Django学习---快速搭建搜索引擎(haystack + whoosh + jieba)
Django下的搜索引擎(haystack + whoosh + jieba)
转载:https://www.cnblogs.com/ftl1012/p/10397553.html
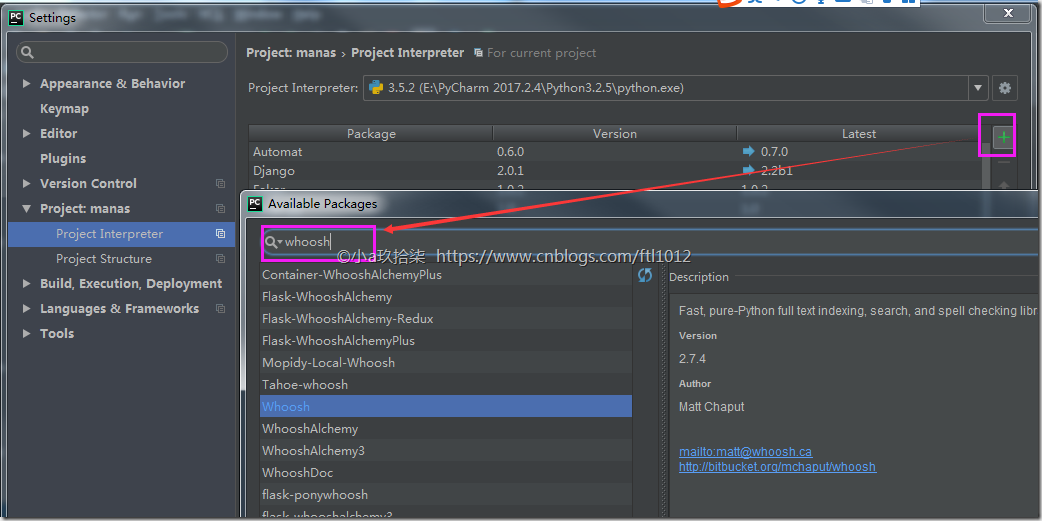
- 软件安装
haystack是django的开源搜索框架,该框架支持Solr,Elasticsearch,Whoosh, 搜索引擎量。
Whoosh是一个搜索引擎使用,这是一个由纯Python实现的全文搜索引擎,没有二进制文件等,比较小巧,配置比较简单,性能略低。
Jieba是由Whoosh自带的是英文分词,对中文的分词支持不是太好,故用jieba替换whoosh的分词组件。
---------------------
|
1
2
3
|
pip install django-haystackpip install whooshpip install jieba |
- 创建项目app
df_goods
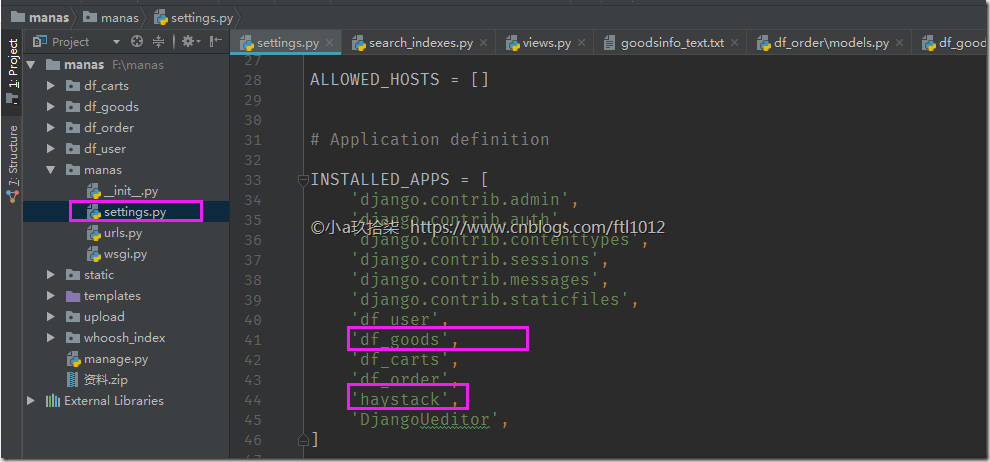
- 修改settings.py:
manas/settings.py
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
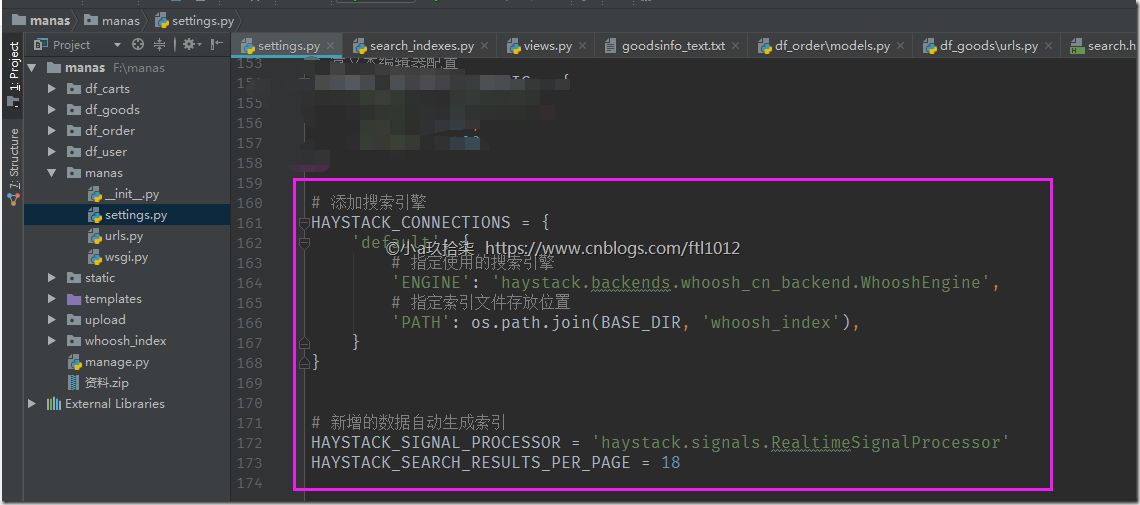
# 添加搜索引擎HAYSTACK_CONNECTIONS = { 'default': { # 指定使用的搜索引擎 'ENGINE': 'haystack.backends.whoosh_cn_backend.WhooshEngine', # 指定索引文件存放位置 'PATH': os.path.join(BASE_DIR, 'whoosh_index'), }} |
|
1
2
3
|
# 新增的数据自动生成索引HAYSTACK_SIGNAL_PROCESSOR = 'haystack.signals.RealtimeSignalProcessor'HAYSTACK_SEARCH_RESULTS_PER_PAGE = 18 |
- 创建索引
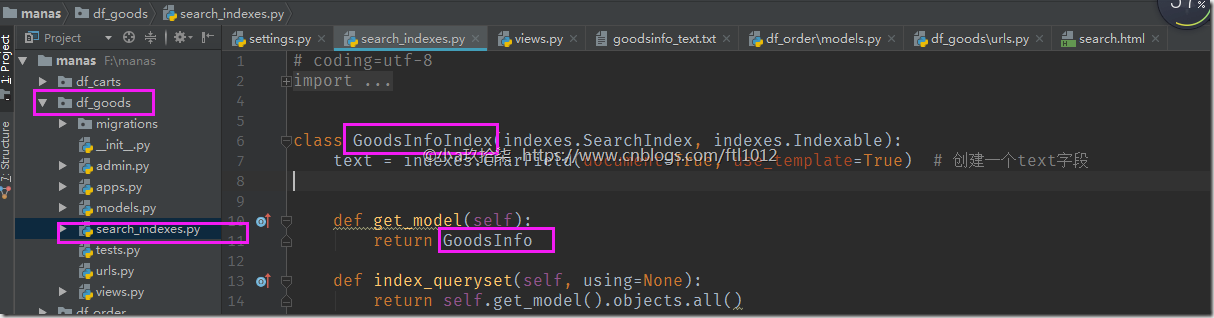
在df_goods目录下简立search_indexes.py文件,文件名不能修改
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
|
# coding=utf-8from haystack import indexesfrom .models import GoodsInfoclass GoodsInfoIndex(indexes.SearchIndex, indexes.Indexable): text = indexes.CharField(document=True, use_template=True) # 创建一个text字段 def get_model(self): return GoodsInfo def index_queryset(self, using=None): return self.get_model().objects.all() |
说明: 每个索引里面必须有且只能有一个字段为 document=True,这代表haystack 和搜索引擎将使用此字段的内容作为索引进行检索(primary field)。其他的字段只是附属的属性,方便调用,并不作为检索数据。如果使用一个字段设置了document=True,则一般约定此字段名为text,这是在SearchIndex类里面一贯的命名,以防止后台混乱,当然名字你也可以随便改,不过不建议改。并且,haystack提供了use_template=True在text字段,这样就允许我们使用数据模板去建立搜索引擎索引的文件,说得通俗点就是索引里面需要存放一些什么东西,例如 GoodsInfo的 gtitle 字段
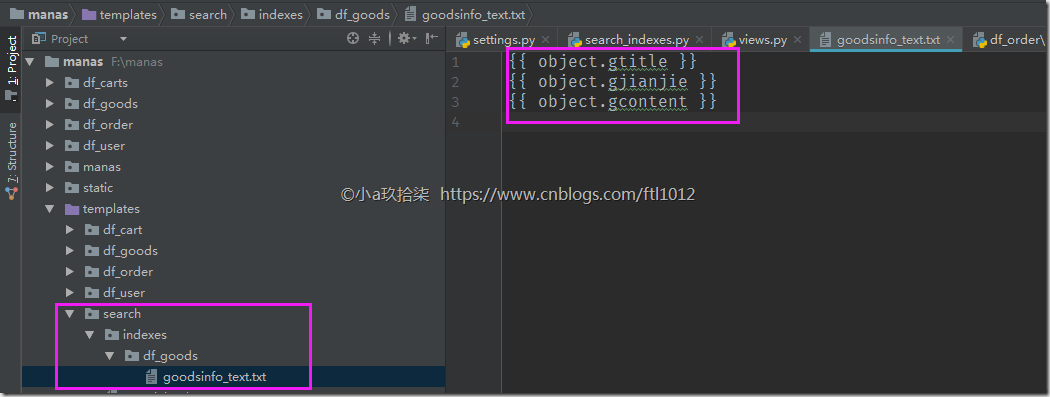
- 创建数据模板路径
templates/search/indexes/df_goods/goodsinfo_text.txt
说明: 数据模板的路径一般为: templates/search/indexes/yourapp/note_text.txt格式
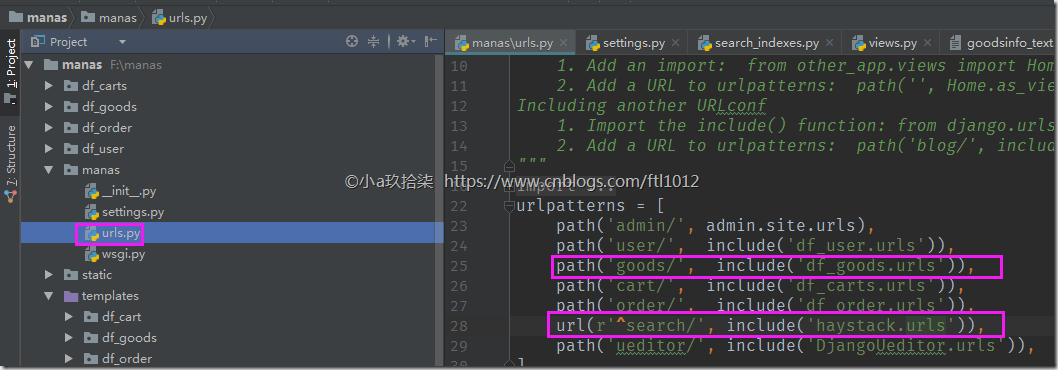
- 配置URL
manas/urls.py
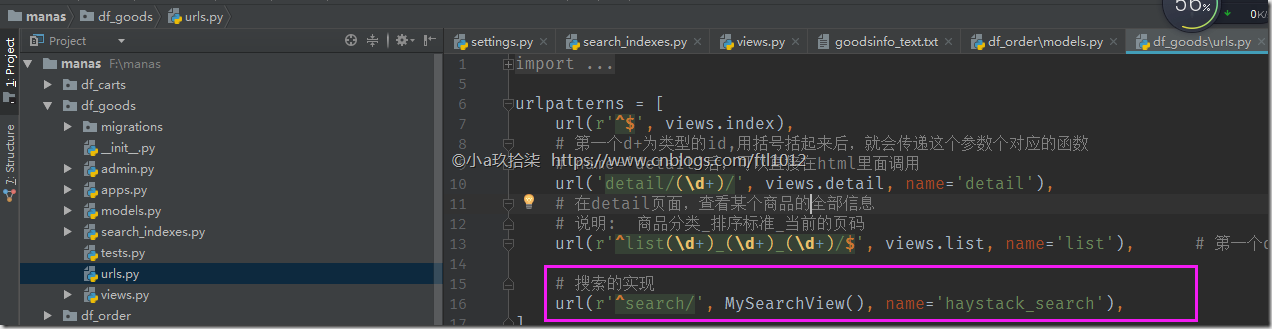
df_goods/urls.py
df_goods/views.py
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
|
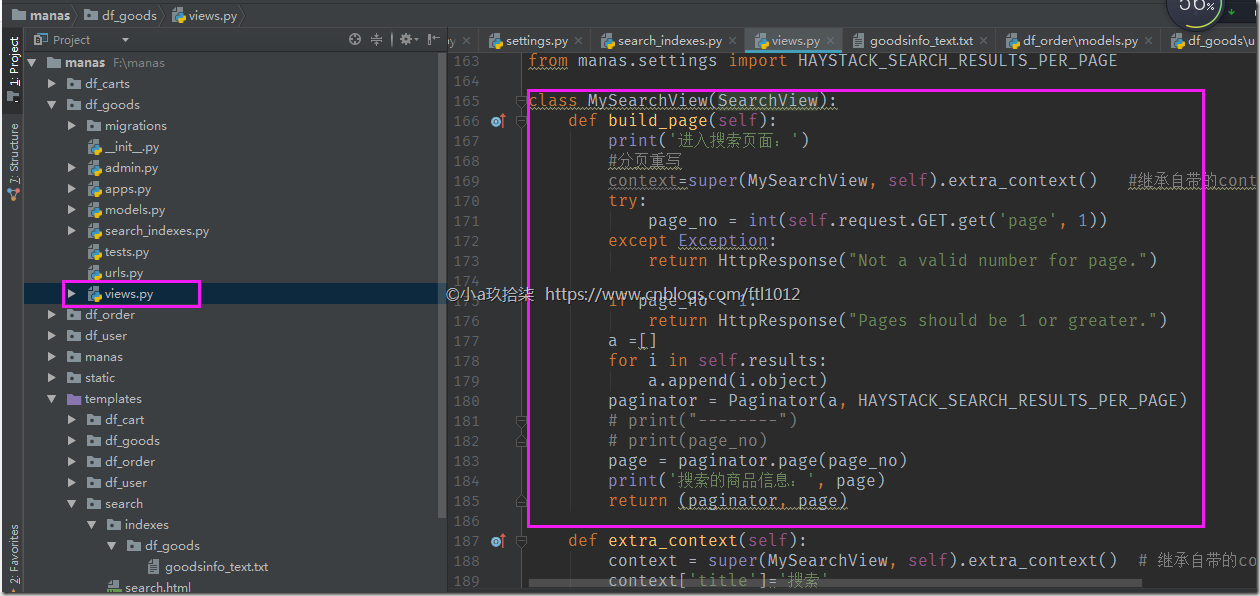
from haystack.views import SearchViewfrom manas.settings import HAYSTACK_SEARCH_RESULTS_PER_PAGEclass MySearchView(SearchView): def build_page(self): print('进入搜索页面:') #分页重写 context=super(MySearchView, self).extra_context() #继承自带的context try: page_no = int(self.request.GET.get('page', 1)) except Exception: return HttpResponse("Not a valid number for page.") if page_no < 1: return HttpResponse("Pages should be 1 or greater.") a =[] for i in self.results: a.append(i.object) paginator = Paginator(a, HAYSTACK_SEARCH_RESULTS_PER_PAGE) # print("--------") # print(page_no) page = paginator.page(page_no) print('搜索的商品信息:', page) return (paginator, page) def extra_context(self): context = super(MySearchView, self).extra_context() # 继承自带的context context['title']='搜索' return context |
创建搜索结果显示的HTML模板路径
templates/search/search.html
SearchView()视图函数默认使用的html模板路径为templates/search/search.html
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
|
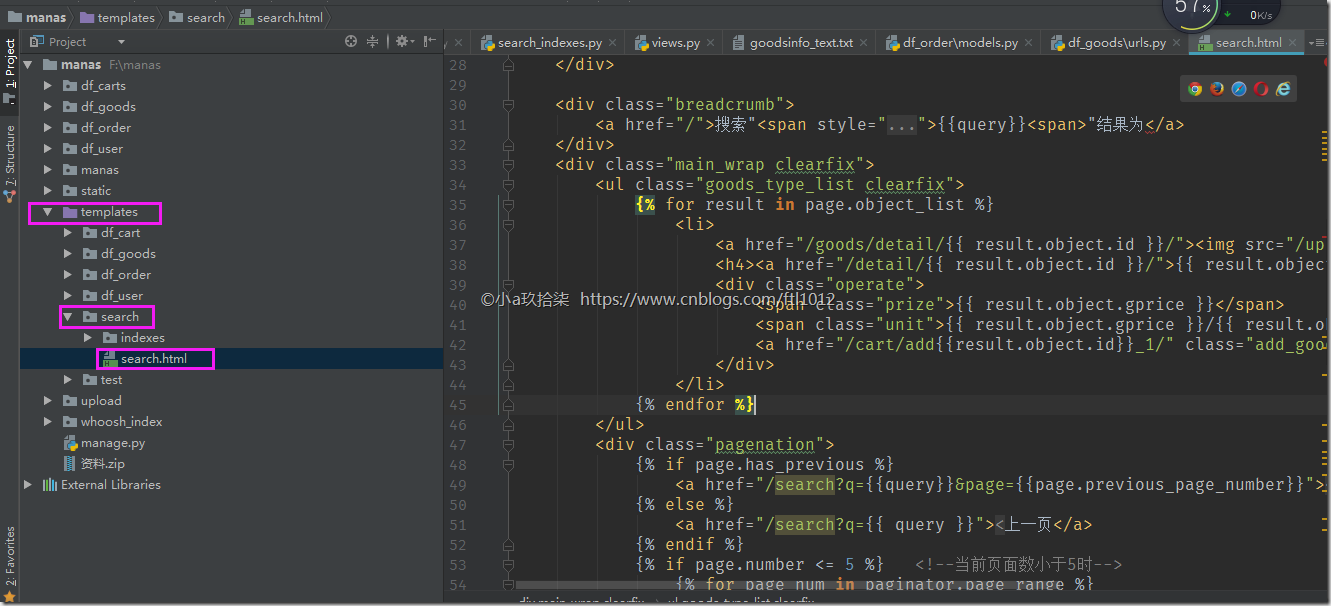
