python 执行系统命令
1.windows命令
1)os.system(command)
在一个子shell中运行command命令,并返回command命令执行完毕后的退出状态
2)使用示例
ping命令
import os
print(os.system("ping baidu.com"))
运行结果:

启动redis服务
import os
os.chdir("D:\\redis-64.3.0.503")
os.system("redis-server.exe")
运行结果:

2.linux命令
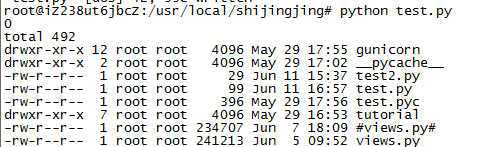
1)os.system(command) 执行命令
import os
os.system("ls -l")
运行结果:
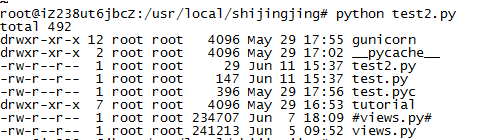
2)os.popen(command) 执行命令,返回结果
import os
result = os.popen("ls -l")
for line in result:
print(line)
运行结果:
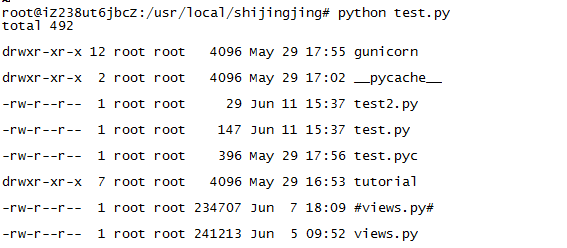
3)commands命令 执行命令,返回状态码,结果
import commands
status, output = commands.getstatusoutput("ls -l")
print(status)
print(output)
运行结果:
4)subprocess模块
可以创建子进程,与子进程的输入/输出/错误管道连通,并可以获得新建进程执行的返回状态
用来替代os.system(),os.popen(),commands等旧的函数或模块,优点是可以是异步的
格式如下:
handle = subprocess.Popen(command, shell=True, stdout=subprocess.PIPE)
使用示例:
handle = subprocess.Popen('ls -l', stdout=subprocess.PIPE, shell=True)
handle = subprocess.Popen(['ls','-l'], stdout=subprocess.PIPE, shell=True)
handle = subprocess.Popen(args='ls -l', stdout=subprocess.PIPE, shell=True)
print handle.stdout.read()
print handle.communicate()[0]



