HashMap存储自定义类型键值
HashMap存储自定义类型键值
Map集合保证key是唯一的:作为key的元素 必须重写hashCode方法和equals方法 以保证key唯一
代码:
自定义的类:
package demo18.Student;
public class perpon {
private String name;
private int age;
public perpon(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public perpon() {
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "perpon{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
'}';
}
}
测试类(使用String作为key 而自己定义的类作为value):
private static void method() {
//创建HashMap集合
HashMap<String, perpon> map = new HashMap<>();
//向HashMap集合中添加数据
map.put("上海",new perpon("张三",18));
map.put("广州",new perpon("李四",18));
map.put("东北",new perpon("王五",18));
map.put("北京",new perpon("赵六",18));
//使用Map集合中的方法entrySet() 把Map集合中多个Entry对象取出来 存储到一个Set集合中
Set<Map.Entry<String, perpon>> set = map.entrySet();
for (Map.Entry<String, perpon> entry : set) {
String key = entry.getKey();
perpon value = entry.getValue();
System.out.println(key+"------->"+value);
}
运行结果:
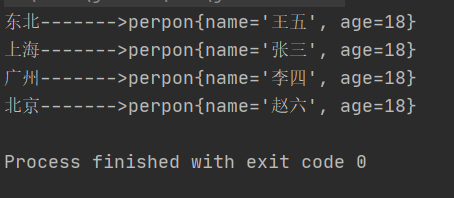
测试类(使用自己定义的类作为key String作为value)
private static void method01() {
//创建HashMap集合 让perpon作为key值
HashMap<perpon, String> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put(new perpon("张三",18),"北京");
map.put(new perpon("李四",18),"北京");
map.put(new perpon("王五",18),"北京");
map.put(new perpon("赵六",18),"北京");
map.put(new perpon("张三",18),"北京");
//使用Map集合中的方法entrySet() 把Map集合中多个Entry对象取出来 存储到一个Set集合中
Set<Map.Entry<perpon, String>> set = map.entrySet();
//使用增强for遍历数组
for (Map.Entry<perpon, String> entry : set) {
String value = entry.getValue();
perpon key = entry.getKey();
System.out.println(key+"------>"+value);
}
}
运行结果:
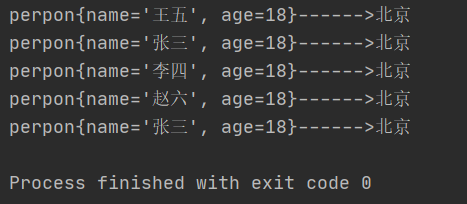
可以看到运行结果中是用两个张三 而且年龄也一样 因为我们没有重写equals方法和hashCode方法
添加equals方法和hashCode方法的perpon类:
public class perpon {
private String name;
private int age;
public perpon(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public perpon() {
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "perpon{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
'}';
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (this == o) return true;
if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false;
perpon perpon = (perpon) o;
return age == perpon.age &&
Objects.equals(name, perpon.name);
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return Objects.hash(name, age);
}
}
测试类:
private static void method01() {
//创建HashMap集合 让perpon作为key值
HashMap<perpon, String> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put(new perpon("张三",18),"北京");
map.put(new perpon("李四",18),"北京");
map.put(new perpon("王五",18),"北京");
map.put(new perpon("赵六",18),"北京");
map.put(new perpon("张三",18),"北京");
//使用Map集合中的方法entrySet() 把Map集合中多个Entry对象取出来 存储到一个Set集合中
Set<Map.Entry<perpon, String>> set = map.entrySet();
//使用增强for遍历数组
for (Map.Entry<perpon, String> entry : set) {
String value = entry.getValue();
perpon key = entry.getKey();
System.out.println(key+"------>"+value);
}
}
}
运行结果:
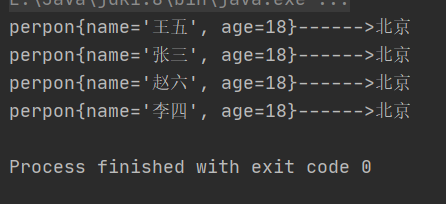
没有同名同年龄的人



【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 地球OL攻略 —— 某应届生求职总结
· 周边上新:园子的第一款马克杯温暖上架
· Open-Sora 2.0 重磅开源!
· 提示词工程——AI应用必不可少的技术
· .NET周刊【3月第1期 2025-03-02】