ASP.NET MVC Form表单验证与Authorize特性
一、Form表单验证
1、基本概念
表单验证是一个基于票据(ticket-based)[也称为基于令牌(token-based)]的系统。当用户登录系统以后,会得到一个包含基于用户信息的票据(ticket)。这些信息被存放在加密过的cookie里面,这些cookie和响应绑定在一起,因此每一次后续请求都会被自动提交到服务器。
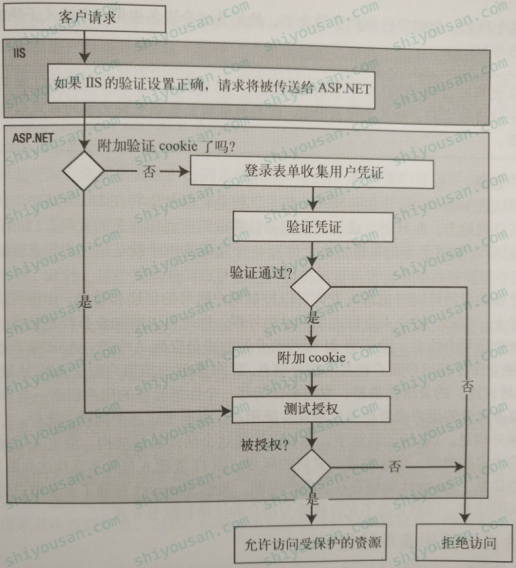
表单验证流程:
(1)、用户请求一个需要验证身份后才可以访问的ASP.NET页面时,ASP.NET运行时验证这个表单验证票据是否有效。如果无效,ASP.NET自动将用户转到登录页面。
(2)、登录页面验证提交的凭证。如果用户验证成功,你只需要告诉ASP.NET架构验证成功(通过调用FormsAuthentication类的一个方法),运行库会自动设置验证cookie(实际上包含了票据)并将用户转到原先请求的页面。
(3)、通过这个请求,运行库检测到验证cookie中包含一个有效票据,然后赋给用户对这个页面的访问权限。
参考以下流程图:
需要的开发工作:
(1)、在web.config配置为表单验证
<authentication mode="Forms">
<forms loginUrl="/Home/Login"></forms>
</authentication>
(2)、创建登录页面
(3)、登录成功后创建凭证(进行Form验证)
方式1:
FormsAuthentication.SetAuthCookie(userName, false); 设置Cookie,其中false,cookie不是永久的,反之,是永久的
方式2:
// 创建ticket凭据
FormsAuthenticationTicket ticket = new FormsAuthenticationTicket(userName, false,1);
//加密ticket凭据
var encryptTicket = FormsAuthentication.Encrypt(ticket);
//写入cookie
Response.Cookies.Add(new HttpCookie(FormsAuthentication.FromCookieName, encryptTicket));
2、表示用户身份的两个对象 IPrincipal IIdentity
public interface IPrincipal { IIdentity Identity { get; } bool IsInRole(string role); }
public interface IIdentity { string Name { get; } string AuthenticationType { get; } bool IsAuthenticated { get; } }
(1)、安全上下文 = 安全信息 = HttpContext.User = IPrincipal
(2)、身份标识 = 用户标识 = HttpContext.User.Identity = IIdentity
(3)、安全上下文 = 身份标识 + 角色信息 + 其他数据
请求经过身份验证的阶段后,或者说AuthenticateRequest事件开始后,才能通过HttpContext.User.Identity获取到具体的身份标识信息,包括用户名(Name),是否已经登录(IsAuthenticated)等属性值,即在HttpApplication.AuthenticateRequest事件中,在此事件中ASP.NET会构建(创建/更新)安全上下文对象(继承IPrincipal接口)和身份标识对象(继承IIdentity接口);用户未登录也会生成一个默认的身份标识,通常称为匿名用户,页面如果不允许匿名用户访问就要跳转到登录页面。
表单验证,验证通过后的身份标识类是FormsIdentity
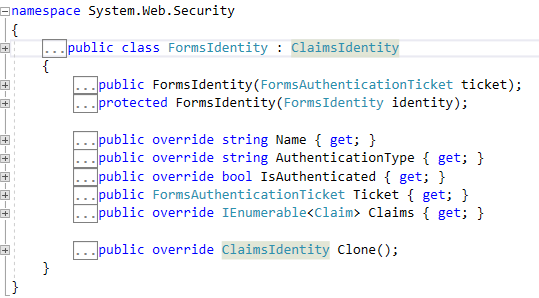
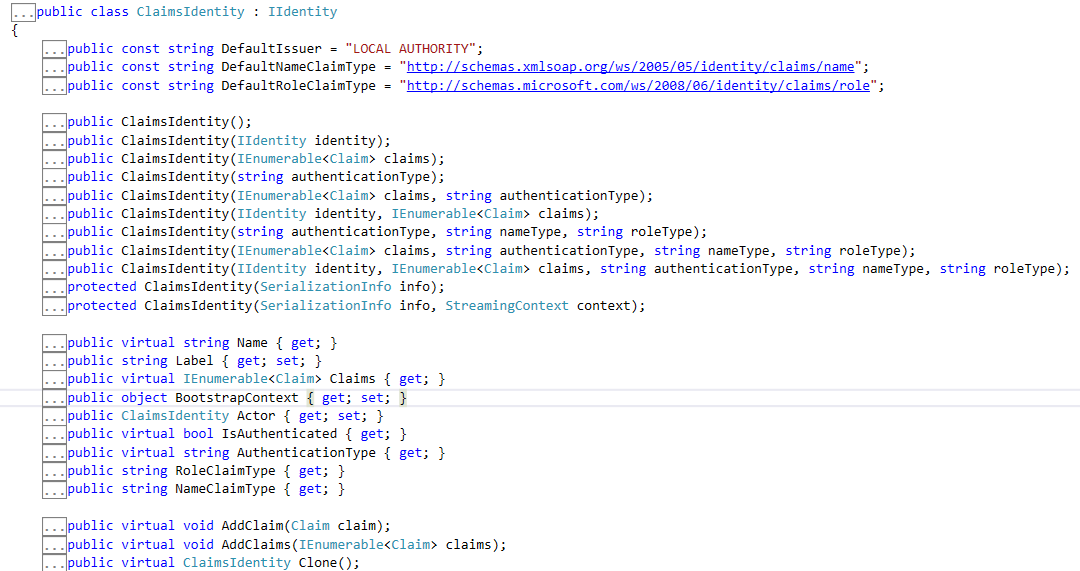
两个需要注意的地方:
(1)、在更早的BeginRequest事件里是完全获取不到用户的身份信息的,毕竟那个时候User.Identity都还没有进行构建。
(2)、在身份验证事件(AuthenticateRequest)过后,HttpContext.User.Identity对象的属性值基本上不会进行改变。除非通过代码重新设置HttpContext.User这个安全上下文对象。
3、FormsAuthentication.SignOut()
只是让包含用户信息票据的Cookie过期,删除表单身份验证的cookie,并没有改变当前用户的身份标识信息,也就是说HttpContext.User.Identity对象是没有任何变化的,IsAuthenticated的值也没有变,一般的账户注销流程里,注销操作的后续都是紧跟着重定向操作,后续发起的新请求才能重新进行身份验证。
一般我们注销的代码有以下两种:
(1)、直接重定向
[HttpPost] public ActionResult SignOut() { FormsAuthentication.SignOut(); //方法一 return Redirect("/Login"); //方法二,需要在配置文件设置默认登录页面 //FormsAuthentication.RedirectToLoginPage(); }
(2)、重新设置HttpContext.User对象
赋值一个空白的用户名从而手动删除掉身份标识,因为User是只读的,所以只能覆盖
[HttpPost] public ActionResult SignOut() { FormsAuthentication.SignOut(); HttpContext.User = new System.Security.Principal.GenericPrincipal(new System.Security.Principal.GenericIdentity(string.Empty), null); return View(); }
4、账户登录后无法获取用户名问题
登录后,通过FormsAuthentication.SetAuthCookie方法或者通过代码将FormsAuthenticationTicket对象添加到响应的Cookie里,都是无法马上获取用户名的,User.Identity.Name属性的值还是为""。这两个方法都只是对包含身份验证票据的Cookie进行操作,用户的身份标识都还没有更新。
解决的方法
(1)、在代码中手动设置HttpContext.User
(2)、做个重定向跳转,而且按照一般的用户账户登录流程,在账户登录后要么跳转到原前请求的URL,要么跳转到某个默认页面。所以一般很少发生这种问题。
二、Authorize特性
1、源码分析
核心代码是AuthorizeCore方法中的user.Identity.IsAuthenticated,Form表单验证通过后就为true,就是上节表单验证后,设置Cookie后。
public class AuthorizeAttribute : FilterAttribute, IAuthorizationFilter { private static readonly char[] _splitParameter = new[] { ',' }; private readonly object _typeId = new object(); private string _roles; private string[] _rolesSplit = new string[0]; private string _users; private string[] _usersSplit = new string[0]; public string Roles { get { return _roles ?? String.Empty; } set { _roles = value; _rolesSplit = SplitString(value); } } public override object TypeId { get { return _typeId; } } public string Users { get { return _users ?? String.Empty; } set { _users = value; _usersSplit = SplitString(value); } } // 核心方法 protected virtual bool AuthorizeCore(HttpContextBase httpContext) { if (httpContext == null) { throw new ArgumentNullException("httpContext"); } //主要验证user.Identity.IsAuthenticated IPrincipal user = httpContext.User; if (!user.Identity.IsAuthenticated) { return false; } if (_usersSplit.Length > 0 && !_usersSplit.Contains(user.Identity.Name, StringComparer.OrdinalIgnoreCase)) { return false; } if (_rolesSplit.Length > 0 && !_rolesSplit.Any(user.IsInRole)) { return false; } return true; } private void CacheValidateHandler(HttpContext context, object data, ref HttpValidationStatus validationStatus) { validationStatus = OnCacheAuthorization(new HttpContextWrapper(context)); } //主要IAuthorizationFilter接口方法 public virtual void OnAuthorization(AuthorizationContext filterContext) { if (filterContext == null) { throw new