Pytorch1.0入门实战二:LeNet、AleNet、VGG、GoogLeNet、ResNet模型详解
LeNet
1998年,LeCun提出了第一个真正的卷积神经网络,也是整个神经网络的开山之作,称为LeNet,现在主要指的是LeNet5或LeNet-5,如图1.1所示。它的主要特征是将卷积层和下采样层相结合作为网络的基本机构,如果不计输入层,该模型共7层,包括2个卷积层,2个下采样层,3个全连接层。

图1.1
注:由于在接入全连接层时,要将池化层的输出转换成全连接层需要的维度,因此,必须清晰的知道全连接层前feature map的大小。卷积层与池化层输出的图像大小,其计算如图1.2所示。

图1.2
本次利用pytorch实现整个LeNet模型,图中的Subsampling层即可看作如今的池化层,最后一层(输出层)也当作全连接层进行处理。
1 import torch as torch 2 import torch.nn as nn 3 class LeNet(nn.Module): 4 def __init__(self): 5 super(LeNet,self).__init__() 6 layer1 = nn.Sequential() 7 layer1.add_module('conv1',nn.Conv2d(1,6,5)) 8 layer1.add_module('pool1',nn.MaxPool2d(2,2)) 9 self.layer1 = layer1 10 11 layer2 = nn.Sequential() 12 layer2.add_module('conv2',nn.Conv2d(6,16,5)) 13 layer2.add_module('pool2',nn.MaxPool2d(2,2)) 14 self.layer2 = layer2 15 16 layer3 = nn.Sequential() 17 layer3.add_module('fc1',nn.Linear(16*5*5,120)) 18 layer3.add_module('fc2',nn.Linear(120,84)) 19 layer3.add_module('fc3',nn.Linear(84,10)) 20 self.layer3 = layer3 21 22 def forward(self, x): 23 x = self.layer1(x) 24 x = self.layer2(x) 25 x = x.view(x.size(0),-1)#转换(降低)数据维度,进入全连接层 26 x = self.layer3(x) 27 return x 28 #代入数据检验 29 y = torch.randn(1,1,32,32) 30 model = LeNet() 31 model(y)
AlexNet
在2010年,斯坦福大学的李飞飞正式组织并启动了大规模视觉图像识别竞赛(ImageNet Large Scale Visual Recognition Challenge,ILSVRC)。在2012年,Alex Krizhevsky、Ilya Sutskever提出了一种非常重要的卷积神经网络模型,它就是AlexNet,如图1.3所示,在ImageNet竞赛上大放异彩,领先第二名10%的准确率夺得了冠军,吸引了学术界与工业界的广泛关注。
AlexNet神经网络相比LeNet:
- 使用ReLU激活函数。在AlexNet之前,神经网络一般都使用sigmoid或tanh作为激活函数,这类函数在自变量非常大或者非常小时,函数输出基本不变,称之为饱和函数。为了提高训练速度,AlexNet使用了修正线性函数ReLU,它是一种非饱和函数,与 sigmoid 和tanh 函数相比,ReLU分片的线性结构实现了非线性结构的表达能力,梯度消失现象相对较弱,有助于训练更深层的网络。
- 使用GPU训练。与CPU不同的是,GPU转为执行复杂的数学和几何计算而设计,AlexNet使用了2个GPU来提升速度,分别放置一半卷积核。
- 局部响应归一化。AlexNet使用局部响应归一化技巧,将ImageNet上的top-1与top-5错误率分别减少了1.4%和1.2%。
- 重叠池化层。与不重叠池化层相比,重叠池化层有助于缓解过拟合,使得AlexNet的top-1和top-5错误率分别降低了0.4%和0.3%。
- 减少过拟合。AlexNet使用了数据扩增与丢失输出两种技巧。数据扩增:a、图像的平移、翻转,b、基于PCA的RGB强度调整。丢失输出技巧(DropOut层),AlexNet以0.5的概率将两个全连接层神经元的输出设置为0,有效阻止了过拟合现象的发生。

