24-面向对象的特征三:多态性
1.多态性的理解
可以理解为一个事物的多种形态。
2.何为多态性:
对象的多态性:父类的引用指向子类的对象(或子类的对象赋给父类的引用)
举例:
Person p = new Man();
Object obj = new Date();
3.多态性的使用:虚拟方法调用
> 有了对象的多态性以后,我们在编译期,只能调用父类中声明的方法,但在运行期,我们实际执行的是子类重写父类的方法。
> 总结:编译,看左边;运行,看右边。
4.多态性的使用前提:
① 类的继承关系 ② 方法的重写
5.多态性的应用举例:
1 //举例一:
2 public void func(Animal animal){//Animal animal = new Dog();
3 animal.eat();
4 animal.shout();
5 }
6 //举例二:
7 public void method(Object obj){
8
9 }
10 //举例三:
11 class Driver{
12
13 public void doData(Connection conn){//conn = new
14 MySQlConnection(); // conn = new OracleConnection();
15 //规范的步骤去操作数据
16 // conn.method1();
17 // conn.method2();
18 // conn.method3();
19 }
20 }
21
6.多态性使用的注意点:
对象的多态性,只适用于方法,不适用于属性(编译和运行都看左边)
************************************************************
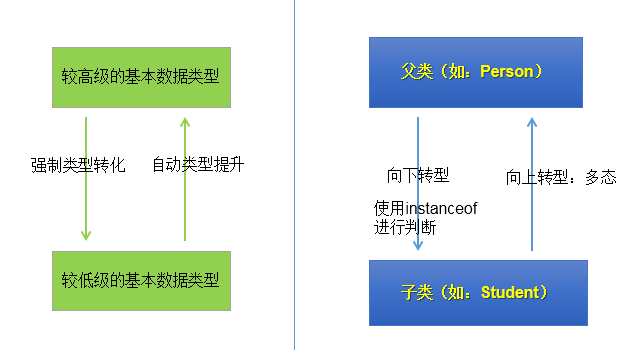
7.关于向上转型与向下转型:
7.1 向上转型:多态
7.2 向下转型:
7.2.1 为什么使用向下转型:
有了对象的多态性以后,内存中实际上是加载了子类特有的属性和方法的,但是由于变量声明为父类类型,导致编译时,只能调用父类中声明的属性和方法。
子类特有的属性和方法不能调用。如何才能调用子类特的属性和方法?使用向下转型。
7.2.2 如何实现向下转型:
使用强制类型转换符:()
7.2.3 使用时的注意点:
① 使用强转时,可能出现ClassCastException的异常。
② 为了避免在向下转型时出现ClassCastException的异常,我们在向下转型之前,先进行instanceof的判断,一旦返回true,就进行向下转型。如果返回false,不进行向下转型。
7.2.4 instanceof的使用:
① a instanceof A:判断对象a是否是类A的实例。如果是,返回true;如果不是,返回false。
② 如果 a instanceof A返回true,则 a instanceof B也返回true.其中,类B是类A的父类。
③ 要求a所属的类与类A必须是子类和父类的关系,否则编译错误。
7.2.5 图示:
8. 面试题:
8.1 谈谈你对多态性的理解?
① 实现代码的通用性。
② Object类中定义的public boolean equals(Object obj){ }
JDBC:使用java程序操作(获取数据库连接、CRUD)数据库(MySQL、Oracle、DB2、SQL Server)
③ 抽象类、接口的使用肯定体现了多态性。(抽象类、接口不能实例化)
8.2 多态是编译时行为还是运行时行为?(解:运行时行为)
1 //证明如下:
2 class Animal {
3 protected void eat() {
4 System.out.println("animal eat food");
5 }
6 }
7
8 class Cat extends Animal {
9 protected void eat() {
10 System.out.println("cat eat fish");
11 }
12 }
13
14 class Dog extends Animal {
15 public void eat() {
16 System.out.println("Dog eat bone");
17 }
18 }
19
20 class Sheep extends Animal {
21 public void eat() {
22 System.out.println("Sheep eat grass");
23 }
24 }
25
26 public class InterviewTest {
27 public static Animal getInstance(int key) {
28 switch (key) {
29 case 0:
30 return new Cat ();
31 case 1:
32 return new Dog ();
33 default:
34 return new Sheep ();
35 }
36 }
37
38 public static void main(String[] args) {
39 int key = new Random().nextInt(3);
40 System.out.println(key);
41 Animal animal = getInstance(key);
42 animal.eat();
43 }
44 }
45
46 /******************************************************/
47 //考查多态的笔试题目
48 public class InterviewTest1 {
49
50 public static void main(String[] args) {
51 Base1 base = new Sub1();
52 base.add(1, 2, 3); //sub_3
53
54 Sub1 s = (Sub1)base;
55 s.add(1,2,3);//sub_2
56
57 Sub1 sub1 = new Sub1();
58 sub1.add(1,2,3,4); //sub_3
59
60 sub1.add(1,new int[]{1,2,3});//sub_3
61 }
62 }
63
64 class Base1 {
65 public void add(int a, int... arr) {
66 System.out.println("base");
67 }
68 }
69
70 class Sub1 extends Base1 {
71 // public void add(int a, int[] arr) {
72 // System.out.println("sub_1");
73 // }
74 public void add(int a, int... arr) {
75 System.out.println("sub_3");
76 }
77
78 public void add(int a, int b, int c) {
79 System.out.println("sub_2");
80 }
81 }


