Avoid GroupByKey
Let's look at two different ways to compute word counts, one using reduceByKey and the other usinggroupByKey:
val words = Array("one", "two", "two", "three", "three", "three")
val wordPairsRDD = sc.parallelize(words).map(word => (word, 1))
val wordCountsWithReduce = wordPairsRDD
.reduceByKey(_ + _)
.collect()
val wordCountsWithGroup = wordPairsRDD
.groupByKey()
.map(t => (t._1, t._2.sum))
.collect()
While both of these functions will produce the correct answer, the reduceByKey example works much better on a large dataset. That's because Spark knows it can combine output with a common key on each partition before shuffling the data.
Look at the diagram below to understand what happens with reduceByKey. Notice how pairs on the same machine with the same key are combined (by using the lamdba function passed intoreduceByKey) before the data is shuffled. Then the lamdba function is called again to reduce all the values from each partition to produce one final result.
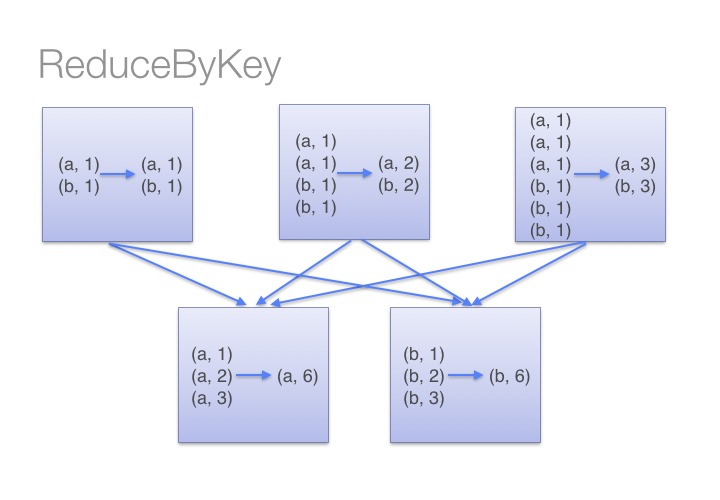
On the other hand, when calling groupByKey - all the key-value pairs are shuffled around. This is a lot of unnessary data to being transferred over the network.
To determine which machine to shuffle a pair to, Spark calls a partitioning function on the key of the pair. Spark spills data to disk when there is more data shuffled onto a single executor machine than can fit in memory. However, it flushes out the data to disk one key at a time - so if a single key has more key-value pairs than can fit in memory, an out of memory exception occurs. This will be more gracefully handled in a later release of Spark so the job can still proceed, but should still be avoided - when Spark needs to spill to disk, performance is severely impacted.
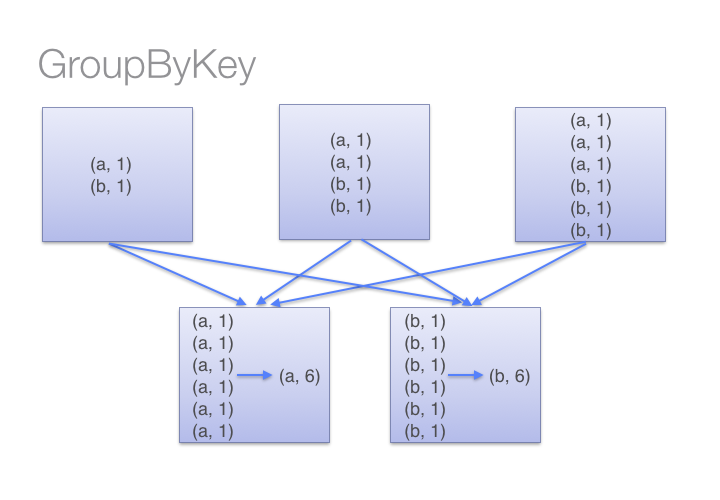
You can imagine that for a much larger dataset size, the difference in the amount of data you are shuffling becomes more exaggerated and different between reduceByKey and groupByKey.
Here are more functions to prefer over groupByKey:
combineByKeycan be used when you are combining elements but your return type differs from your input value type.foldByKeymerges the values for each key using an associative function and a neutral "zero value".


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号