<ul class="goods_type_list clearfix"> {% for result in page.object_list %} <li> <a href="/goods/detail/{{ result.object.id }}/"><img src="/upload/{{ result.object.gpic }}"></a> <h4><a href="/detail/{{ result.object.id }}/">{{ result.object.gtitle }}</a></h4> <div class="operate"> <span class="prize">{{ result.object.gprice }}</span> <span class="unit">{{ result.object.gprice }}/{{ result.object.gunit }}</span> <a href="/cart/add{{result.object.id}}_1/" class="add_goods" title="加入购物车"></a> </div> </li> {% endfor %} </ul> <div class="pagenation"> {% if page.has_previous %} <a href="/search?q={{query}}&page={{page.previous_page_number}}"><上一页</a> {% else %} <a href="/search?q={{ query }}"><上一页</a> {% endif %} {% if page.number <= 5 %} <!--当前页面数小于5时--> {% for page_num in paginator.page_range %} {%if forloop.counter <= 5 %} <a href="/search?q={{query}}&page={{page_num}}" {% if page.number == page_num %} class="active" {% endif %} >{{ page_num }}</a> {%endif%} {% endfor %} {% else %} {% if page.number|add:1 > paginator.num_pages %} <a href="/search?q={{query}}&page={{page.number|add:-4}}">{{ page.number|add:-4}}</a> {% endif %} {% if page.number|add:2 > paginator.num_pages %} <a href="/search?q={{query}}&page={{page.number|add:-3}}">{{ page.number|add:-3}}</a> {% endif %} <a href="/search?q={{query}}&page={{page.number|add:-2}}" >{{ page.number|add:-2}}</a> <a href="/search?q={{query}}&page={{page.number|add:-1}}">{{ page.number|add:-1}}</a> <a href="/search?q={{query}}&page={{page.number}}" class="active">{{ page.number }}</a> {% if page.number|add:1 <= paginator.num_pages %} <a href="/search?q={{query}}&page={{page.number|add:1}}">{{ page.number|add:1}}</a> {% endif %} {% if page.number|add:2 <= paginator.num_pages %} <a href="/search?q={{query}}&page={{page.number|add:2}}">{{ page.number|add:2}}</a> {% endif %} {% endif %} {% if page.has_next %} <a href="/search?q={{query}}&page={{page.next_page_number}}">下一页></a> {% else %} <a href="/search?q={{query}}&page={{paginator.num_pages}}">下一页></a> {% endif %} </div> </div>{% endblock body %} |
