Rasa初始化聊天机器人的配置
本文详细介绍了使用 rasa init 初始化聊天机器人项目的配置,包括 nlu.yml、rules.yml、stories.yml、test_stories.yml、config.yml、credentials.yml、domain.yml、endpoints.yml 等文件。如下所示:
│ config.yml
│ credentials.yml
│ domain.yml
│ endpoints.yml
│ graph.html
│ requirements.txt
│
├─actions
│ actions.py
│ __init__.py
│
├─data
│ nlu.yml
│ rules.yml
│ stories.yml
│
├─models
└─tests
test_stories.yml
一.nlu.yml 文件
version: "3.1"
nlu:
- intent: greet
examples: |
- hey
- hello
- hi
- hello there
- good morning
- good evening
- moin
- hey there
- let's go
- hey dude
- goodmorning
- goodevening
- good afternoon
- intent: goodbye
examples: |
- cu
- good by
- cee you later
- good night
- bye
- goodbye
- have a nice day
- see you around
- bye bye
- see you later
- intent: affirm
examples: |
- yes
- y
- indeed
- of course
- that sounds good
- correct
- intent: deny
examples: |
- no
- n
- never
- I don't think so
- don't like that
- no way
- not really
- intent: mood_great
examples: |
- perfect
- great
- amazing
- feeling like a king
- wonderful
- I am feeling very good
- I am great
- I am amazing
- I am going to save the world
- super stoked
- extremely good
- so so perfect
- so good
- so perfect
- intent: mood_unhappy
examples: |
- my day was horrible
- I am sad
- I don't feel very well
- I am disappointed
- super sad
- I'm so sad
- sad
- very sad
- unhappy
- not good
- not very good
- extremly sad
- so saad
- so sad
- intent: bot_challenge
examples: |
- are you a bot?
- are you a human?
- am I talking to a bot?
- am I talking to a human?
(1)greet:欢迎语,比如你好等。
(2)goodbye:比如再见等。
(3)affirm:肯定,比如是的等。
(4)deny:否定,比如不等。
(5)mood_great:心情好,比如开心等。
(6)mood_unhappy:心情不好,比如沮丧等。
(7)bot_challenge:不在上述意图当中,就是 bot 无法识别意图。
二.rules.yml
version: "3.1"
rules:
- rule: Say goodbye anytime the user says goodbye
steps:
- intent: goodbye
- action: utter_goodbye
- rule: Say 'I am a bot' anytime the user challenges
steps:
- intent: bot_challenge
- action: utter_iamabot
规则就是当识别到这个意图(intent)的时候,就执行相应的动作(action)。如下所示:
responses:
utter_goodbye:
- text: "Bye"
utter_iamabot:
- text: "I am a bot, powered by Rasa."
(1)当遇到 goodbye 意图的时候,就要执行 utter_goodbye 这个动作。
(2)当遇到 bot_challenge 意图的时候,就要执行 utter_iamabot 这个动作。
三.stories.yml
version: "3.1"
stories:
- story: happy path
steps:
- intent: greet
- action: utter_greet
- intent: mood_great
- action: utter_happy
- story: sad path 1
steps:
- intent: greet
- action: utter_greet
- intent: mood_unhappy
- action: utter_cheer_up
- action: utter_did_that_help
- intent: affirm
- action: utter_happy
- story: sad path 2
steps:
- intent: greet
- action: utter_greet
- intent: mood_unhappy
- action: utter_cheer_up
- action: utter_did_that_help
