CSS 基础 例子 定位及z-index
position 属性指定了元素的定位类型。
position 属性的四个值:
- static 不设置默认为该值,即没有定位,元素出现在正常的流中。不能使用top,bottom,left,right和z-index。
- relative 是相对其正常位置,它原本所占的空间不会改变,经常被用来作为绝对定位元素的容器块。
- absolute 相对于最近的已定位(非static)父元素,如果元素没有已定位的父元素,那么它的位置相对于<html>,使元素的位置与文档流无关,因此不占据空间。
- fixed 相对于浏览器窗口是固定位置。即使窗口是滚动的它也不会移动,改变窗口大小也不会移动。其它特性同absolute定位。
默认是按照标准流显示,指定position属性后,再指定 top, bottom, left, right属性来进行定位。
z-index 元素的定位与文档流无关,所以,会导致元素重叠,这涉及到重叠元素间的显示顺序,z-index,用来控制显示顺序,值越高越显示前边,可以指定负数
注意:两个定位元素重叠,没有指定z - index,后边定位的元素显示在前边。
一、标准顺序排列文档
1、标准流
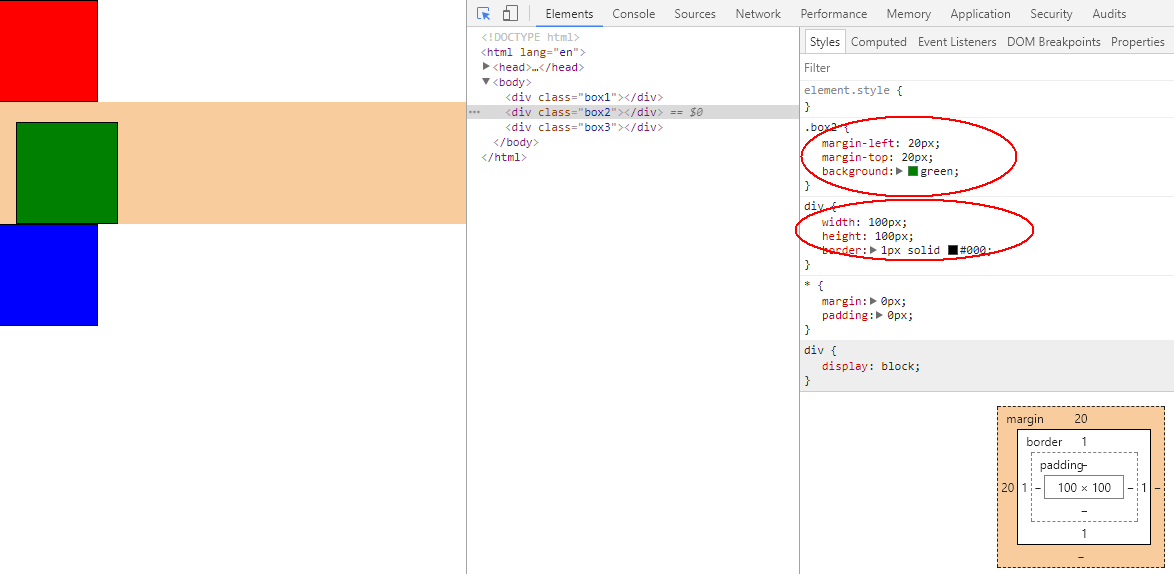
三个div,从上而下排列,第二个div的margin-left和margin-top为20px。块元素,标准流,每个div大小是100px*100px,border为1px
html代码如下:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>定位</title> <style> *{ margin: 0px; padding: 0px; } div{ width: 100px; height: 100px; border: 1px solid #000; } .box1{ background: red; } .box2{ margin-left: 20px; margin-top: 20px; background: green; } .box3{ background: blue; } </style> </head> <body> <div class="box1"></div> <div class="box2"></div> <div class="box3"></div> </body> </html>
运行结果:
2、相对定位
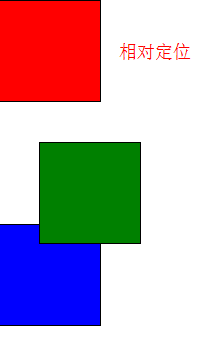
对第二个元素添加属性,在原来基础上,向下和向左移动了20px,原来的margin-left和margin-top还是有效。
top:20px;
left:20px;
position:relative;
html代码如下:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>定位</title> <style> *{ margin: 0px; padding: 0px; } div{ width: 100px; height: 100px; border: 1px solid #000; } .box1{ background: red; } .box2{ margin-left: 20px; margin-top: 20px; background: green; /*添加以下三个属性*/ top:20px; left:20px; position:relative; } .box3{ background: blue; } </style> </head> <body> <div class="box1"></div> <div class="box2"></div> <div class="box3"></div> </body> </html>
运行结果

