python---读取/写入excel用例数据
使用excel管理用例
①、读取excel的用例数据,每一类参数保存在list中返回;
②、那么接下来使用unitest编写用例时,可以去调用这个函数。使用里面的数据;
个人认为好处是,大部分人还是习惯excel的编写用例习惯,将实际用例与代码分离,有助于分工和维护
一、在excel中写好用例后,在python(unitest)中调用
1 #写文件 2 import xlwt; 3 #读文件 4 import xlrd; 5 #若要对excel文件进行修改必须!要引入这个工具模块,其中含有复制和修改功能---------注意引入方式 6 import xlutils; 7 from xltuils.copy import copy; 8 9 10 import unittest; 11 import requests; 12 #使用写文件模式打开文件 13 open_workbook=xlrd.open_workbook(r'D:\Users\4399-3046\Desktop\test.xls'); 14 #最终返回的是文件类型 15 print(open_workbook); 16 #打印该文件下,对应数据表的行数 17 #print(open_workbook.sheet_by_name('mytest').nrows); 18 19 #打印该文件下,对应数据表的列数 20 #print(open_workbook.sheet_by_name('mytest').ncols); 21 #for item_rows in range(1,open_workbook.sheet_by_name('mytest').nrows): 22 #for item_cols in range(1,open_workbook.sheet_by_name('mytest').ncols): 23 #print(open_workbook.sheet_by_name('mytest').cell(item_rows,item_cols)); 24 25 26 #循环打印出所有数据,并分别保存在list中 27 #编号 28 listkey=[]; 29 #测试地址 30 listurl=[]; 31 #提交方式 32 listtype=[]; 33 #参数1 34 listcanshu1=[]; 35 #参数2 36 listcanshu2=[]; 37 #预期结果 38 listyuqi=[]; 39 #实际结果 40 listresult=[]; 41 #在unitest框架中,通过调用参数,执行用例,将实际结果比对预期结果是否一致,若一致,则通过,否则用例失败,并将实际结果写入excel中(写入代码后文将写到) 42 for item_row in range(1,open_workbook.sheet_by_name('mytest').nrows): 43 #获取用例编号 44 listkey.append(open_workbook.sheet_by_name('mytest').cell(item_row,0).value); 45 # 获取参数1 46 listcanshu1.append(open_workbook.sheet_by_name('mytest').cell(item_row, 1).value); 47 # 获取参数2 48 listcanshu2.append(open_workbook.sheet_by_name('mytest').cell(item_row, 2).calue); 49 # 获取预期结果 50 listyuqi.append(open_workbook.sheet_by_name('mytest').cell(item_row, 3).value); 51 # 获取实际结果 52 listresult.append(open_workbook.sheet_by_name('mytest').cell(item_row, 4).value);------------->注意:必须要有【.value】,因为返回的是dict字典,而实际我们只需要其中的具体值 53 54 55 print(listkey); 56 print(listcanshu1); 57 print(listcanshu2); 58 print(listyuqi); 59 print(listresult);
运行结果:

2、新建文件,并在新文件中写入数据
1 open_workbook=xlwt.Workbook();---定义一个工作簿 2 3 4 new_sheet=open_workbook.add_sheet('lianxi',cell_overwrite_ok = True);----在工作簿中新增一个工作表,自定义一个工作表名称
注意1:若当前单元格已经有值,无法重复写入覆盖原有,会提示异常,需要在新建表单sheet时,就要指定,可以重复写入【cell_overwrite_ok = True】,默认是false
5 new_sheet.write(0,5,'lianxi_test');-----在工作表中写入数据(注意:写入数据只在工作表sheet中生效)---
注意2:如果当前目录下已存在同名的工作簿名称,则会报错
6 open_workbook.save(r'D:\Users\Desktop\test01.xls');----保存工作簿(需要指定地址和名称)
3、在已有文件下excel下,写入数据
1#思路:打开文件----复制文件----在文件中写入数据----删除原文件----保存新文件
#打开当前已经存在的工作簿 2 open_workbook2=xlrd.open_workbook(r'D:\Users\Desktop\test.xls'); 3 #复制当前工作簿 4 open_sheet2=copy(open_workbook2);
#打开置顶索引的工作表 5 open_ws=open_sheet2.get_sheet(3); 6 #在指定的单元格写入数据 7 open_ws.write(1,4,'TEST');
