Java引用类型
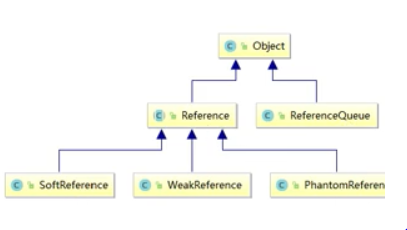
Java引用结构
强引用:
当内存不足时,JVM进行内存回收,但是,对强引用的对象,JVM就算发生OOM也不会回收
把一个对象赋值给一个引用,这个引用就是强引用,表明这个对象还活着,即这个对象是可达的,即不会被JVM回收,即使以后不会用到这个对象。因此强引用是Java发生内存泄露的主要原因。
一个普通的对象,如果没有其他的引用关系,只要超过了对象的作用域或者显式的将强引用赋值为null,一般认为是可以被垃圾回收的。
Object o1 = new Object(); Object o2 = o1; o1 = null; System.gc(); System.out.println(o2)//o2不会被回收
软引用:
软引用是一种被弱化的引用,当内存足够时,不会被回收,内存不足时,软引用被回收。
Object o1 = new Object(); SoftReference<Object> s = new SoftReference<>(o1); System.out.println(o1); System.out.println(s.get()); o1 = null; System.out.println(o1);//null System.out.println(s.get());//内存足够,不回收 //配置小内存,构造大对象,导致内存回收 -xmx5m -xms5m -xx:+PrintGCDetails Object o1 = new Object(); SoftReference<Object> s = new SoftReference<>(o1); System.out.println(o1); System.out.println(s.get()); o1 = null; try{ byte[] b = new byte[10* 1024 * 1024]; }finally{ System.out.println(o1); System.out.println(s.get());//被系统回收 }
弱引用:
java.lang.ref.WeakReference实现,当系统GC时,都会被回收
Object o1 = new Object(); WeakReference<Object> w = new WeakReference<>(o1); o1 = null; System.out.println(o1);//null System.out.println(w.get());//内存足够或者不足够,都被回收

WeakHashMap<>():
public class WeakHashMapDemo { public static void main(String[] args){ weakHashMap(); } static void weakHashMap(){ WeakHashMap<Integer, String> weakHashMap = new WeakHashMap<>(); Integer i = new Integer(2); String value = "weakHashMap"; weakHashMap.put(i, value); System.out.println(weakHashMap); i = null; System.gc(); System.out.println(weakHashMap);//被回收 } }
虚引用:幽灵应用
虚引用并不会影响对象的生命周期,如果一个对象仅有虚引用,就和没有任何应用一样,任何时候都可能被回收。不能单独使用也不能通过它访问对象,必须和引用队列ReferenceQueue一同使用。虚引用的作用仅用于监控一个对象的回收状态,提供了一种对象被finalize之后,做某些事情的机制,PhantomReference的get方法总是返回null,因此无法获得引用的对象。
其意义在于说明一个对象已经进入finalization阶段,可以被gc回收,用来实现比finalization更灵活的机制。
引用队列:ReferenceQueue<>:WeakReference的对象被回收之前要被放到引用队列中一下。虚引用和弱引用常用
gc之前,finalize之前被放到引用队列
public static void main(String[] args){ Object o = new Object(); ReferenceQueue<Object> referenceQueue = new ReferenceQuyaobeue<>(); WeakReference<Object> weakReference = new WeakReference<>(o, referenceQueue); System.out.println(o); System.out.println(referenceQueue.poll()); System.out.println(weakReference.get()); o = null;System.gc(); System.out.println("!!!!!!!!!"); System.out.println(o); System.out.println(referenceQueue.poll()); System.out.println(weakReference.get()); }
java.lang.Object@4554617c
null
java.lang.Object@4554617c
!!!!!!!!!
null
java.lang.ref.WeakReference@74a14482
null


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号