相对定位前后对比:

3、绝对定位
把position属性改成absolute
html代码如下:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>绝对定位</title> <style> *{ margin: 0px; padding: 0px; } div{ width: 100px; height: 100px; border: 1px solid #000; } .box1{ background: red; } .box2{ margin-left: 20px; margin-top: 20px; background: green; /*添加以下三个属性*/ top:20px; left:20px; /*改成absolute*/ position:absolute; } .box3{ background: blue; } </style> </head> <body> <div class="box1"></div> <div class="box2"></div> <div class="box3"></div> </body> </html>
运行结果:

运行前后对比:


3、fixed定位
为了演示把最后一个div高度设置大点,再改变窗口大小使其出现滚动条
html代码
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>fixed定位</title> <style> *{ margin: 0px; padding: 0px; } div{ width: 100px; height: 100px; border: 1px solid #000; } .box1{ background: red; } .box2{ margin-left: 20px; margin-top: 20px; background: green; /*添加以下三个属性*/ top:20px; left:20px; /*改成fixed*/ position:fixed; } .box3{ /*添加宽度*/ height: 700px; background: blue; } </style> </head> <body> <div class="box1"></div> <div class="box2"></div> <div class="box3"></div> </body> </html>
运行结果:
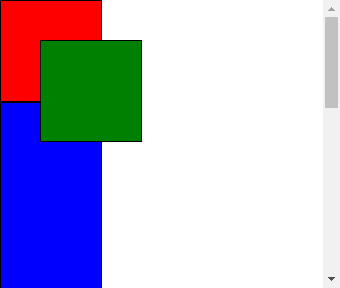 移动滚动条后
移动滚动条后 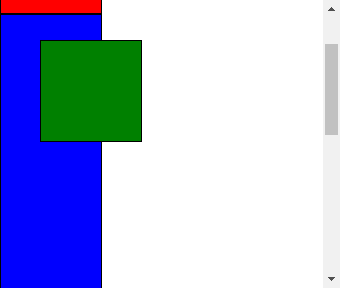
再看下标准文档流
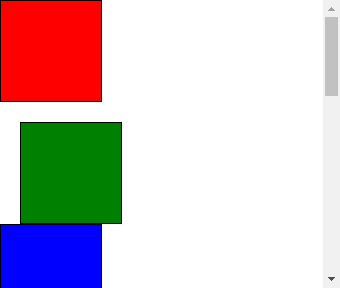
二、父子顺序排列文档
1、标准流
一个div包含两个div。
html代码:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <title></title> <style type="text/css"> * { margin: 0px; padding: 0px;
background-color: blue;
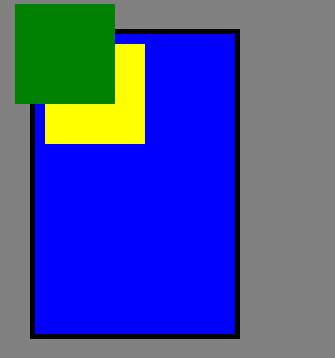
} #f { width: 200px; height: 300px; border: solid 5px black; padding: 0px; background-color: blue } #s1 { width: 100px; height: 100px; background-color:yellow } #s2 { width: 100px; height: 100px; background-color: green; } </style> </head> <body> <div id="f"> <div id="s1"> </div> <div id="s2"> </div> </div> </body> </html>
运行结果:
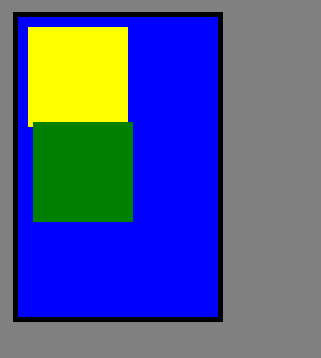
2、相对定位
单独父元素相对定位:
父元素直接相对定位,子元素按正常流显示,所以下边例子,子元素和父元素一起向右和下移动15px
html代码
<!DOCTYPE html><html lang="en">
<head> <title></title> <style type="text/css"> * { margin: 0px; padding: 0px;
background-color: blue;
} #f { width: 200px; height: 300px; border: solid 5px black; padding: 0px; background-color: blue; /*加了下边三句*/ position: relative; top: 15px; left: 15px; } #s1 { width: 100px; height: 100px; background-color:yellow } #s2 { width: 100px; height: 100px; background-color: green; } </style> </head> <body> <div id="f"> <div id="s1"> </div> <div id="s2"> </div> </div> </body> </html>
运行结果: 这是标准流:


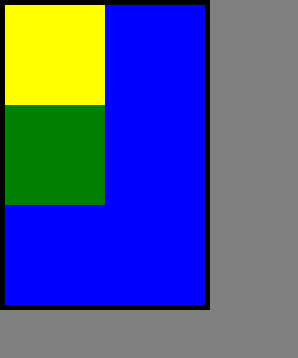
三个元素都相对定位:
都在其应该所在位置进行了偏移
html代码:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <title></title> <style type="text/css"> * { margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background-color: gray } #f { width: 200px; height: 300px; border: solid 5px black; padding: 0px; background-color: blue; /*加了下边三句*/ position: relative; top: 15px; left: 15px; } #s1 { width: 100px; height: 100px; background-color:yellow; /*加了下边三句*/ position: relative; top: 10px; left: 10px; } #s2 { width: 100px; height: 100px; background-color: green; /*加了下边三句*/ position: relative; top: 5px; left: 15px; } </style> </head> <body> <div id="f"> <div id="s1"> </div> <div id="s2"> </div> </div> </body> </html>
运行结果: 这是标准流

2、绝对定位
单独为两个子元素设定绝对定位
根据原则:找到最近定位的父元素作为基准,如果都没有找到就以html为基准,直接进行偏移,此例为后者,以html为基准。
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <title></title> <style type="text/css"> * { margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background-color: gray } #f { width: 200px; height: 300px; border: solid 5px black; padding: 0px; background-color: blue; } #s1 { width: 100px; height: 100px; background-color:yellow; /*加了下边三句*/ position: absolute; top: 10px; left: 10px; } #s2 { width: 100px; height: 100px; background-color: green; /*加了下边三句*/ position: absolute; top: 5px; left: 15px; } </style> </head> <body> <div id="f"> <div id="s1"> </div> <div id="s2"> </div> </div> </body> </html>
运行结果: 这是标准流:
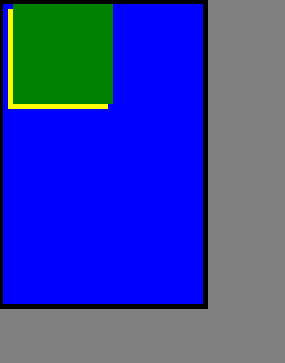

同时为直接父元素进行定位:
注意,如果父元素设置了margin,border,padding等属性,那么这个定位点将忽略padding,将会从padding开始的地方(即只从padding的左上角开始)进行定位。
html代码:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <title></title> <style type="text/css"> * { margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background-color: gray } #f { width: 200px; height: 300px; border: solid 5px black; padding: 0px; background-color: blue; /*加了下边三句*/ position: relative; top: 10px; left: 10px; } #s1 { width: 100px; height: 100px; background-color:yellow; /*加了下边三句*/ position: absolute; top: 10px; left: 10px; } #s2 { width: 100px; height: 100px; background-color: green; /*加了下边三句*/ position: absolute; top: 5px; left: 15px; } </style> </head> <body> <div id="f"> <div id="s1"> </div> <div id="s2"> </div> </div> </body> </html>
运行结果: 这是标准流:
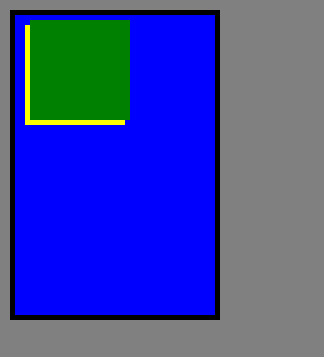

3、fixed定位
fixed是一种特殊的absolute,fixed总是按照浏览器的窗口进行定位,不是body为参照,因为若有滚动条滚动其位置也不会动。f为相对定位,s1增加absolute定位方式,s2 增加fixed定位方式。
s2以body为原点,f相对定位,即以自身原来位置左上角为原点,而s1以直接定位父元素为基准,即f
html代码:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <title></title> <style type="text/css"> * { margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background-color: gray } #f { width: 200px; height: 300px; border: solid 5px black; padding: 0px; background-color: blue; /*加了下边三句*/ position: relative; top: 30px; left: 30px; } #s1 { width: 100px; height: 100px; background-color:yellow; /*加了下边三句*/ position: absolute; top: 10px; left: 10px; } #s2 { width: 100px; height: 100px; background-color: green; /*加了下边三句*/ position: fixed; top: 5px; left: 15px; } </style> </head> <body> <div id="f"> <div id="s1"> </div> <div id="s2"> </div> </div> </body> </html>
运行结果: 这是标准流: