“串”学习——三种表示方法
串有三种表示方法:
str.h
#ifndef _STR_H #define _STR_H #define MAXSTRING 255 typedef unsigned char STR[MAXSTRING+1]; void NewStr(STR &s,char *str); void ClearStr(STR &s); int StrCompare(STR s,STR t); int StrConcat(STR &s,STR t); int SubStr(STR &s,STR t,int pos,int len); #endif
str.cpp
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include"str.h"
void NewStr(STR &s,char *str)
{
int i;
if(str == NULL)
return;
for(i=0; str[i]; i++)
s[i] = str[i];
s[i] = 0;
}
void ClearStr(STR &s)
{
s[0] = 0;
}
int StrCompare(STR s,STR t)
{
int i;
for(i=0; s[i] && t[i] ;i++)
if(s[i] != t[i])
return s[i] - t[i];
if(s[i])
return 1;
else if(t[i])
return -1;
else
return 0;
}
int StrConcat(STR &s,STR t)
{
int i,j;
for(i=0; s[i] ;i++);
for(j=0; t[j] && i<= MAXSTRING ;i++,j++)
s[i] = t[j];
if(i>MAXSTRING && t[j])
{
ClearStr(s);
return 0;
}
s[i] = 0;
}
int SubStr(STR &s,STR t,int pos,int len)
{
int i,j;
for(i=0; i<pos -1; i++)
if(!t[i]) return 0;
for(j=0; j<len && t[i] ;i++,j++)
s[j] = t[i];
if(j!=len)
{
ClearStr(s);
return 0;
}else{
s[j] = 0;
return 1;
}
}
testString.cpp
#include<stdio.h>
#include "str.h"
void main()
{
int res;
STR t,s;
NewStr(s,"hello");
printf("s=%s\n",s);
NewStr(t,"hello");
res = StrCompare(s,t);
if(res == 0)
printf("s==t\n");
else if(res > 0)
printf("s > t\n");
else
printf("s < t\n");
NewStr(t," world");
StrConcat(s,t);
printf("s=%s\n",s);
ClearStr(t);
SubStr(t,s,2,6);
printf("t=%s\n",t);
ClearStr(s);
}
str.h
#ifndef _STR_H
#define _STR_H
typedef struct
{
char *ch;
int len;
}STR;
STR *NewStr(char *str);
void DestroyStr(STR *s);
void ClearStr(STR *s);
int StrCompare(STR *s,STR *t);
int StrConcat(STR *s,STR *t);
STR * SubStr(STR *s,int pos,int len);
#endif
str.c
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include"str.h"
//根据char[]创建字符串
STR *NewStr(char *str)
{
STR * s = NULL;
int i;
s = (STR *)malloc(sizeof(STR));
if(s == NULL) return NULL;
//循环到str[i]==\0时结束,i就是字符串的长度
for(i = 0; str[i] ; ++i);
s->ch = (char *)malloc((i + 1) * sizeof(char));
if(s->ch == NULL)
{
free(s);
return NULL;
}
//将str中内容搬到s.ch里
s->len = i;
while(i>=0)
{
s->ch[i] = str[i];
--i;
}
return s;
}
void DestroyStr(STR *s)
{
free(s->ch);
free(s);
}
void ClearStr(STR *s)
{
free(s->ch);
s->ch = NULL;
s->len = 0;
}
int StrCompare(STR *s,STR *t)
{
int i;
for(i = 0; i < s->len && i < t->len;i++)//abc abcde
//s->ch[i]ASCII码大则返回正数代表大于关系
//如果s->ch[i]比较小,则返回负数代表小于关系
if(s->ch[i] != t->ch[i])
