ASP.NET Web API 框架研究 核心的消息处理管道
ASP.NET Web API 的核心框架是一个由一组HttpMessageHandler有序组成的双工消息处理管道;寄宿监听到请求接受后,把消息传入该管道经过所有HttpMessageHandler处理后,目标HttpController会被激活,对应Action方法被执行,生成响应消息也会进入管道经过所有HttpMessageHandler处理,处理后消息又流回寄宿,其把响应信息返回给客户端;可以判断出消息处理管道与寄宿是相互独立的,其是一个通过一组HttpMessageHandler对请求和响应进行处理,独立于寄宿的消息处理管道。
简单概括下,请求消息进入消息处理管道时,默认会创建一个HttpServer(继承自DelagatingHandler),作为消息处理管道的头部,其构造函数中指定了HttpConfiguration和Dispatcher,HttpConfiguration中保存了用户自定义的消息处理管道的中间部分的处理器,用户可以把自定义处理器往里边添加,而Dispatcher默认指定了一个HttpRoutingDispatcher类型的HttpMessageHandler,作为消息处理管道的末尾,在执行HttpServer的SendAsync方法时候,会确保消息处理管道创建,即调用了HttpClientFactory.CreatePipeline方法,把HttpConfiguration中的自定义消息处理器集合按添加顺序通过InnerHandler连接起来,并在末尾添加上HttpRoutingDispatcher这个默认指定的管道尾部处理器,然后HttpServer的SendAsync方法会启动管道中的第一个处理器的SendAsync,启动链式调用,直到管道尾部的HttpRoutingDispatcher,其主要功能是路由以及消息分发,路由主要是指其会先从HttpMessagRequest中获取路由数据(Web Host模式下,ASP.NET路由解析后会把路由变量数据放到HttpRequestMessage属性字典中),如果获取不到路由数据,则直接进行路由解析(Self Host模式下),解析到的数据同样要放到HttpRequestMessage属性字典中,消息分派功能是指,在HttpRoutingDispatcher构造函数中指定了一个内部消息处理器HttpControllerDispatcher,其主要完成HttpController激活、Action的执行以及异步执行后响应消息的返回。
一、涉及的类及源码分析
HttpMessageHandler、DelegatingHandler、HttpMessageInvoker、HttpClientFactory在程序集System.Net.Http中,其它类都在System.Web.Http程序集中,主要类和成员如下图:
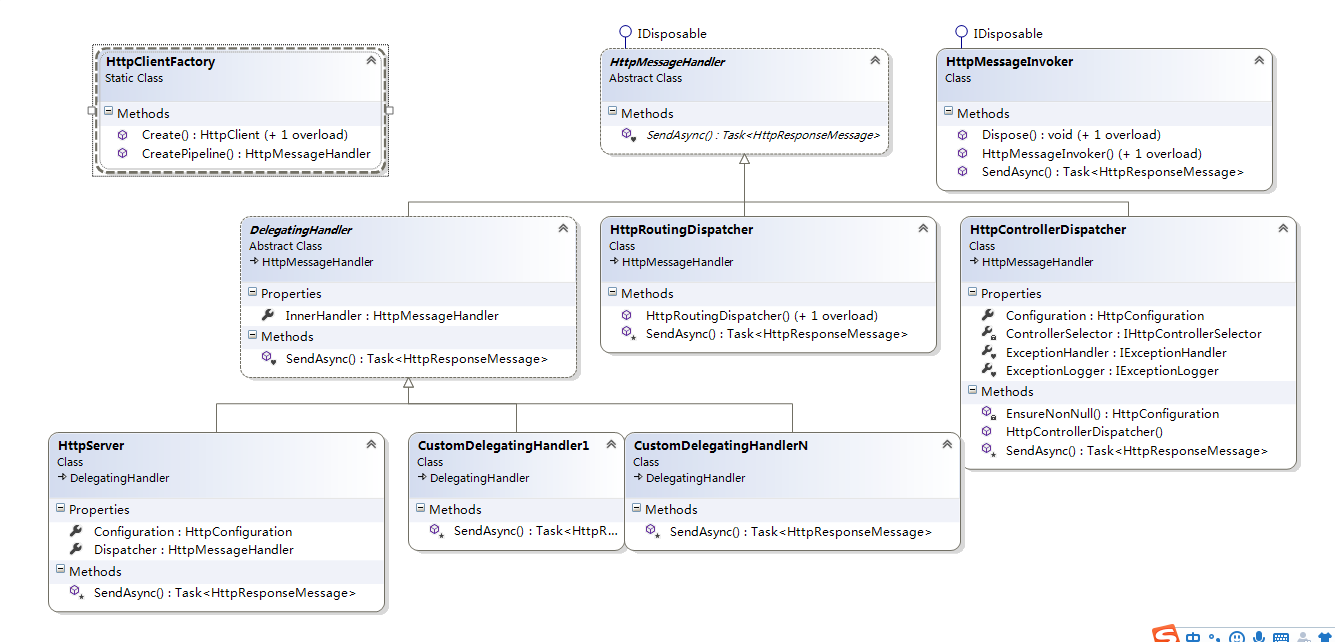
1、HttpMessageHandler
管道中的一个消息处理器,每个处理器负责单一处理功能,整个消息处理管道就是由一个个这种消息处理器链接而成。
是个抽象类,继承自IDisposable,可以学习下Dispose模式的用法,通用逻辑在抽象类里完成,如Dispose()方法,特殊的资源回收由子类重写实现,只有个核心抽象方法SendAsync也由子类来实现。
public abstract class HttpMessageHandler : IDisposable
{
protected HttpMessageHandler()
{
if (Logging.On)
Logging.Enter(Logging.Http, (object)this, ".ctor", (string)null);
if (!Logging.On)
return;
Logging.Exit(Logging.Http, (object)this, ".ctor", (string)null);
}
protected internal abstract Task<HttpResponseMessage> SendAsync(HttpRequestMessage request, CancellationToken cancellationToken);
protected virtual void Dispose(bool disposing)
{
}
public void Dispose()
{
this.Dispose(true);
GC.SuppressFinalize((object)this);
}
}
2、DelegatingHandler
是一个抽象类,继承自HttpMessageHandler,消息处理管道中的每个HttpMessageHandler就是通过该类InnerHandler链接在一起执行的,其保存着通过构造函数传入(或直接设置属性)的下一个HttpMessageHandler,在重写的方法SendAsync中完成自己的逻辑后,调用InnerHandler(下一个HttpMessageHandler)的SendAsync,以此方式重复执行,直到整个链上的消息处理器执行完,HttpMessageHandler链的组装不在这里完成,后边会说明。
这也是设计模式职责链模式的应用。
public abstract class DelegatingHandler : HttpMessageHandler
{
private HttpMessageHandler innerHandler;
private volatile bool operationStarted;
private volatile bool disposed;
public HttpMessageHandler InnerHandler
{
get
{
return this.innerHandler;
}
set
{
if (value == null)
throw new ArgumentNullException(nameof(value));
this.CheckDisposedOrStarted();
if (Logging.On)
Logging.Associate(Logging.Http, (object)this, (object)value);