说明:首先可以看到模板里使用了的变量有query,page,paginator。query就是我们搜索的字符串; page就是我们的返回结果,page有object_list属性。
- 创建搜索引擎文件夹whoosh_index(settings.py已配置)
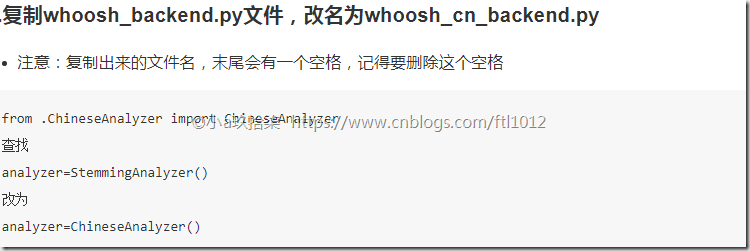
- 创建ChineseAnalyzer.py文件
- 保存在haystack的安装文件夹下,Linux路径如“/home/python/.virtualenvs/django_py2/lib/python2.7/site-packages/haystack/backends”
- 保存在haystack的安装文件,Window路径 C:\Users\Administrator\AppData\Roaming\Python\Python35\site-packages\haystack\backends.
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
|
import jiebafrom whoosh.analysis import Tokenizer, Tokenclass ChineseTokenizer(Tokenizer): def __call__(self, value, positions=False, chars=False, keeporiginal=False, removestops=True, start_pos=0, start_char=0, mode='', **kwargs): t = Token(positions, chars, removestops=removestops, mode=mode, **kwargs) seglist = jieba.cut(value, cut_all=True) for w in seglist: t.original = t.text = w t.boost = 1.0 if positions: t.pos = start_pos + value.find(w) if chars: t.startchar = start_char + value.find(w) t.endchar = start_char + value.find(w) + len(w) yield tdef ChineseAnalyzer(): return ChineseTokenizer() |