- intent: deny
- action: utter_goodbye
1.这个场景包括 3 条路线
(1)happy path 路线
用户:你好(意图:greet) 机器人:你好(动作:utter_greet) 用户:很开心(mood_great) 机器人:很好,加油(动作:utter_happy)
(2)sad path 1 路线用户:你好(意图:greet) 机器人:你好(动作:utter_greet) 用户:心情不好(意图:mood_unhappy) 机器人:要开心起来(动作:utter_cheer_up) 机器人:那对你有帮助吗?(动作:utter_did_that_help) 用户:是的(意图:affirm) 机器人:很好,加油(动作:utter_happy)
(3)sad path 2 路线用户:你好(意图:greet) 机器人:你好(动作:utter_greet) 用户:心情不好(意图:mood_unhappy) 机器人:要开心起来(动作:utter_cheer_up) 机器人:那对你有帮助吗?(动作:utter_did_that_help) 用户:没有(意图:deny) 机器人:再见(动作:utter_goodbye)
2.rasa visualize 可视化 Story
rasa visualize 命令的主要工作是分析 Rasa 项目中的对话故事(stories)文件并生成一个交互式的图形,以可视化对话流程。交互图的节点代表了用户意图和机器人动作,边表示它们之间的转换关系。这种可视化工具有助于直观地理解对话流程,特别是在对话逻辑比较复杂的情况下。以下是该命令的工作原理:
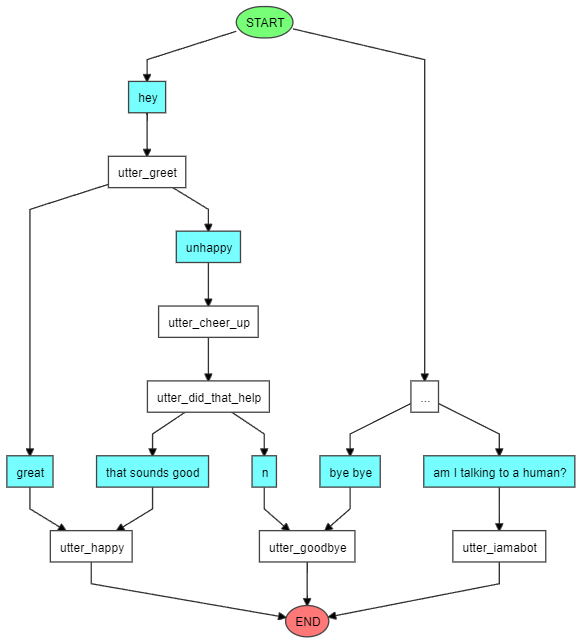
(1)读取 Stories 文件
首先,rasa visualize 命令会读取项目中的 stories 文件(通常是 data/stories.yml)。这些文件包含了对话故事,定义了用户意图和机器人动作之间的交互流程。
(2)构建交互图
通过解析 stories 文件,命令会构建一个对话交互图。这个图表示用户和机器人在对话中的交互流程,以及相应的用户意图和机器人动作。
(3)生成可视化HTML文件
rasa visualize 命令会将构建的对话交互图转换为一个 HTML 文件,其中包含了图形表示以及相应的节点和边。这个 HTML 文件包含了交互式元素,允许用户通过鼠标交互浏览对话流程。
(4)在浏览器中打开HTML文件
最后,命令会在默认的浏览器中打开生成的 HTML 文件,让用户能够通过图形化界面来查看对话的流程。
四.config.yml 文件
# 配置配方
# https://rasa.com/docs/rasa/model-configuration/
recipe: default.v1
# assistant项目唯一标识符
# 此默认值必须替换为部署中的唯一assistant名称
assistant_id: 20231231-104634-violent-plate
# Rasa NLU的配置
# https://rasa.com/docs/rasa/nlu/components/
language: en
pipeline: null
# # 没有为NLU管道提供配置。以下默认管道用于训练你的模型。
# # 如果想自定义它,请取消注释并调整管道。
# # 有关更多信息,请参见https://rasa.com/docs/rasa/tuning-your-model。
# - name: WhitespaceTokenizer
# - name: RegexFeaturizer
# - name: LexicalSyntacticFeaturizer
# - name: CountVectorsFeaturizer
# - name: CountVectorsFeaturizer
# analyzer: char_wb
# min_ngram: 1
# max_ngram: 4
# - name: DIETClassifier
# epochs: 100
# constrain_similarities: true
# - name: EntitySynonymMapper
# - name: ResponseSelector
# epochs: 100
# constrain_similarities: true
# - name: FallbackClassifier
# threshold: 0.3
# ambiguity_threshold: 0.1
# Rasa Core的配置
# https://rasa.com/docs/rasa/core/policies/
policies: null
# # 没有为策略提供配置。以下默认策略用于训练你的模型。
# # 如果想自定义它们,请取消注释并调整策略。
# # 有关更多信息,请参见https://rasa.com/docs/rasa/policies。
# - name: MemoizationPolicy
# - name: RulePolicy
# - name: UnexpecTEDIntentPolicy
# max_history: 5
# epochs: 100
# - name: TEDPolicy
# max_history: 5
# epochs: 100
# constrain_similarities: true
主要是提供关于 Rasa NUL(管道配置)、Rasa Core(策略配置)、recipe(配方配方)、assistant_id(唯一标识符配置)、language(语言)的配置。需要注意的是,当 pipeline: null 和 policies: null 时,执行默认的管道和策略。
五.domain.yml
version: "3.1"
intents:
- greet
- goodbye
- affirm
- deny
- mood_great
- mood_unhappy
- bot_challenge
responses:
utter_greet:
- text: "Hey! How are you?"