this.innerHandler = value;
}
}
protected DelegatingHandler()
{
}
protected DelegatingHandler(HttpMessageHandler innerHandler)
{
this.InnerHandler = innerHandler;
}
//重写的核心方法SendAsync
protected internal override Task<HttpResponseMessage> SendAsync(HttpRequestMessage request, CancellationToken cancellationToken)
{
if (request == null)
throw new ArgumentNullException(nameof(request), SR.net_http_handler_norequest);
//确保资源没回收,且innerHandler不为空
this.SetOperationStarted();
return this.innerHandler.SendAsync(request, cancellationToken);
}
protected override void Dispose(bool disposing)
{
if (disposing && !this.disposed)
{
this.disposed = true;
//销毁innerHandler
if (this.innerHandler != null)
this.innerHandler.Dispose();
}
base.Dispose(disposing);
}
private void CheckDisposed()
{
if (this.disposed)
throw new ObjectDisposedException(this.GetType().FullName);
}
private void CheckDisposedOrStarted()
{
this.CheckDisposed();
if (this.operationStarted)
throw new InvalidOperationException(SR.net_http_operation_started);
}
private void SetOperationStarted()
{
this.CheckDisposed();
//innerHandler 不能为null
if (this.innerHandler == null)
throw new InvalidOperationException(SR.net_http_handler_not_assigned);
if (this.operationStarted)
return;
this.operationStarted = true;
}
}
3、HttpServer
消息处理管道的第一个消息处理器,继承自DelegatingHandler,其由两个重要属性Configuration和Dispatcher,Configuration属性(HttpConfiguration类型)用于配置整个消息处理管道,可在构造函数中指定,而Dispatcher属性存放了在构造函数中默认创建的HttpRoutingDispatcher,其是消息处理管道的最后一个HttpMessageHandler ,另外,重写了虚方法Dispose,实现了对Configuration的资源回收,HttpConfiguration也实现了IDisposable。
消息处理管道的头和尾都确定了,中间部分是可扩展定制的,HttpConfiguration有个只读属性MessageHandlers,其用来创建整个消息处理管道,即创建一个链式结构,成员是DelegatingHandler,所以自定义的处理器都要继承自DelegatingHandler,而且都要添加进MessageHandlers,互相间通过InnerHandler属性链接起来。
但是,什么时候把这个管道组装起来呢?在HttpServer执行SendAsync方法时,先会调用EnsureInitialized确保消息处理管道已经被创建,之后才会启动管道,链式调用每个处理器,EnsureInitialized方法最后通过 HttpClientFactory.CreatePipeline(_dispatcher, _configuration.MessageHandlers)进行管道创建。由此也可以得出,创建HttpServer实例的时候,管道还没有创建,所以实例化HttpServer对象之后马上往HttpConfiguration的MessageHandlers添加处理器,也是会添加进管道执行的。
public class HttpServer : DelegatingHandler
{
// 匿名Principal需要线程安全的初始化,所以使用静态字段初始化器
private static readonly IPrincipal _anonymousPrincipal = new GenericPrincipal(new GenericIdentity(String.Empty), new string[0]);
private readonly HttpConfiguration _configuration;
private readonly HttpMessageHandler _dispatcher;
private IExceptionLogger _exceptionLogger;
private IExceptionHandler _exceptionHandler;
private bool _disposed;
private bool _initialized = false;
private object _initializationLock = new object();
private object _initializationTarget;
public HttpServer()
: this(new HttpConfiguration())
{
}