#移除原有的文件 8 os.remove(r'D:\Users\4399-3046\Desktop\test.xls')
#保存新文件 9 open_sheet2.save(r'D:\Users\4399-3046\Desktop\test.xls');
运行结果:

4、扩展--结合python-unitest,通常我们需要将执行结果自动写入表格中
5、拓展--将写文件和读文件,分别封装为公共方法调用(已完成)
1 #by zhonghuihong 2 import xlwt; 3 import xlrd; 4 from xlutils.copy import copy; 5 import os; 6 #此接口主要用于excel数据的读取和写入 7 8 def get_excel_data(paths,sheetName): 9 open_workbook=xlrd.open_workbook(paths); 10 open_sheet=open_workbook.sheet_by_name(sheetName); 11 rows=open_sheet.nrows; 12 listkey = []; 13 listcanshu1 = []; 14 listcanshu2 = []; 15 listyuqi = []; 16 listresult = []; 17 for item_row in range(1, rows): 18 listkey.append(open_sheet.cell(item_row, 0).value); 19 listcanshu1.append(open_sheet.cell(item_row, 1).value); 20 listcanshu2.append(open_sheet.cell(item_row, 2).value); 21 listyuqi.append(open_sheet.cell(item_row, 3).value); 22 listresult.append(open_sheet.cell(item_row, 4).value); 23 return listkey,listcanshu1,listcanshu2,listyuqi,listresult; 24 25 26 def write_excel_data(paths,sheet_id,rows_id,cols_id,values): 27 open_workbook2 = xlrd.open_workbook(paths); 28 open_sheet2 = copy(open_workbook2); 29 open_ws = open_sheet2.get_sheet(sheet_id); 30 open_ws.write(rows_id,cols_id,values); 31 os.remove(paths); 32 open_sheet2.save(paths); 33 return 'success';
遇到的问题
1、读取的整数变成浮点类型,解决办法
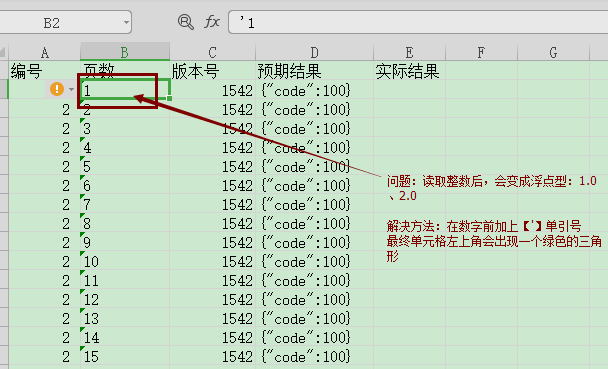
2、脚本中引入copy方法,但提示TypeError: 'module' object is not callable的解决办法:将引入语句写成from xlutils.copy import copy;
3、指定sheet时(ow.get_sheet[0];),提示TypeError: 'method' object is not subscriptable
产生原因:subscriptable的意思是可有下标,错误的原因就是:对象不具有下标,即把不具有下标操作的对象用成了对象[i],比如int对象变量[i]就会报错。仔细检查错误行。
代码最终优化:
*增加try--exception异常捕获
*增加写入输入不能为空
1 #写数据(文件薄,表格id,行id,列id,要写的内容) 2 def write_excel_data(paths,sheet_id,rows_id,cols_id,values): 3 if(len(values)==0 ): 4 return '写入数据不能为空'; 5 else: 6 7 try: 8 #如果写入位置已经有值, 会直接使用新内容覆盖 9 open_workbook2 = xlrd.open_workbook(paths); 10 open_sheet2 = copy(open_workbook2); 11 open_ws = open_sheet2.get_sheet(sheet_id); 12 open_ws.write(rows_id, cols_id, values); 13 os.remove(paths); 14 open_sheet2.save(paths); 15 16 return 'success'; 17 except Exception as e: 18 return e; 19 20 21 #读取excel_data(文件薄地址,表格名)
#通过循环读出指定表格中的所有数据,以列表格式输出
22 def get_excel_data(paths,sheetName): 23 open_workbook = xlrd.open_workbook(paths); 24 open_sheet = open_workbook.sheet_by_name(sheetName); 25 26 if open_sheet.nrows <= 1: 27 return '文件总行数小于1,请确认'; 28 29 else: 30 res = [] 31 j = 1 32 for i in list(range(open_sheet.nrows-1)): 33 s = {}; 34 #行编号 35 s['rowNum'] = i+1; 36 values = open_sheet.row_values(j) 37 for x in list(range(open_sheet.ncols)): 38 keys=open_sheet.row_values(0); 39 s[keys[x]] = values[x]; 40 res.append(s); 41 j += 1; 42 return res;