utter_cheer_up:
- text: "Here is something to cheer you up:"
image: "https://i.imgur.com/nGF1K8f.jpg"
utter_did_that_help:
- text: "Did that help you?"
utter_happy:
- text: "Great, carry on!"
utter_goodbye:
- text: "Bye"
utter_iamabot:
- text: "I am a bot, powered by Rasa."
session_config:
session_expiration_time: 60 # 会话过期时间,单位秒
carry_over_slots_to_new_session: true # 是否将上一个会话的槽位带入到新的会话中
主要是意图(intent),响应(response)和会话(session)配置。
六.credentials.yml
# 这个文件包含了你的机器人使用的语音和聊天平台的凭证。
# https://rasa.com/docs/rasa/messaging-and-voice-channels
rest:
# # 你不需要在这里提供任何东西 - 这个频道不需要任何凭证
#facebook:
# verify: "<verify>"
# secret: "<your secret>"
# page-access-token: "<your page access token>"
#slack:
# slack_token: "<your slack token>"
# slack_channel: "<the slack channel>"
# slack_signing_secret: "<your slack signing secret>"
#socketio:
# user_message_evt: <event name for user message>
# bot_message_evt: <event name for bot messages>
# session_persistence: <true/false>
socketio:
user_message_evt: user_uttered # 用户消息事件
bot_message_evt: bot_uttered # 机器人消息事件
session_persistence: false # 会话持久化
#mattermost:
# url: "https://<mattermost instance>/api/v4"
# token: "<bot token>"
# webhook_url: "<callback URL>"
# 这个entry是在你使用Rasa企业版时需要的。这个entry代表了Rasa企业版的“频道”的凭证,即与你的机器人交谈并与访客共享。
rasa:
url: "http://localhost:5002/api"
(1)socketio 配置
user_message_evt: 用户消息事件。在使用 Socket.IO 通道时,Rasa 将监听该事件来接收来自用户的消息。bot_message_evt: 机器人消息事件。在使用 Socket.IO 通道时,Rasa 将通过该事件向用户发送消息。session_persistence: 会话持久化。设置为false表示不保存对话状态,每次连接都是新的对话。
(2)rasa 配置
url:http://localhost:5002/api:最早这部分配置是为了在使用 Rasa X 时提供凭证信息。但是现在 Rasa X 已经体制维护了,所以成了现在的 Rasa 企业版。
(3)Facebook、Slack、Mattermost 配置
每个注释后面的配置项提供了针对特定平台(如 Facebook、Slack、Mattermost)的配置示例。这些示例包括验证令牌、密钥、访问令牌等信息,这些信息是在连接到相应平台时所需的。你应该根据你的实际情况替换这些示例值。如果你没有使用某个平台,可以将相应的部分注释掉或删除。确保只保留你实际使用的平台的配置信息。
七.endpoints.yml 文件
# 这个文件包含了你的机器人可以使用的不同端点。
# 服务器从中拉取模型的位置。
# https://rasa.com/docs/rasa/model-storage#fetching-models-from-a-server
#models:
# url: http://my-server.com/models/default_core@latest
# wait_time_between_pulls: 10 # [optional](default: 100)
# 服务器运行自定义操作。
# https://rasa.com/docs/rasa/custom-actions
action_endpoint:
url: "http://localhost:5055/webhook"
# Tracker store用于存储对话。默认情况下,对话存储在内存中。
# https://rasa.com/docs/rasa/tracker-stores
#tracker_store:
# type: redis
# url: <host of the redis instance, e.g. localhost>
# port: <port of your redis instance, usually 6379>
# db: <number of your database within redis, e.g. 0>
# password: <password used for authentication>
# use_ssl: <whether or not the communication is encrypted, default false>
#tracker_store:
# type: mongod
# url: <url to your mongo instance, e.g. mongodb://localhost:27017>
# db: <name of the db within your mongo instance, e.g. rasa>
# username: <username used for authentication>
# password: <password used for authentication>
# Event broker which all conversation events should be streamed to.
# 所有对话事件都应该流式传输到的Event broker。
# https://rasa.com/docs/rasa/event-brokers
#event_broker:
# url: localhost
# username: username
# password: password
# queue: queue
这个配置文件定义了 Rasa 机器人在不同端点上的配置。确保根据你的需求正确配置这些端点。如果不需要使用远程模型、自定义操作、或者对话存储,你可以注释掉相应的部分。以下是对每个部分的详细解释:
(1)模型服务器端点(models)
url: 指定了从服务器中拉取模型的位置。可以设置为训练好的模型所在的服务器地址。通常,这个配置项用于从远程服务器获取最新的模型。 wait_time_between_pulls: 可选配置,用于设置两次拉取模型之间的等待时间。默认值是100毫秒。
注释掉这个部分的配置意味着使用本地文件系统中的模型,而不是从远程服务器拉取。
(2)自定义操作端点(action_endpoint)
url: 指定了运行自定义操作的服务器地址。当 Rasa 接收到执行自定义操作的请求时,它会将请求发送到这个地址。这个地址应该指向运行自定义操作的服务器。
(3)对话存储(tracker_store)
type: 指定了对话存储的类型。可以选择使用redis或mongod作为对话存储后端。注释掉这部分的配置将使用默认的内存存储,对话数据将在内存中保留,服务器重新启动后将丢失。具体的配置参数(如 url、port、db、username、password等)取决于选择的存储类型。
(4)事件代理(event_broker)
url: 指定了事件代理的地址。事件代理用于将所有对话事件流式传输到指定的位置。可以选择使用例如 RabbitMQ 或 Redis 作为事件代理,将对话事件发送到其它系统中。注释掉这部分的配置表示不使用事件代理。
参考文献
[0] 本文源码(rasa-v2024010101):https://github.com/ai408/nlp-engineering/tree/main/知识工程-对话系统/公众号代码/rasa-v2024010101
[1] Rasa 领域:https://rasa.com/docs/rasa/domain/
[2] Rasa 架构:https://rasa.com/docs/rasa/arch-overview/#!
[3] Rasa 模型配置:https://rasa.com/docs/rasa/model-configuration/
[4] Rasa 动作:https://rasa.com/docs/rasa/actions/
[5] Rasa 评估:https://rasa.com/docs/rasa/markers/
NLP工程化
1.本公众号以对话系统为中心,专注于Python/C++/CUDA、ML/DL/RL和NLP/KG/DS/LLM领域的技术分享。
2.本公众号Roadmap可查看飞书文档:https://z0yrmerhgi8.feishu.cn/wiki/Zpewwe2T2iCQfwkSyMOcgwdInhf
NLP工程化

飞书文档






【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 阿里最新开源QwQ-32B,效果媲美deepseek-r1满血版,部署成本又又又降低了!
· 开源Multi-agent AI智能体框架aevatar.ai,欢迎大家贡献代码
· Manus重磅发布:全球首款通用AI代理技术深度解析与实战指南
· 被坑几百块钱后,我竟然真的恢复了删除的微信聊天记录!
· AI技术革命,工作效率10个最佳AI工具