return s->ch[i] - t->ch[i];
//s比t短时返回负数,比t长时返回正,一样长返回0
return s->len - t->len;
}
int StrConcat(STR *s,STR *t)
{
//s,t都指向一块内存区,而他们合并后的内存区一定比他们大
char *temp = NULL;
int i;
temp = (char *)malloc((s->len + t->len +1) * sizeof(char));
if(temp == NULL) return 0;
for(i = 0;i < s->len ;i++)
temp[i] = s->ch[i];
for(; i < s->len + t->len ;i++)
temp[i] = t->ch[i - s->len];
temp[i] = 0;
ClearStr(s);
s->ch = temp;
s->len = i;
return 1;
}
STR * SubStr(STR *s,int pos,int len)
{
STR * t = NULL;
if(pos < 1 || pos > s->len || len < 0 || len > s->len - pos)
return NULL;
t = NewStr("");
ClearStr(t);
t->ch = (char *)malloc((len + 1) * sizeof(char));
if(t->ch == NULL) return NULL;
t->len = len;
//把有效的len位字符搬到t里面去
for(--len ;len >= 0;-- len)
t->ch[len] = s->ch[pos - 1 + len];
t->ch[t->len] = 0;
return t;
}
testString.c
#include<stdio.h>
#include "str.h"
void main()
{
int res;
STR *t = NULL,*s = NewStr("hello");
printf("s=%s,len=%d\n",s->ch,s->len);
t = NewStr("hello");
res = StrCompare(s,t);
if(res == 0)
printf("s==t\n");
else if(res > 0)
printf("s > t\n");
else
printf("s < t\n");
t = NewStr(" world");
StrConcat(s,t);
printf("s=%s,len=%d\n",s->ch,s->len);
DestroyStr(t);
t = SubStr(s,2,5);
printf("t=%s,len=%d\n",t->ch,t->len);
DestroyStr(s);
}
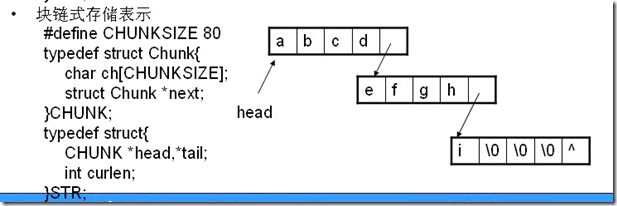
str.h
#ifndef _STR_H
#define _STR_H
#define CHUNKSIZE 4
typedef struct Chunk
{
char ch[CHUNKSIZE];
struct Chunk *next;
}CHUNK;
typedef struct
{
CHUNK *head,*tail;
int curlen;
}STR;
STR *NewStr(char *str);
void DestroyStr(STR *s);
void ClearStr(STR *s);
int StrCompare(STR *s,STR *t);
int StrConcat(STR *s,STR *t);
STR * SubStr(STR *s,int pos,int len);
void PrintStr(STR *s);
#endif
str.c
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include"str.h"
//根据char[]创建字符串
STR *NewStr(char *str)
{
int i,j;
CHUNK *temp;
STR *s = (STR *)malloc(sizeof(STR));
s->head = (CHUNK *)malloc(sizeof(CHUNK));
s->tail = s->head;
s->tail->next = NULL;
s->curlen = 1;
for(i=0,j=0; str[i] ;i++,j++){
if(j == CHUNKSIZE){
temp = (CHUNK *)malloc(sizeof(CHUNK));
temp->next = NULL;
s->tail->next = temp;
s->tail = temp;
s->curlen ++;
j=0;
}
s->tail->ch[j] = str[i];
}
if(j == CHUNKSIZE)//有用的字符占满了最后一块空间
{
temp = (CHUNK *)malloc(sizeof(CHUNK));
temp->next = NULL;
s->tail->next = temp;
s->tail = temp;
s->curlen ++;
j=0;
}
//填掉空白部分
for(;j<CHUNKSIZE;j++)
s->tail->ch[j] = 0;
return s;
}
void DestroyStr(STR *s)
{
CHUNK * temp = s->head;
while(temp)
