vue生态系统之vuex
一、webpack生成项目
1、webpack
在需要建立项目的目录中进行初始化项目
E:\vueProject>vue init webpack vuexpj

? Project name vuexpj ? Project description A Vue.js project ? Author bright <bright@live.com> ? Vue build (Use arrow keys) ? Vue build standalone ? Install vue-router? Yes ? Use ESLint to lint your code? No ? Set up unit tests No ? Setup e2e tests with Nightwatch? No
2、项目组件关系图
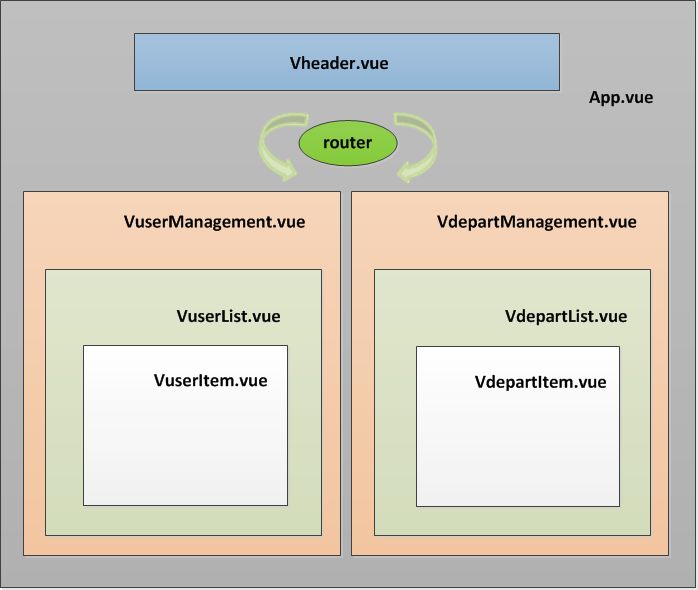
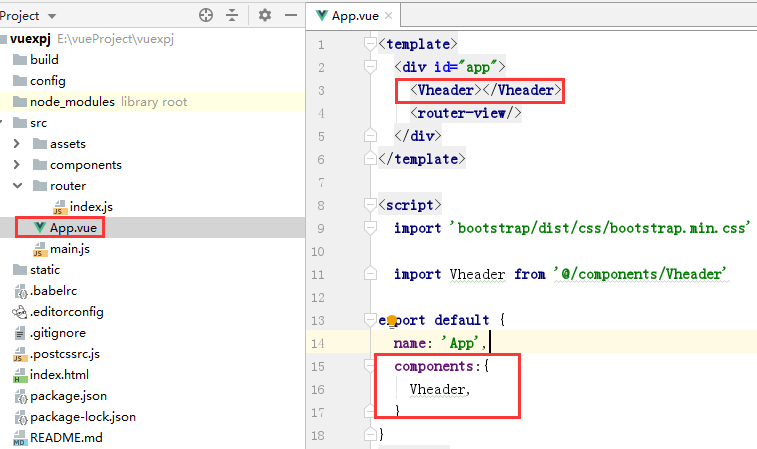
在父组件App.vue中导入Vheader.vue组件:

<template>
<div id="app">
<Vheader></Vheader>
<router-view/>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import 'bootstrap/dist/css/bootstrap.min.css'
import Vheader from '@/components/Vheader'
export default {
name: 'App',
components:{
Vheader,
}
}
</script>
<style scoped>
</style>
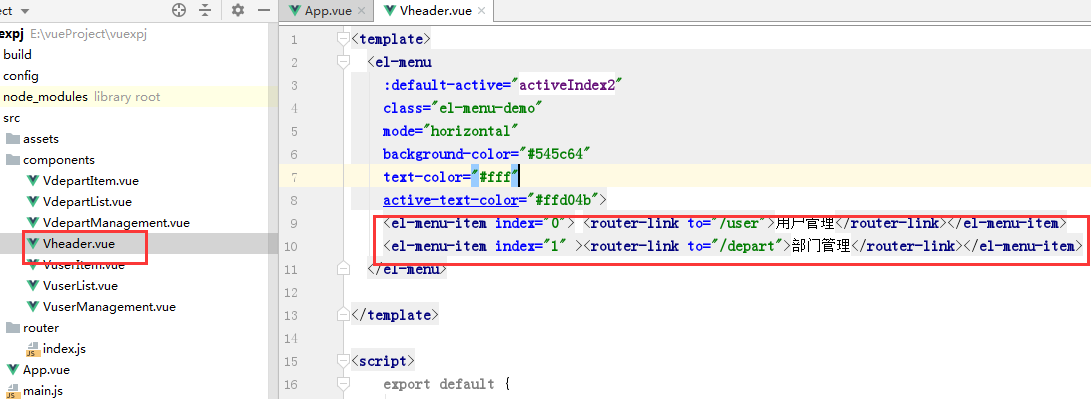
在Vheader.vue组件中渲染路由:

<template> <el-menu :default-active="activeIndex2" class="el-menu-demo" mode="horizontal" background-color="#545c64" text-color="#fff" active-text-color="#ffd04b"> <el-menu-item index="0"> <router-link to="/user">用户管理</router-link></el-menu-item> <el-menu-item index="1" ><router-link to="/depart">部门管理</router-link></el-menu-item> </el-menu> </template> <script> export default { name: "Vheader", data:function () { return { activeIndex2: '0', } }, methods:{ //在当前组件内调用 }, computed:{ //在在当前组件内调用 } } </script> <style scoped> /*设置scoped,只对当前组件样式起作用*/ </style>
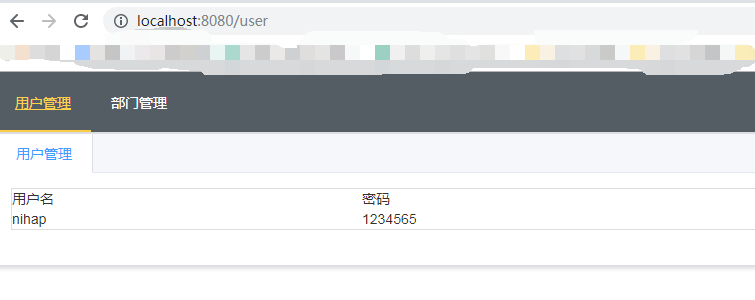
在父组件App.vue中设置路由出口,路由对应组件的内容在这里输出:
<template> <div id="app"> <Vheader></Vheader> <router-view/> </div> </template>
这里对应的VuserList组件就是所有的用户信息,而VuserItem就是每一条的用户信息,假设现在父组件App.vue已经从数据库接收到了用户的数据,那么如何才能在VuserItem上进行渲染呢?这牵扯到父子组件的传值问题,可以利用props进行传值,但是这样一层一层的传递是相当麻烦的,此时可以使用vuex处理复杂传值的问题了。
二、vuex
1、安装vuex
E:\vueProject\vuexpj>npm install vuex --save
2、使用vuex
(1)导入模块
在main.js中导入模块
import Vuex from 'vuex'
(2)注册到全局
在main.js文件中进行注册
Vue.use(Vuex);
(3)创建store
const store = new Vuex.Store({ state: { //这里面的状态跟每一个数据属性有关 UserList:[] }, mutations: { } });
(4)挂载到根实例上
new Vue({ el: '#app', router, store, //挂载到根实例中 components: { App }, template: '<App/>' });