//默认创建了 HttpRoutingDispatcher作为消息处理管道的最后一个HttpMessageHandler
public HttpServer(HttpConfiguration configuration)
: this(configuration, new HttpRoutingDispatcher(configuration))
{
}
public HttpServer(HttpMessageHandler dispatcher)
: this(new HttpConfiguration(), dispatcher)
{
}
public HttpServer(HttpConfiguration configuration, HttpMessageHandler dispatcher)
{
if (configuration == null)
{
throw Error.ArgumentNull("configuration");
}
if (dispatcher == null)
{
throw Error.ArgumentNull("dispatcher");
}
IPrincipal principal = Thread.CurrentPrincipal;
_dispatcher = dispatcher;
_configuration = configuration;
}
//消息管道最后一个处理器
public HttpMessageHandler Dispatcher
{
get { return _dispatcher; }
}
//应用的全局配置,存放了注册的自定义处理器集合
public HttpConfiguration Configuration
{
get { return _configuration; }
}
//只用于单元测试
internal IExceptionLogger ExceptionLogger
{
get
{
if (_exceptionLogger == null)
{
_exceptionLogger = ExceptionServices.GetLogger(_configuration);
}
return _exceptionLogger;
}
set
{
_exceptionLogger = value;
}
}
//只用于单元测试
internal IExceptionHandler ExceptionHandler
{
get
{
if (_exceptionHandler == null)
{
_exceptionHandler = ExceptionServices.GetHandler(_configuration);
}
return _exceptionHandler;
}
set
{
_exceptionHandler = value;
}
}
//释放非托管资源和托管资源(disposing为true)
protected override void Dispose(bool disposing)
{
if (!_disposed)
{
_disposed = true;
if (disposing)
{
_configuration.Dispose();
}
}
base.Dispose(disposing);
}
//核心方法,先要确保消息处理管道要被创建,才触发消息处理管道处理器依次执行
protected override async Task<HttpResponseMessage> SendAsync(HttpRequestMessage request, CancellationToken cancellationToken)
{
if (request == null)
{
throw Error.ArgumentNull("request");
}
if (_disposed)
{
return request.CreateErrorResponse(HttpStatusCode.ServiceUnavailable, SRResources.HttpServerDisposed);
}
//确保管道已经被创建
EnsureInitialized();
// 获取当前同步上下文
SynchronizationContext context = SynchronizationContext.Current;
if (context != null)
{
//将当前同步上下文存放到请求对象中的属性字典中,后续操作需要在此同步上下文中执行,可以从请求对象属性字典中获取
request.SetSynchronizationContext(context);
}
// 将 HttpConfiguration作为一个参数添加到请求对象属性字典中
request.SetConfiguration(_configuration);
// 确保有一个principal,如果没有就创建一个匿名的principal
IPrincipal originalPrincipal = Thread.CurrentPrincipal;
if (originalPrincipal == null)
{
Thread.CurrentPrincipal = _anonymousPrincipal;
}
// 确保在request context存在一个 principal ,如果存在一个.request context
HttpRequestContext requestContext = request.GetRequestContext();
if (requestContext == null)
{
requestContext = new RequestBackedHttpRequestContext(request);
request.SetRequestContext(requestContext);
}
try
{
ExceptionDispatchInfo exceptionInfo;
try
{
//执行方法,启动链式处理器执行
return await base.SendAsync(request, cancellationToken);
}
catch (OperationCanceledException)
{
throw;
}
