1 感知机
“知错能改”算法梗概:
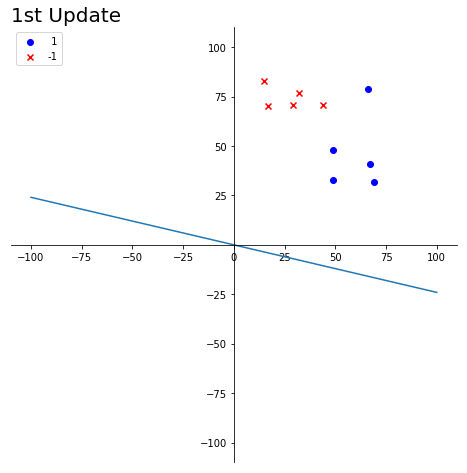
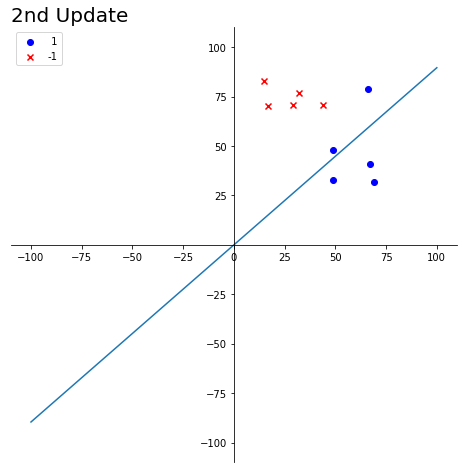
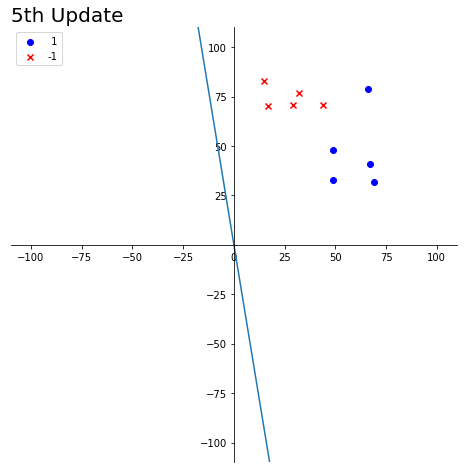
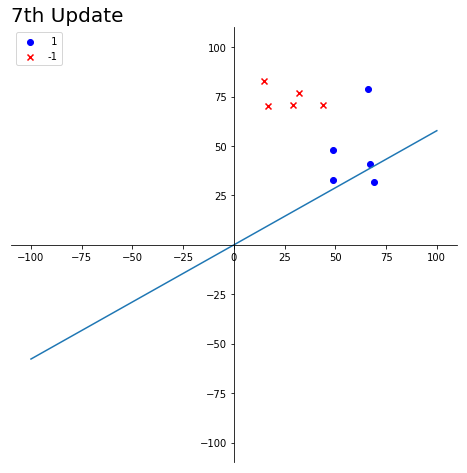
目标:w1x1+w2x2=0是一条经过原点的直线,找到合适的参数w1,w2使得该直线的较好的区分两组数据
- 随机初始化参数w1,w2. 之前的法向量为(w1, w2)
- 开始迭代:
- 当对某一个数据错误的分类后,对两个参数w1, w2进行更新,(w1, w2).T是直线的法向量
- 具体的更新方法为 (new_w1, new_w2).T = (w1, w2).T + label * (x1, x2).T。即当
- 当所有的数据分类都正确时退出
上面的动图中:
- 粉红与紫色的分界线被认为是寻找的直线
- w(t)代表之前直线的法向量,w(t+1)表示更新得到的法向量
- 黑色标记表示当前直线下分类错误的点
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
%matplotlib inline
# 设置随机种子
np.random.seed(325)
# 随机生成o数据
o_data_x = np.random.randint(40, 80, 5)
o_data_y = np.random.randint(20, 80, 5)
o_label = np.array([1,1,1,1,1])
# 随机生成x数据
x_data_x = np.random.randint(10, 50, 5)
x_data_y = np.random.randint(60, 90, 5)
x_label = np.array([-1,-1,-1,-1,-1])
# 随机生成初始直线法向量
w1_w2 = np.random.random(2)
w1_w2
array([0.37665966, 0.86833482])
def plot(w1_w2, time):
"""
画图函数
parametes:
1. w1_w2 --- numpy.ndarray类型,shape:(2,),意为直线的法向量
2. time --- int类型,意为第几次更新,初始值为0
"""
# 设置画布
plt.figure(figsize=(8, 8))
plt.xlim([-110, 110])
plt.ylim([-110, 110])
# 作点
plt.scatter(o_data_x, o_data_y, c='b', marker='o', label=' 1')
plt.scatter(x_data_x, x_data_y, c='r', marker='x', label='-1')
plt.legend(loc='upper left')
# 作初始线
t = np.linspace(-100, 100, 18)
plt.plot(t, -w1_w2[0]/w1_w2[1]*t)
# 获取当前的坐标轴, gca = get current axis
ax = plt.gca()
# 设置标题,也可用plt.title()设置
if time == 0:
title_name = 'Inital'
elif time == 1:
title_name = '1st Update'
elif time == 2:
title_name = '2nd Update'
elif time == 3:
title_name = '3rd Update'