{
s->head = s->head->next;
free(temp);
temp = s->head;
}
free(s);
}
void ClearStr(STR *s)
{
for(;s->head;s->head = s->head->next)
free(s->head);
s->head = s->tail = NULL;
s->curlen = 0;
}
int StrCompare(STR *s,STR *t)
{
int i;
CHUNK *s1 = s->head,*t1 = t->head;
for(i = 0; s1 && t1 ;i++)
{
if(s1->ch[i] != t1->ch[i])
return s1->ch[i] - t1->ch[i];
if(i == CHUNKSIZE-1)
{
s1 = s1->next;
t1 = t1->next;
i = -1;
}
}
if(s1)
return 1;
else if(t1)
return -1;
else
return 0;
}
int StrConcat(STR *s,STR *t)
{
CHUNK * temp,*s1 = s->tail,*t1 = t->head;
int i,j;
for(i=0;s1->ch[i];i++);
for(j=0;;i++,j++)
{
if(i == CHUNKSIZE){
temp = (CHUNK *)malloc(sizeof(CHUNK));
temp->next = NULL;
s1->next = temp;
s1 = temp;
s->curlen ++;
i=0;
}
if(j == CHUNKSIZE){
t1 = t1->next;
j=0;
}
if(t1->ch[j])
s1->ch[i] = t1->ch[j];
else
break;
}
if(i == CHUNKSIZE)//有用的字符占满了最后一块空间
{
temp = (CHUNK *)malloc(sizeof(CHUNK));
temp->next = NULL;
s1->next = temp;
s1 = temp;
s->curlen ++;
i=0;
}
//填掉空白部分
for(;i<CHUNKSIZE;i++)
s1->ch[i] = 0;
return 1;
}
STR * SubStr(STR *s,int pos,int len)
{
int i,j,k;
CHUNK * s1 = s->head,*temp;
STR * t = (STR *)malloc(sizeof(STR));
t->head = (CHUNK *)malloc(sizeof(CHUNK));
t->tail = t->head;
t->tail->next = NULL;
t->curlen = 1;
for(i=0,j=0; s1 && i < pos - 1;i++,j++)
{
if(j == CHUNKSIZE - 1)
{
s1 = s1->next;
j = -1;
}
}
if(!s1)return 0;
for(k = 0; s1 && i<pos - 1 + len ;i++,j++,k++)
{
if(k == CHUNKSIZE){
temp = (CHUNK *)malloc(sizeof(CHUNK));
temp->next = NULL;
t->tail->next = temp;
t->tail = temp;
t->curlen ++;
k=0;
}
t->tail->ch[k] = s1->ch[j];
if(j == CHUNKSIZE - 1)
{
s1 = s1->next;
j = -1;
}
}
if(k == CHUNKSIZE)//有用的字符占满了最后一块空间
{
temp = (CHUNK *)malloc(sizeof(CHUNK));
temp->next = NULL;
t->tail->next = temp;
t->tail = temp;
t->curlen ++;
k=0;
}
//填掉空白部分
for(;k<CHUNKSIZE;k++)
t->tail->ch[k] = 0;
return t;
}
void PrintStr(STR *s)
{
int i;
CHUNK * temp = s->head;
for(i=0; temp ;i++)
{
if(temp->ch[i])
printf("%c",temp->ch[i]);
else
break;
if(i == CHUNKSIZE - 1)
{
temp = temp->next;
i = -1;
}
}
printf("\n");
}
testString.c
#include<stdio.h>
#include "str.h"
void main()
{
int res;
STR *t = NULL,*s = NewStr("hello");
PrintStr(s);
t = NewStr("hello");
res = StrCompare(s,t);
if(res == 0)
printf("s==t\n");
else if(res > 0)
printf("s > t\n");
else
printf("s < t\n");
t = NewStr(" world");
StrConcat(s,t);
PrintStr(s);
DestroyStr(t);
t = SubStr(s,2,6);
PrintStr(t);
DestroyStr(s);
}