catch (HttpResponseException exception)
{
return exception.Response;
}
catch (Exception exception)
{
exceptionInfo = ExceptionDispatchInfo.Capture(exception);
}
Debug.Assert(exceptionInfo.SourceException != null);
ExceptionContext exceptionContext = new ExceptionContext(exceptionInfo.SourceException,
ExceptionCatchBlocks.HttpServer, request);
await ExceptionLogger.LogAsync(exceptionContext, cancellationToken);
HttpResponseMessage response = await ExceptionHandler.HandleAsync(exceptionContext,
cancellationToken);
if (response == null)
{
exceptionInfo.Throw();
}
return response;
}
finally
{
Thread.CurrentPrincipal = originalPrincipal;
}
}
private void EnsureInitialized()
{
LazyInitializer.EnsureInitialized(ref _initializationTarget, ref _initialized, ref _initializationLock, () =>
{
Initialize();
return null;
});
}
protected virtual void Initialize()
{
//初始化_configuration,见下边的_configuration.EnsureInitialized
_configuration.EnsureInitialized();
// 创建管道,见下一个类说明HttpClientFactory的CreatePipeline
InnerHandler = HttpClientFactory.CreatePipeline(_dispatcher, _configuration.MessageHandlers);
}
private static HttpConfiguration EnsureNonNull(HttpConfiguration configuration)
{
if (configuration == null)
{
throw new ArgumentNullException("configuration");
}
return configuration;
}
}
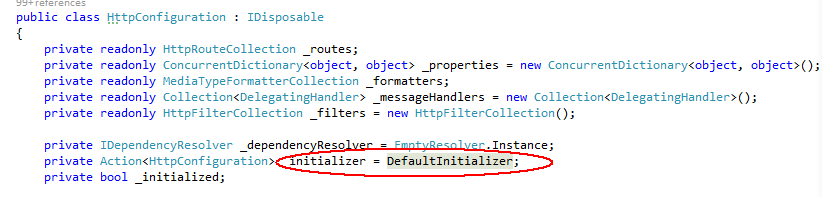
_configuration.EnsureInitialized()代码如下:


4、HttpClientFactory
静态类根据管道默认指定最后一个处理器以及用户注册的所有处理器你集合来创建消息处理管道,整个管道是把集合里的每个处理器按先后顺序连接起来,并在最后链上默认指定的最后一个处理器 的dispatcher,由此也可以得出,消息处理器的执行顺序也就是添加到 HttpConfiguration的消息处理器集合中的顺序。
public static class HttpClientFactory
{
public static HttpClient Create(params DelegatingHandler[] handlers)
{
return Create(new HttpClientHandler(), handlers);
}
public static HttpClient Create(HttpMessageHandler innerHandler, params DelegatingHandler[] handlers)
{
HttpMessageHandler pipeline = CreatePipeline(innerHandler, handlers);
return new HttpClient(pipeline);
}
//HttpServer调用的创建管道方法
public static HttpMessageHandler CreatePipeline(HttpMessageHandler innerHandler, IEnumerable<DelegatingHandler> handlers)
{
if (innerHandler == null)
{
throw Error.ArgumentNull("innerHandler");
}
if (handlers == null)
{
return innerHandler;
}
HttpMessageHandler pipeline = innerHandler;
//先将自定义集合里的处理器倒转顺序
IEnumerable<DelegatingHandler> reversedHandlers = handlers.Reverse();
foreach (DelegatingHandler handler in reversedHandlers)
{
if (handler == null)
{
throw Error.Argument("handlers", Properties.Resources.DelegatingHandlerArrayContainsNullItem, typeof(DelegatingHandler).Name);
}
if (handler.InnerHandler != null)
{
throw Error.Argument("handlers", Properties.Resources.DelegatingHandlerArrayHasNonNullInnerHandler, typeof(DelegatingHandler).Name, "InnerHandler", handler.GetType().Name);
