; i < WIDTH; i++)
{
*ptr++ = erase;
}
screen += ROW_SIZE;
pos += ROW_SIZE;
}
// 超过,感觉是直接重头开始
else
{
memcpy((void *)MEM_BASE, (void *)screen, SCR_SIZE);
pos -= (screen - MEM_BASE);
screen = MEM_BASE;
}
set_screen();
}
static void command_lf()
{
if (y + 1 < HEIGHT)
{
y++;
pos += ROW_SIZE;
return;
}
scroll_up();
}
static void command_bs()
{
if (x)
{
x--;
pos -= 2;
*(u16 *)pos = erase;
}
}
static void command_cr()
{
pos -= (x << 1);
x = 0;
}
static void command_del()
{
*(u16 *)pos = erase;
}
void console_write(char *buf, u32 count)
{
char ch;
while (count--)
{
ch = *buf++;
switch (ch)
{
case ASCII_NUL:
break;
case ASCII_ENQ:
break;
case ASCII_BEL: // \a
break;
case ASCII_BS: // \b
command_bs();
break;
case ASCII_HT: // \t
break;
case ASCII_LF: // \n
command_lf();
command_cr();
break;
case ASCII_VT: // \v
break;
case ASCII_FF: // \f
command_lf();
break;
case ASCII_CR: // \r
command_cr();
break;
case ASCII_DEL:
command_del();
break;
default:
if (x >= WIDTH)
{
x -= WIDTH;
pos -= ROW_SIZE;
command_lf();
}
*((char *)pos) = ch;
pos++;
*((char *)pos) = attr;
pos++;
x++;
break;
}
}
set_cursor();
}
下面简单测试下吧,kernel主函数如下
char message[] = "hello system...\n";
void kernel_init()
{
console_init();
u32 count = 20;
while (count--)
{
console_write(message, sizeof(message) - 1);
}
}
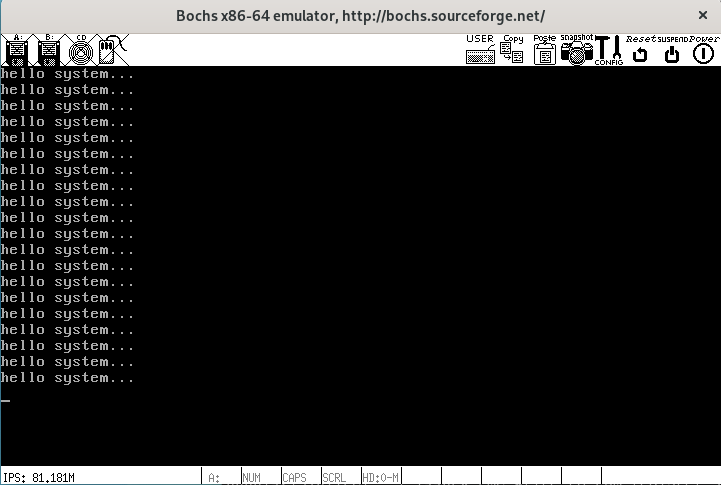
可以看到打印了20次,且每次都换行了,成功啦