ArgumentNullException("filterContext"); } if (OutputCacheAttribute.IsChildActionCacheActive(filterContext)) { throw new InvalidOperationException(MvcResources.AuthorizeAttribute_CannotUseWithinChildActionCache); } bool skipAuthorization = filterContext.ActionDescriptor.IsDefined(typeof(AllowAnonymousAttribute), inherit: true) || filterContext.ActionDescriptor.ControllerDescriptor.IsDefined(typeof(AllowAnonymousAttribute), inherit: true); if (skipAuthorization) { return; } //调用AuthorizeCore if (AuthorizeCore(filterContext.HttpContext)) { HttpCachePolicyBase cachePolicy = filterContext.HttpContext.Response.Cache; cachePolicy.SetProxyMaxAge(new TimeSpan(0)); cachePolicy.AddValidationCallback(CacheValidateHandler, null /* data */); } else { HandleUnauthorizedRequest(filterContext); } } protected virtual void HandleUnauthorizedRequest(AuthorizationContext filterContext) { filterContext.Result = new HttpUnauthorizedResult(); } protected virtual HttpValidationStatus OnCacheAuthorization(HttpContextBase httpContext) { if (httpContext == null) { throw new ArgumentNullException("httpContext"); } //调用AuthorizeCore bool isAuthorized = AuthorizeCore(httpContext); return (isAuthorized) ? HttpValidationStatus.Valid : HttpValidationStatus.IgnoreThisRequest; } internal static string[] SplitString(string original) { if (String.IsNullOrEmpty(original)) { return new string[0]; } var split = from piece in original.Split(_splitParameter) let trimmed = piece.Trim() where !String.IsNullOrEmpty(trimmed) select trimmed; return split.ToArray(); } }
基本使用:
[Authorize] public ActionResult Index2() { return View(); }
2、集群环境下的单点登录
在多个WEB服务器情况下,登录后,把cookie数据可以放在统一的Redis或Mongodb服务器上,把sessionId当键值。在验证时候,自定义一个Authorize特性,重载
AuthorizeCore方法,根据sessionId从Redis或Mongodb服务器上获取cookie数据,来验证是否登录。
3、表单认证过程详解
Forms认证的流程设计4次的消息交换,其具体步骤如下所示。
步骤1:用户通过浏览器匿名向IIS发起请求,假设地址为"/home",它会收到状态为"302, Found"的相应,这是一个用于实现"重定向"的http响应,它通过location报头表示的重定向地址指向登录的页面,之前访问的地址将作为查询字符串returnURL的值。
步骤2:浏览器接受到该请求后,针对重定向的地址发送请求,登录页面最终被呈现在浏览器。
步骤3:用户输入正确的用户名密码后提交表单,服务器在接受到请求之后提取它们对用户实施认证,认证成功后,它会生成一个安全令牌或者认证票据。接下来,通过查询字符串returnURL表示的原始请求地址,作为另一个状态为"302, Found"响应的Location报头,而经过加密/签名的安全令牌作为该响应的Cookie。
步骤4:这个代表安全令牌的Cookie将自动附加到浏览器后续的请求中,服务器直接利用它对请求实施认证。Cookie的名称、过期策略以及采用的保护等级均可以通过配置来控制。在禁用Cookie的情况下,安全令牌会直接作为URL的一部分传送。