}
//由于倒排了,最后handler.InnerHandler指向的是参数传进来的默认指定的最后一个处理器(非自定义处理器)
handler.InnerHandler = pipeline;
//由于倒排了,最后pipeline指向的是倒排之前的第一个handler
pipeline = handler;
}
//这样返回的是,把集合里的每个处理器按先后顺序连接起来,并在最后链上默认指定的最后一个处理器 的dispatcher
return pipeline;
}
}
5、HttpRoutingDispatcher
在HttpServer中默认指定的消息管道的最后一个消息处理器,它继承自HttpMessageHandler而不是DelegatingHandler,它负责HttpController激活和Action的执行,而在构造函数中除了指定HttpConfiguration参数以及一个重要的defaultHandler参数HttpControllerDispatcher(也是继承自HttpMessageHandler),HttpController激活、Action的执行以及后续的操作都是它来执行。
HttpController激活和Action的执行需要路由系统解析出来的路由变量数据,在Web Host模式下,ASP.NET路由系统解析出路由数据后会存放在HttpRequestMessage的属性字典中,所以直接从其中获取就行,如果获取不到,说明可能是Self Host模式,利用路由匹配出路由数据,如果匹配出数据,同时将其数据存放到HttpRequestMessage的属性字典,如果没匹配出路由数据,说明路由匹配不了,直接错误响应。
HttpControllerDispatcher被封装成HttpMessageInvoker,调用其SendAsync(request, cancellationToken)方法。
所以,HttpRoutingDispatcher有两大功能:
- 路由:如果当前请求中不存在路由数据,就会直接解析进而生成封装路由数据的HttpRouteData,注意的是获取路由变量后会删除缺省的(RouteParameter.Optional)路由变量
- 消息分发:将请求直接分发给在创建时候指定的HttpControllerDispatcher进一步处理
public class HttpRoutingDispatcher : HttpMessageHandler
{
private readonly HttpConfiguration _configuration;
private readonly HttpMessageInvoker _defaultInvoker;
public HttpRoutingDispatcher(HttpConfiguration configuration)
: this(configuration, new HttpControllerDispatcher(configuration))
{
}
public HttpRoutingDispatcher(HttpConfiguration configuration, HttpMessageHandler defaultHandler)
{
if (configuration == null)
{
throw Error.ArgumentNull("configuration");
}
if (defaultHandler == null)
{
throw Error.ArgumentNull("defaultHandler");
}
_configuration = configuration;
//HttpControllerDispatcher被封装成HttpMessageInvoker
_defaultInvoker = new HttpMessageInvoker(defaultHandler);
}
protected override Task<HttpResponseMessage> SendAsync(HttpRequestMessage request, CancellationToken cancellationToken)
{
// 先从HttpRequestMessage属性字典中 获取路由数据,(Web Host模式下,ASP.NET路由解析出来的路由变量会存放到HttpRequestMessage 属性字典中)
IHttpRouteData routeData = request.GetRouteData();
if (routeData == null)
{
//获取不到,直接解析(Self Host模式)
routeData = _configuration.Routes.GetRouteData(request);
if (routeData != null)
{
//获取到的话,就设置到从HttpRequestMessage属性字典中
request.SetRouteData(routeData);
}
}
//为空说明路由不匹配,404 Not Found
if (routeData == null || (routeData.Route != null && routeData.Route.Handler is StopRoutingHandler))
{
request.Properties.Add(HttpPropertyKeys.NoRouteMatched, true);
return Task.FromResult(request.CreateErrorResponse(
HttpStatusCode.NotFound,
Error.Format(SRResources.ResourceNotFound, request.RequestUri),
SRResources.NoRouteData));
}
//删除缺省的(RouteParameter.Optional)路由变量,比较隐蔽的逻辑
routeData.RemoveOptionalRoutingParameters();
var invoker = (routeData.Route == null || routeData.Route.Handler == null) ?