|
1
|
|
-
1
<strong>添加中文搜索文件</strong>
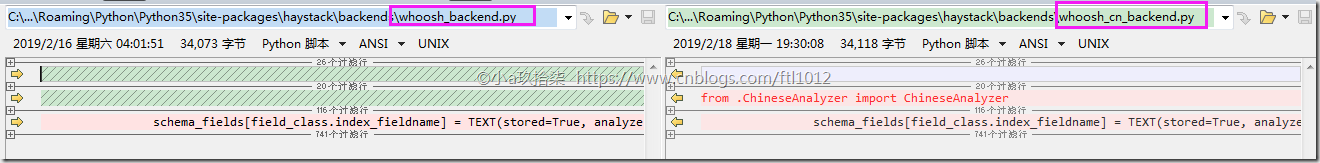
修改完成后2个文件的对比
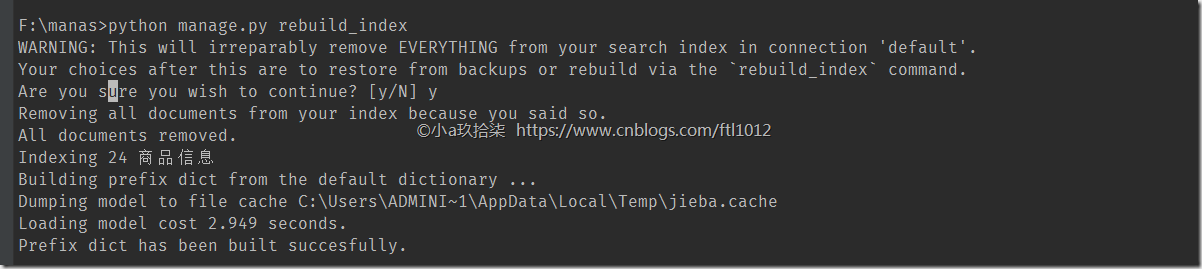
- 生成索引
python manage.py rebuild_index(可选更新索引)python manage.py update_index- 界面显示
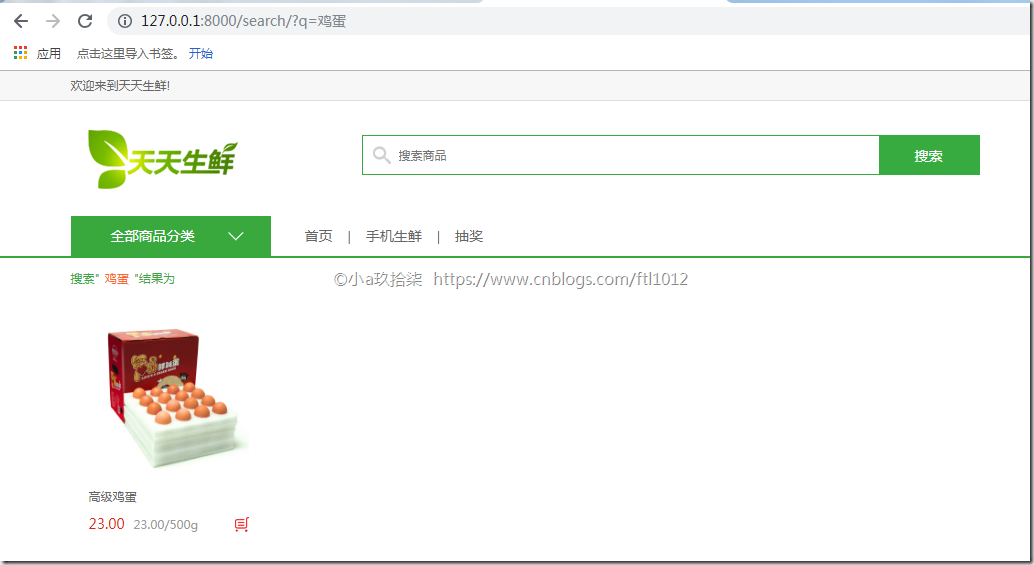
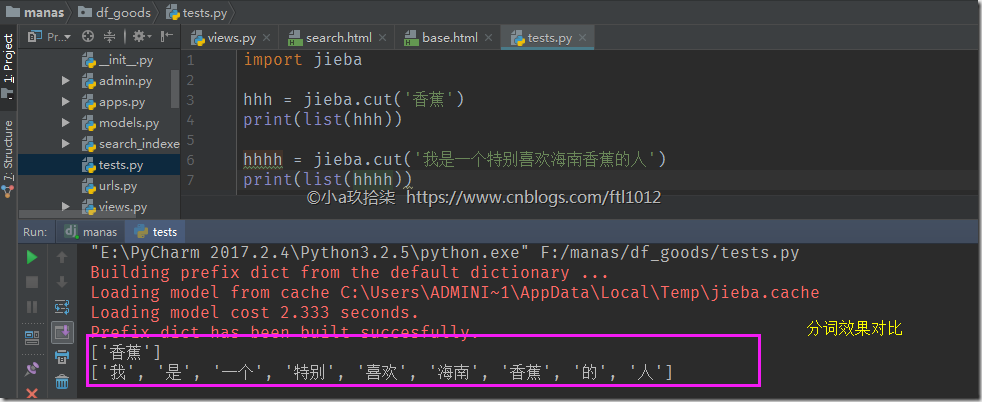
说明:如果我们的文字描述比较少,就会导致分词的效果不明显,所以建议文字描述的时候多一些,这样便于jieba分词
附带分词文件下载;
jieba的简单实用
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
import jiebalist0 = jieba.cut('小明硕士毕业于中国科学院计算所,后在哈佛大学深造', cut_all=True)print('全模式', list(list0))# ['小', '明', '硕士', '毕业', '于', '中国', '中国科学院', '科学', '科学院', '学院', '计算', '计算所', '', '', '后', '在', '哈佛', '哈佛大学', '大学', '深造']list1 = jieba.cut('小明硕士毕业于中国科学院计算所,后在哈佛大学深造', cut_all=False)print('精准模式', list(list1))# ['小明', '硕士', '毕业', '于', '中国科学院', '计算所', ',', '后', '在', '哈佛大学', '深造']list2 = jieba.cut_for_search('小明硕士毕业于中国科学院计算所,后在哈佛大学深造')print('搜索引擎模式', list(list2))# ['小明', '硕士', '毕业', '于', '中国', '科学', '学院', '科学院', '中国科学院', '计算', '计算所', ',', '后', '在', '哈佛', '大学', '哈佛大学', '深造'] |