WITH RECURSIVE 递归 与with as 子查询部分
1 计算1到100的累加的结果。 2 WITH RECURSIVE t(n) AS ( 3 VALUES (1) 4 UNION ALL 5 SELECT n+1 FROM t WHERE n < 100 6 ) 7 SELECT sum(n) FROM t;
sum
5050
=======================================
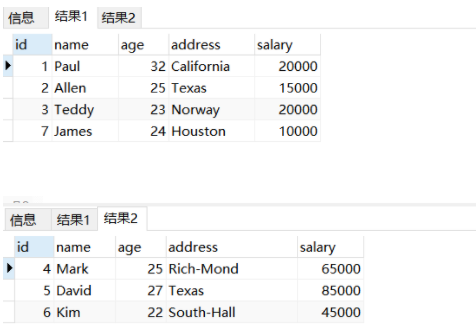
1 /* 2 https://www.yiibai.com/html/postgresql/2013/080565.html 3 create table company ( 4 id int , 5 name varchar (60), 6 age int , 7 address varchar (30), 8 salary int 9 ); 10 insert into company values(1,'Paul',32,'California',20000); 11 insert into company values(2,'Allen',25, 'Texas',15000); 12 insert into company values(3,'Teddy',23,'Norway',20000); 13 insert into company values(4,'Mark',25,'Rich-Mond',65000); 14 insert into company values(5,'David',27,'Texas',85000); 15 insert into company values(6,'Kim',22,'South-Hall',45000); 16 insert into company values(7,'James',24,'Houston',10000); 17 */ 18 19 --递归WITH 20 --找到小于20000的薪金总和 21 22 WITH RECURSIVE t(n) AS ( 23 VALUES (0) 24 UNION ALL 25 SELECT salary FROM company WHERE salary < 20000 26 ) 27 SELECT SUM(n) FROM t 28 29 --删除指定的公司行,RETURNING子句返回它们的内容;然后主查询读取输出,并将其插入到COMPANY1 表: 30 31 CREATE TABLE COMPANY1( 32 ID INT PRIMARY KEY NOT NULL, 33 NAME TEXT NOT NULL, 34 AGE INT NOT NULL, 35 ADDRESS CHAR(50), 36 SALARY REAL 37 ); 38 WITH moved_rows AS ( 39 DELETE FROM COMPANY 40 WHERE 41 SALARY >= 30000 42 RETURNING * 43 ) 44 INSERT INTO COMPANY1 (SELECT * FROM moved_rows); 45 46 SELECT * FROM COMPANY; 47 SELECT * FROM COMPANY1;
============================================================================
定义下面这样的表,存储每个区域(省、市、区)的id,名字及上级区域的pid
1 create table tb(id varchar(3) , pid varchar(3) , name varchar(10)); 2 3 insert into tb values('002' , 0 , '浙江省'); 4 insert into tb values('001' , 0 , '广东省'); 5 insert into tb values('003' , '002' , '衢州市'); 6 insert into tb values('004' , '002' , '杭州市') ; 7 insert into tb values('005' , '002' , '湖州市'); 8 insert into tb values('006' , '002' , '嘉兴市') ; 9 insert into tb values('007' , '002' , '宁波市'); 10 insert into tb values('008' , '002' , '绍兴市') ; 11 insert into tb values('009' , '002' , '台州市'); 12 insert into tb values('010' , '002' , '温州市') ; 13 insert into tb values('011' , '002' , '丽水市'); 14 insert into tb values('012' , '002' , '金华市') ; 15 insert into tb values('013' , '002' , '舟山市'); 16 insert into tb values('014' , '004' , '上城区') ; 17 insert into tb values('015' , '004' , '下城区'); 18 insert into tb values('016' , '004' , '拱墅区') ; 19 insert into tb values('017' , '004' , '余杭区') ; 20 insert into tb values('018' , '011' , '金东区') ; 21 insert into tb values('019' , '001' , '广州市') ; 22 insert into tb values('020' , '001' , '深圳市') ;
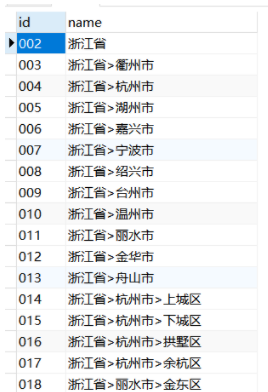
需要查出某个省,比如浙江省,管辖的所有市及市辖地区
with RECURSIVE cte as ( select a.id,cast(a.name as varchar(100)) from tb a where id='002' union all select k.id,cast(c.name||'>'||k.name as varchar(100)) as name from tb k inner join cte c on c.id = k.pid )select id,name from cte ;
==============================================================================
with as
with as 也称作子查询部分;提高sql语句可读性,减少嵌套冗余
–相当于建了个e临时表
with e as (select * from scott.emp e where e.empno=7499)
select * from e;
–相当于建了e、d临时表
with
e as (select * from scott.emp),
d as (select * from scott.dept)
select * from e, d where e.deptno = d.deptno;
其实就是把一大堆重复用到的sql语句放在with as里面,取一个别名,后面的查询就可以用它,这样对于大批量的sql语句起到一个优化的作用,而且清楚明了。
向一张表插入数据的with as用法
insert into table2
with
s1 as (select rownum c1 from dual connect by rownum <= 10),
s2 as (select rownum c2 from dual connect by rownum <= 10)
select a.c1, b.c2 from s1 a, s2 b where…;
select s1.sid, s2.sid from s1 ,s2需要有关联条件,不然结果会是笛卡尔积。
with as 相当于虚拟视图。
with as短语,也叫做子查询部分(subquery factoring),可以让你做很多事情,定义一个sql片断,该sql片断会被整个sql语句所用到。有的时候,是为了让sql语句的可读性更高些,也有可能是在union all的不同部分,作为提供数据的部分。
特别对于union all比较有用。因为union all的每个部分可能相同,但是如果每个部分都去执行一遍的话,则成本太高,所以可以使用with as短语,则只要执行一遍即可。如果with as短语所定义的表名被调用两次以上,则优化器会自动将with as短语所获取的数据放入一个temp表里,如果只是被调用一次,则不会。而提示materialize则是强制将with as短语里的数据放入一个全局临时表里。很多查询通过这种方法都可以提高速度。
with sql1 as (select to_char(a) s_name from test_tempa), sql2 as (select to_char(b) s_name from test_tempb where not exists (select s_name from sql1 where rownum=1)) select * from sql1 union all select * from sql2 union all select ‘no records’ from dual where not exists (select s_name from sql1 where rownum=1) and not exists (select s_name from sql2 where rownum=1);
WITH语句的优点:
(1). SQL可读性增强。比如对于特定with子查询取个有意义的名字等。
(2)、with子查询只执行一次,将结果存储在用户临时表空间中,可以引用多次,增强性能。
举例:在进行导入EXCEL的过程中,有时候,需要将数据存储在临时表中,当下一次在进行导入的时候,进行清除临时表的数据,但是这时候,有时候发生并发问题的话,两个用户可能会分别操作对方的数据,所以,可能造成混乱,但是可以使用WITH函数和UNION语句拼接一个SQL语句,存储在SESSION中,当需要导出错误信息的时候,可以使用该语句构造数据。
to:https://blog.csdn.net/dufemt/article/details/80773394