图1.3
利用pytorch实现AlexNet网络,由于当时,GPU的计算能力不强,因此Alex采用了2个GPU并行来计算,如今的GPU计算能力,完全可以替代。
1 import torch.nn as nn 2 import torch 3 4 class AlexNet(nn.Module): 5 def __init__(self,num_classes): 6 super(AlexNet,self).__init__() 7 self.features = nn.Sequential( 8 nn.Conv2d(3,64,11,4,padding=2), 9 # inplace=True,是对于Conv2d这样的上层网络传递下来的tensor直接进行修改,好处就是可以节省运算内存,不用多储存变量 10 nn.ReLU(inplace=True), 11 nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3,stride=2), 12 13 nn.Conv2d(64,192,kernel_size=5,padding=2), 14 nn.ReLU(inplace=True), 15 nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3,stride=2), 16 17 nn.Conv2d(192,384,kernel_size=3,padding=1), 18 nn.ReLU(inplace=True), 19 nn.Conv2d(384,256,kernel_size=3,padding=1), 20 nn.ReLU(inplace=True), 21 22 nn.Conv2d(256,256,kernel_size=3,padding=1), 23 nn.ReLU(inplace=True), 24 nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3,stride=1) 25 ) 26 self.classifier = nn.Sequential( 27 nn.Dropout(), 28 nn.Linear(256*6*6,4096), 29 nn.ReLU(inplace=True), 30 nn.Dropout(), 31 nn.Linear(4096,4096), 32 nn.ReLU(inplace=True), 33 nn.Linear(4096,num_classes) 34 ) 35 def forward(self, x): 36 x = self.features(x) 37 x = x.view(x.size(0),-1) 38 x = self.classifier(x) 39 return x
VGGNet
在2014年,参加ILSVRC竞赛的“VGG”队在ImageNet上获得了比赛的亚军。VGG的核心思想是利用较小的卷积核来增加网络的深度。常用的有VGG16、VGG19两种类型。VGG16拥有13个卷积层(核大小均为3*3),5个最大池化层,3个全连接层。VGG19拥有16个卷积层(核大小均为3*3),5个最大池化层,3个全连接层,如图1.4所示。

图1.4
加深结构都使用ReLU激活函数,VGG19比VGG16的区别在于多了3个卷积层,利用pytorch实现整VG16模型,VGG19同理。
1 import torch as torch 2 import torch.nn as nn 3 4 class VGG16(nn.Module): 5 def __init__(self,num_classes): 6 super(VGG16,self).__init__() 7 self.features = nn.Sequential( 8 nn.Conv2d(3,64,kernel_size=3,padding=1), 9 nn.ReLU(inplace=True), 10 nn.Conv2d(64,64,kernel_size=3,padding=1), 11 nn.ReLU(inplace=True), 12 13 nn.Conv2d(64,128,kernel_size=3,padding=1), 14 nn.ReLU(inplace=True), 15 nn.Conv2d(128, 128, kernel_size=3, padding=1), 16 nn.ReLU(inplace=True), 17 18 nn.Conv2d(128, 256, kernel_size=3, padding=1), 19 nn.ReLU(inplace=True), 20 nn.Conv2d(256, 256, kernel_size=3, padding=1), 21 nn.ReLU(inplace=True), 22 nn.Conv2d(256, 256, kernel_size=3, padding=1), 23 nn.ReLU(inplace=True), 24 25 nn.Conv2d(256, 512, kernel_size=3, padding=1), 26 nn.ReLU(inplace=True), 27 nn.Conv2d(512, 512, kernel_size=3, padding=1), 28 nn.ReLU(inplace=True), 29 nn.Conv2d(512, 512, kernel_size=3, padding=1), 30 nn.ReLU(inplace=True), 31 32 nn.Conv2d(512, 512, kernel_size=3, padding=1), 33 nn.ReLU(inplace=True), 34 nn.Conv2d(512, 512, kernel_size=3, padding=1), 35 nn.ReLU(inplace=True), 36 nn.Conv2d(512, 512, kernel_size=3, padding=1), 37 nn.ReLU(inplace=True) 38 ) 39 40 self.classifier = nn.Sequential( 41 nn.Linear(512*7*7,4096), 42 nn.ReLU(inplace=True), 43 nn.Dropout(), 44 45 nn.Linear(4096,4096), 46 nn.ReLU(True), 47 nn.Dropout(), 48 49 nn.Linear(4096,num_classes) 50 ) 51 def forward(self, x): 52 x = self.features(x), 53 x = x.view(x.size(0),-1) 54 x = self.classifier(x) 55 return x
GoogLeNet
GoogLeNet专注于加深网络结构,与此同时引入了新的基本结构——Inception模块,从而来增加网络的宽度。GoogLeNet一共22层,它没有全连接层,在2014年的比赛中获得了冠军。
每个原始Inception模块由previous layer、并行处理层及filter concatenation层组成,如图1.5。并行处理层包含4个分支,即1*1卷积分支,3*3卷积分支,5*5卷积分支和3*3最大池化分支。一个关于原始Inception模块的最大问题是,5*5卷积分支即使采用中等规模的卷积核个数,在计算代价上也可能是无法承受的。这个问题在混合池化层之后会更为突出,很快的出现计算量的暴涨。
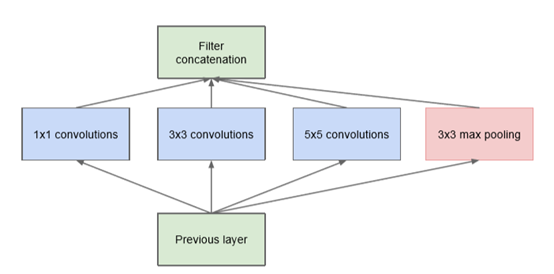
图1.5
为了克服原始Inception模块上的困难,GoogLeNet推出了一个新款,即采用1*1的卷积层来降低输入层的维度,使网络参数减少,因此减少网络的复杂性,如图1.6。因此得到降维Inception模块,称为inception V1。

图1.6
从GoogLeNet中明显看出,共包含9个Inception V1模块,如图1.7所示。所有层均采用了ReLU激活函数。

图1.7
自从2014年过后,Inception模块不断的改进,现在已发展到V4。GoogLeNet V2中的Inception参考VGGNet用两个3*3核的卷积层代替了具有5*5核的卷积层,与此同时减少了一个辅助分类器,并引入了Batch Normalization(BN),它是一个非常有用的正则化方法。V3相对于V2的学习效率提升了很多倍,并且训练时间大大缩短了。在ImageNet上的top-5错误率为4.8%。Inception V3通过改进V2得到,其核心思想是将一个较大的n*n的二维卷积拆成两个较小的一维卷积n*1和1*n。Inception V3有三种不同的结构(Base的大小分别为35*35、17*17、8*8),如图1.8所示,其中分支可能嵌套。GoogLeNet也只用了一个辅助分类器,在ImageNet上top-5的错误率为3.5%。Inception V4是一种与Inception V3类似或更复杂的网络模块。V4在ImageNet上top-5的错误率为3.08%。

图1.8
接下来利用pytorch实现GoogLeNet中的Inception V2模块,其实整个GoogLeNet都是由Inception模块构成的。
1 import torch.nn as nn 2 import torch as torch 3 import torch.nn.functional as F 4 import torchvision.models.inception 5 class BasicConv2d(nn.Module): 6 def __init__(self,in_channels,out_channels,**kwargs): 7 super(BasicConv2d,self).__init__() 8 self.conv = nn.Conv2d(in_channels,out_channels,bias=False,**kwargs) 9 self.bn = nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels,eps=0.001) 10 def forward(self, x): 11 x = self.conv(x) 12 x = self.bn(x) 13 return F.relu(x,inplace=True) 14 15 class Inception(nn.Module): 16 def __init__(self,in_channels,pool_features): 17 super(Inception,self).__init__() 18 self.branch1X1 = BasicConv2d(in_channels,64,kernel_size = 1) 19 20 self.branch5X5_1 = BasicConv2d(in_channels,48,kernel_size = 1) 21 self.branch5X5_2 = BasicConv2d(48,64,kernel_size=5,padding = 2) 22 23 self.branch3X3_1 = BasicConv2d(in_channels,64,kernel_size = 1) 24 self.branch3X3_2 = BasicConv2d(64,96,kernel_size = 3,padding = 1) 25 # self.branch3X3_2 = BasicConv2d(96, 96, kernel_size=1,padding = 1) 26 27 self.branch_pool = BasicConv2d(in_channels,pool_features,kernel_size = 1) 28 def forward(self, x): 29 branch1X1 = self.branch1X1(x) 30 31 branch5X5 = self.branch5X5_1(x) 32 branch5X5 = self.branch5X5_2(branch5X5) 33 34 branch3X3 = self.branch3X3_1(x) 35 branch3X3 = self.branch3X3_2(branch3X3) 36 37 branch_pool = F.avg_pool2d(x,kernel_size = 3,stride = 1,padding = 1) 38 branch_pool = self.branch_pool(branch_pool) 39 40 outputs = [branch1X1,branch3X3,branch5X5,branch_pool] 41 return torch.cat(outputs,1)
ResNet
随着神经网络的深度不断的加深,梯度消失、梯度爆炸的问题会越来越严重,这也导致了神经网络的学习与训练变得越来越困难。有些网络在开始收敛时,可能出现退化问题,导致准确率很快达到饱和,出现层次越深、错误率反而越高的现象。让人惊讶的是,这不是过拟合的问题,仅仅是因为加深了网络。这便有了ResNet的设计,ResNet在2015年的ImageNet竞赛获得了冠军,由微软研究院提出,通过残差模块能够成功的训练高达152层深的网络,如图1.10所示。
ReNet与普通残差网络不同之处在于,引入了跨层连接(shorcut connection),来构造出了残差模块。
在一个残差模块中,一般跨层连接只有跨2~3层,如图1.9所示,但是不排除跨更多的层,跨一层的实验效果不理想。在去掉跨连接层,用其输出用H(x),当加入跨连接层时,F(x) 与H(x)存在关系:F(x):=H(x)-X,称为残差模块。既可以用全连接层构造残差模块,也可以用卷积层构造残差模块。基于残差模块的网络结构非常的深,其深度可达1000层以上。
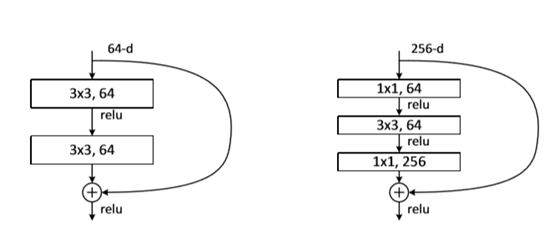
图1.9

图1.10
用于ImageNet的5种深层残差网络结构,如图1.11所示。

图1.11
从何凯明的论文中也读到plain-18、plain-34(即未加shotcut层)错误率比ResNet-18、ResNet-34(加了shotcut层)大了很多,如图1.12所示。

图1.12
下面利用pytorch实现ReNet的残差学习单元,此处参考了torchvision的model。
1 import torch.nn as nn 2 def conv3x3(in_planes, out_planes, stride=1): 3 """3x3 convolution with padding""" 4 return nn.Conv2d(in_planes, out_planes, kernel_size=3, stride=stride, 5 padding=1, bias=False) 6 class BasicBlock(nn.Module): 7 expansion = 1 8 def __init__(self, inplanes, planes, stride=1, downsample=None): 9 super(BasicBlock, self).__init__() 10 self.conv1 = conv3x3(inplanes, planes, stride) 11 self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(planes) 12 self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True) 13 self.conv2 = conv3x3(planes, planes) 14 self.bn2 = nn.BatchNorm2d(planes) 15 self.downsample = downsample 16 self.stride = stride 17 18 def forward(self, x): 19 residual = x 20 out = self.conv1(x) 21 out = self.bn1(out) 22 out = self.relu(out) 23 out = self.conv2(out) 24 out = self.bn2(out) 25 if self.downsample is not None: 26 residual = self.downsample(x) 27 out += residual 28 out = self.relu(out) 29 return out
当然,不管是LeNet,还是VGGNet,亦或是ResNet,这些经典的网络结构,pytorch的torchvision的model中都已经实现,并且还有预训练好的模型,可直接对模型进行微调便可使用。



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号