3、获取用户数据
Vuex 是一个专为 Vue.js 应用程序开发的状态管理模式。它采用集中式存储管理应用的所有组件的状态。
- State
Vuex使用单一状态树,用一个对象就包含了全部的应用层级状态。这也意味着,每个应用将仅仅包含一个 store 实例。单一状态树让我们能够直接地定位任一特定的状态片段。由于 Vuex 的状态存储是响应式的,从 store 实例中读取状态最简单的方法就是在计算属性中返回某个状态。
当父组件App.vue页面所有的DOM元素加载完成,页面结构加载完成,就可以向后台API请求数据了,此时需要在App.vue组件中利用mounted方法(页面结构加载完成后执行)发送ajax请求数据:
mounted(){ var _this=this; #_this获取的是Vue实例 //当页面DOM元素即页面结构加载完成后执行此方法 $.ajax({ url:'http://127.0.0.1:8000/api/userdata/', dataType:'JSON', methods:'GET', success:function (data) { _this.$store.state.UserList=data; //Json数据自动解析为对象,并且将数据更新为state中的UserList
} }) }

#urls urlpatterns = [ path('api/userdata/', views.getAllUser), ] #views def getAllUser(request): queryset=models.UserInfo.objects.values('username','password') UserList=list(queryset) print(UserList) return HttpResponse(json.dumps(UserList,ensure_ascii=False))
此时store实例的状态中UserList就有数据了,store实例是每一个组件都可以使用其中的状态,现在将数据渲染在VuserList组件中:首先在VuserList组件的计算属性中从store实例中获取state状态的UserList
computed:{ getAllUserList(){ return this.$store.state.UserList } }
然后,在VuserList组建的模板中进行渲染
<table class="table table-hover"> <tr class="active"> <td>用户名</td> <td>密码</td> </tr> <VuserItem v-for="item in getAllUserList" :userinfo="item"></VuserItem> </table>
这里可以看出来,循环每一条用户数据,然后自定义属性userinfo,并且将每一个用户数据传给其子组件VuserItem,在VuserItem中接收每一个用户数据,并且渲染:
<script> export default { name: "VuserItem", data:function () { return { } }, //在VuserItem中验证数据类型,接收数据 props:{ userinfo:Object, } } </script>
//渲染单条数据
<template>
<tr>
<td>{{userinfo.username}}</td>
<td>{{userinfo.password}}</td>
</tr>
</template>
4、添加用户数据
- Mutation
更改 Vuex 的 store 中的状态的唯一方法是提交 mutation。Vuex 中的 mutation 非常类似于事件:每个 mutation 都有一个字符串的 事件类型 (type) 和 一个 回调函数 (handler)。这个回调函数就是我们实际进行状态更改的地方,并且它会接受 state 作为第一个参数:
在VuserList组件中,增加添加按钮:

<button type="button" class="btn btn-info" @click="addOneUser">添加</button>
在VuserList组件中,增加addOneUser方法:
addOneUser() { $('#addModal').modal('show') },
点击之后弹出模态对话框,用于添加数据:
<div class="modal fade" id="addModal" tabindex="-1" role="dialog" aria-labelledby="myModalLabel"> <div class="modal-dialog" role="document"> <div class="modal-content"> <div class="modal-header"> <button type="button" class="close" data-dismiss="modal" aria-label="Close"><span aria-hidden="true">×</span></button> <h4 class="modal-title" id="myModalLabel">创建用户</h4> </div> <div class="modal-body"> <form id="fm" class="form-horizontal"> <div class="form-group"> <label for="username" class="col-sm-2 control-label">姓名</label> <div class="col-sm-10"> <input type="text" class="form-control" name="username" placeholder="姓名" v-model="getUsername"> </div> </div> <div class="form-group"> <label for="password" class="col-sm-2 control-label">密码</label> <div class="col-sm-10"> <input type="text" class="form-control" name="password" placeholder="密码" v-model="getPassword"> </div> </div> </form> </div> <div class="modal-footer"> <span id="errorMsg" style="color: red;"></span> <button type="button" class="btn btn-default" data-dismiss="modal">取消</button> <button type="button" class="btn btn-primary" @click="isSave">保存</button> <el-button :plain="true" @click="open2"></el-button> <!--保存成功提示--> <el-button :plain="true" @click="open4"></el-button> <!--保存失败提示--> </div> </div> </div> </div>
可以看到使用v-model获取值,相当于v-model给计算属性getUsername,getPassword赋值:
computed: { getAllUserList() { return this.$store.state.UserList }, getUsername: { set(newValue) { this.$store.state.UserObject.username = newValue//将获取的username 值保存在store实例的state状态中 }, get() { return this.$store.state.UserObject.username //返回store实例的state状态中password } }, getPassword:{ set(newValue) { this.$store.state.UserObject.password = newValue //将获取的password值保存在store实例的state状态中 }, get() { return this.$store.state.UserObject.password //返回store实例的state状态中password } } } }
在main.js文件中新建的store实例中保存UserObject状态:

const store = new Vuex.Store({ state: { //这里面的状态跟每一个数据属性有关 UserList: [], UserObject: { username: '', password: '' }, },
此时,在VuserList组件的方法中写入点击保存按钮向后台API提交数据了:
//发送数据 isSave(){ var _this = this; //获取Vue实例对象,Ajax中的this不是实例本身 var data={ //通过计算属性获取数据,实际也是从store实例的状态中拿到数据 username:this.getUsername, password:this.getPassword, // csrfmiddlewaretoken: '{{ csrf_token }}' }; $.ajax({ url:'http://127.0.0.1:8000/api/addUser/', method:'post', dataType:'JSON', contentType: 'application/json', //发送的数据类型为json,所以自己发送的数据必须保证为json data:JSON.stringify(data), //发送json数据 success:function (data) { console.log(data); if(data.state){ _this.open2(); //执行保存成功提示函数 _this.getUsername=''; //添加成功后将input框置空 _this.getPassword='' }else { _this.open4(); //执行保存失败提示函数 } _this.$store.state.UserList.push(data.user); //将添加成功的数据添加到状态,用于页面更新 } }); $('#addModal').modal('hide') //发送成功后模态对话框消失 }

open2(){ this.$message({ message: '恭喜你,创建用户成功!', type: 'success' }); },

open4() { this.$message.error('对不起,创建用户失败!'); },
这样在后台接收数据进行处理接可以了:

#urls urlpatterns = [ path('api/addUser/', views.addUser), ] #views def addUser(request): retDict={ 'code':1000, 'state':False, 'msg':'存储失败' } userjson=request.body #json数据存储在request.body中 userdict=json.loads(str(userjson,encoding='utf8')) obj=models.UserInfo.objects.create(username=userdict['username'],password=userdict['password']) print(obj) if obj: retDict['code']=2000 retDict['state']=True retDict['msg']='存储成功' retDict['user']={'username':obj.username,'password':obj.password} return HttpResponse(json.dumps(retDict,ensure_ascii=False))
截止到这里,我们还是没有使用mutition,但是也完成了对应的功能,但是,可以发现,我们在改变store实例的state状态时,是通过赋值或者其它手段:
_this.$store.state.UserList.push(data.user); //将添加成功的数据添加到状态,用于页面更新
官方文档上说更改 Vuex 的 store 中的状态的唯一方法是提交 mutation,这里就需要做一些改变了,我们将所有与Ajax的操作交给Mutation来做,然后在需要的地方通过store.commit方法唤醒:
(1)获取数据使用mutation
//在App.vue中 //mounted方法页面加载完成后触发该方法 mounted(){ //在这个地方触发对应mutation方法,也就是getAllUser,通过ajax获取所有的数据 this.$store.commit('getAllUser'); } //在main.js文件中 mutations: { //在App.vue组件中来提交该方法触发,向后端获取数据 getAllUser(state){ //当页面DOM元素即页面结构加载完成后执行此方法 $.ajax({ url:'http://127.0.0.1:8000/api/userdata/', dataType:'JSON', methods:'GET', success:function (data) { state.UserList=data; } }) } }
(2)添加数据使用mutation
//在VuserList.vue组件中 //发送数据 isSave(){ var data={ //通过计算属性获取数据,实际也是从store实例的状态中拿到数据 username:this.getUsername, password:this.getPassword, // csrfmiddlewaretoken: '{{ csrf_token }}' }; //在这个地方触发对应mutation方法,也就是gaddUser,通过ajax提交所有的数据 this.$store.commit( { type: 'addUser', data:data, getUsername:this.getUsername, getPassword:this.getPassword, successfunc: this.open2, failturefunc:this.open4, } ); $('#addModal').modal('hide') //发送成功后模态对话框消失 } //在main.js文件中 mutations: { //在VuserList组件中提交该方法触发,向后端提交数据 addUser(state,payload){ $.ajax({ url:'http://127.0.0.1:8000/api/addUser/', method:'post', dataType:'JSON', contentType: 'application/json', //发送的数据类型为json,所以自己发送的数据必须保证为json data:JSON.stringify(payload.data), //发送json数据 success:function (data) { console.log(data); if(data.state){ payload.successfunc(); //执行保存成功提示函数 payload.getUsername=''; //添加成功后将input框置空 payload.getPassword='' }else { payload.failturefunc(); //执行保存失败提示函数 } state.UserList.push(data.user); //将添加成功的数据添加到状态,用于页面更新 } }); } }
虽然使用mutition了,但是mutation 必须是同步函数,那么如何使用异步操作呢?
- Action
Action 类似于 mutation,不同在于:
(1)Action 提交的是 mutation,而不是直接变更状态。
(2)Action 可以包含任意异步操作。
页面中需要做如下更改:
(1)获取数据
//1、在App.vue组件中分发action,这样触发action函数执行 mounted(){ //在这个地方触发对应mutation方法,也就是getAllUser,通过ajax获取所有的数据 // this.$store.commit('getAllUser'); //更改为: this.$store.dispatch('getAllUser') } //2、在main.js的action中 //用于执行异步函数操作,并且提交的是mutation actions:{ //context与 store 实例具有相同方法和属性 getAllUser(context){ $.ajax({ url:'http://127.0.0.1:8000/api/userdata/', dataType:'JSON', methods:'GET', success:function (data) { //保存返回的数据状态,mutation修改state状态,所以传给mutation处理 context.commit('GETALLUSER',data) //传递的是后台的数据 } }) }, }); //3、在main.js的mutations中,因为action不能与state直接交互,它提交mutation mutations: { //在action中提交的mutation方法 GETALLUSER(state,data){ state.UserList=data; }, },
(2)添加数据
//1、在VuserList.vue组件中分发action,这样触发action函数执行 this.$store.dispatch( { type: 'addUser', data:data, getUsername:this.getUsername, getPassword:this.getPassword, successfunc: this.open2, failturefunc:this.open4, } ); //2、在main.js的action中 //用于执行异步函数操作,并且提交的是mutation actions:{ addUser(context,payload){ $.ajax({ url:'http://127.0.0.1:8000/api/addUser/', method:'post', dataType:'JSON', contentType: 'application/json', //发送的数据类型为json,所以自己发送的数据必须保证为json data:JSON.stringify(payload.data), //发送json数据 success:function (data) { if(data.state){ payload.successfunc(); //执行保存成功提示函数 payload.getUsername=''; //添加成功后将input框置空 payload.getPassword='' }else { payload.failturefunc(); //执行保存失败提示函数 } //保存返回的数据状态,mutation修改state状态,所以传给mutation处理 context.commit('ADDUSER',data); //data是后台数据 } }); } } //3、在main.js的mutations中,因为action不能与state直接交互,它提交mutation mutations: { //在action中提交的mutation方法 ADDUSER(state,data){ state.UserList.push(data.user); //将添加成功的数据添加到状态,用于页面更新 } },
Vue对用户的增删改查完整操作,详见:https://www.cnblogs.com/shenjianping/p/11254442.html



