Linux 服务管理两种方式service和systemctl
Linux 服务管理两种方式service和systemctl
1.service命令
service命令其实是去/etc/init.d目录下,去执行相关程序
# service命令启动redis脚本
service redis start
# 直接启动redis脚本
/etc/init.d/redis start
# 开机自启动
update-rc.d redis defaults
其中脚本需要我们自己编写
2.systemctl命令
systemd是Linux系统最新的初始化系统(init),作用是提高系统的启动速度,尽可能启动较少的进程,尽可能更多进程并发启动。
systemd对应的进程管理命令是systemctl
1)systemctl命令兼容了service
即systemctl也会去/etc/init.d目录下,查看,执行相关程序
systemctl redis start
systemctl redis stop
# 开机自启动
systemctl enable redis
2)systemctl命令管理systemd的资源Unit
systemd的Unit放在目录/usr/lib/systemd/system(Centos)或/etc/systemd/system(Ubuntu)

主要有四种类型文件.mount,.service,.target,.wants
.mount文件
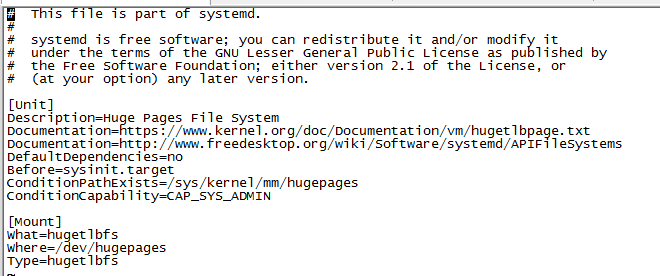
.mount文件定义了一个挂载点,[Mount]节点里配置了What,Where,Type三个数据项
等同于以下命令:
mount -t hugetlbfs /dev/hugepages hugetlbfs
.service文件
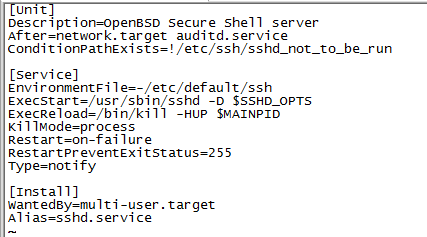
.service文件定义了一个服务,分为[Unit],[Service],[Install]三个小节
[Unit]
Description:描述,
After:在network.target,auditd.service启动后才启动
ConditionPathExists: 执行条件
[Service]
EnvironmentFile:变量所在文件
ExecStart: 执行启动脚本
Restart: fail时重启
[Install]
Alias:服务别名
WangtedBy: 多用户模式下需要的
.target文件
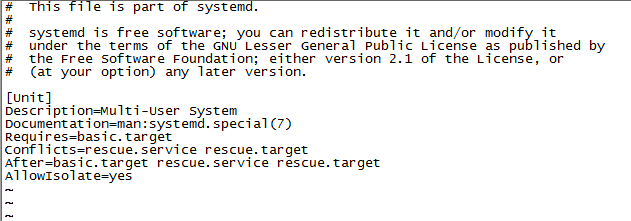
.target定义了一些基础的组件,供.service文件调用
.wants文件

.wants文件定义了要执行的文件集合,每次执行,.wants文件夹里面的文件都会执行





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语,封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· .NET Core 中如何实现缓存的预热?
· 从 HTTP 原因短语缺失研究 HTTP/2 和 HTTP/3 的设计差异
· AI与.NET技术实操系列:向量存储与相似性搜索在 .NET 中的实现
· 基于Microsoft.Extensions.AI核心库实现RAG应用
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语 ── 封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· 地球OL攻略 —— 某应届生求职总结
· 提示词工程——AI应用必不可少的技术
· Open-Sora 2.0 重磅开源!
· 周边上新:园子的第一款马克杯温暖上架