else:
title_name = str(time) + 'th Update'
ax.set_title(title_name, fontsize=20, loc='left')
# 设置右边框和上边框,隐藏
ax.spines['right'].set_color('none')
ax.spines['top'].set_color('none')
# 设置x坐标轴为下边框,设置y坐标轴为左边框
ax.xaxis.set_ticks_position('bottom')
ax.yaxis.set_ticks_position('left')
# 设置下边框, 左边框在(0, 0)的位置
ax.spines['bottom'].set_position(('data', 0))
ax.spines['left'].set_position(('data', 0))
# 设置刻度
ax.set_xticks([-100, -75, -50, -25, 0, 25, 50, 75, 100])
ax.set_yticks([-100, -75, -50, -25, 25, 50, 75, 100])
# 保存图片
print("w1_w2 = ", w1_w2)
plt.savefig(title_name + '.jpg')
# 初始态
plot(w1_w2, 0)
w1_w2 = [0.37665966 0.86833482]

# 整合数据
train_X = np.vstack((np.hstack((o_data_x, x_data_x)),np.hstack((o_data_y, x_data_y))))
train_y = np.hstack((o_label, x_label))
# 转置
train_X = train_X.T
# 查看数据
print("train_x:\n{0}\ntrain_y:\n{1}".format(train_X, train_y))
train_x:
[[49 33]
[49 48]
[67 41]
[66 79]
[69 32]
[17 70]
[15 83]
[29 71]
[44 71]
[32 77]]
train_y:
[ 1 1 1 1 1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1]
# 迭代更新
cnt = 0
while True:
result = np.sign(np.dot(train_X, w1_w2))
# 已经能够正确分类了
if (result == train_y).all():
break
else:
# 找到不能正确分类的那些数据并更新W1_w2
for i in range(train_X.size):
if result[i] != train_y[i]:
w1_w2 += train_X[i] * train_y[i]
cnt += 1
plot(w1_w2, cnt)
break
w1_w2 = [-16.62334034 -69.13166518]
w1_w2 = [ 32.37665966 -36.13166518]
w1_w2 = [81.37665966 11.86833482]
w1_w2 = [ 64.37665966 -58.13166518]
w1_w2 = [130.37665966 20.86833482]
w1_w2 = [113.37665966 -49.13166518]
w1_w2 = [ 69.37665966 -120.13166518]
w1_w2 = [118.37665966 -87.13166518]