_defaultInvoker : new HttpMessageInvoker(routeData.Route.Handler, disposeHandler: false);
return invoker.SendAsync(request, cancellationToken);
}
}
6、HttpMessageInvoker
public class HttpMessageInvoker : IDisposable
{
private volatile bool disposed;
private bool disposeHandler;
private HttpMessageHandler handler;
public HttpMessageInvoker(HttpMessageHandler handler)
: this(handler, true)
{
}
public HttpMessageInvoker(HttpMessageHandler handler, bool disposeHandler)
{
if (Logging.On)
Logging.Enter(Logging.Http, (object)this, ".ctor", (object)handler);
if (handler == null)
throw new ArgumentNullException(nameof(handler));
if (Logging.On)
Logging.Associate(Logging.Http, (object)this, (object)handler);
this.handler = handler;
this.disposeHandler = disposeHandler;
if (!Logging.On)
return;
Logging.Exit(Logging.Http, (object)this, ".ctor", (string)null);
}
public virtual Task<HttpResponseMessage> SendAsync(HttpRequestMessage request, CancellationToken cancellationToken)
{
if (request == null)
throw new ArgumentNullException(nameof(request));
this.CheckDisposed();
if (Logging.On)
Logging.Enter(Logging.Http, (object)this, nameof(SendAsync), Logging.GetObjectLogHash((object)request) + ": " + (object)request);
Task<HttpResponseMessage> task = this.handler.SendAsync(request, cancellationToken);
if (Logging.On)
Logging.Exit(Logging.Http, (object)this, nameof(SendAsync), (object)task);
return task;
}
public void Dispose()
{
this.Dispose(true);
GC.SuppressFinalize((object)this);
}
protected virtual void Dispose(bool disposing)
{
if (!disposing || this.disposed)
return;
this.disposed = true;
if (!this.disposeHandler)
return;
this.handler.Dispose();
}
private void CheckDisposed()
{
if (this.disposed)
throw new ObjectDisposedException(this.GetType().FullName);
}
}
7、HttpControllerDispatcher
HttpController激活、Action的执行以及后续的操作最终都是它来执行的,也是继承自HttpMessageHandler,我们可以说它是隶属于HttpRoutingDispatcher的一个HttpMessageHandler,而HttpRoutingDispatcher可以作为消息处理管道的最有一个处理器。
public class HttpControllerDispatcher : HttpMessageHandler
{
private readonly HttpConfiguration _configuration;
private IHttpControllerSelector _controllerSelector;
public HttpControllerDispatcher(HttpConfiguration configuration)
{
if (configuration == null)
{
throw Error.ArgumentNull("configuration");
}
_configuration = configuration;
}
public HttpConfiguration Configuration
{
get { return _configuration; }
}
private IHttpControllerSelector ControllerSelector
{
get
{
if (_controllerSelector == null)
{
_controllerSelector = _configuration.Services.GetHttpControllerSelector();
}
return _controllerSelector;
}
}
//核心方法,里边的细节是控制器的创建及其Action方法执行的细节,放到后边再说
protected override async Task<HttpResponseMessage> SendAsync(HttpRequestMessage request, CancellationToken cancellationToken)
{
if (request == null)
{
throw Error.ArgumentNull("request");
}
ExceptionDispatchInfo exceptionInfo;
HttpControllerContext controllerContext = null;
try
{
//生成控制器描述符
HttpControllerDescriptor controllerDescriptor = ControllerSelector.SelectController(request);
if (controllerDescriptor == null)
{
return request.CreateErrorResponse(
HttpStatusCode.NotFound,
Error.Format(SRResources.ResourceNotFound, request.RequestUri),
SRResources.NoControllerSelected);
}
//生成控制器创建控制器
IHttpController controller = controllerDescriptor.CreateController(request);
if (controller == null)
{
return request.CreateErrorResponse(
HttpStatusCode.NotFound,
Error.Format(SRResources.ResourceNotFound, request.RequestUri),
SRResources.NoControllerCreated);
}
//创建控制器上下文
controllerContext = CreateControllerContext(request, controllerDescriptor, controller);
//控制器执行
return await controller.ExecuteAsync(controllerContext, cancellationToken);
}
catch (OperationCanceledException)
{
throw;
}
catch (HttpResponseException httpResponseException)
{
return httpResponseException.Response;
}
catch (Exception exception)
{
exceptionInfo = ExceptionDispatchInfo.Capture(exception);
}
if (response == null)
{
exceptionInfo.Throw();
}
return response;
}
//创建HttpControllerContext
private static HttpControllerContext CreateControllerContext(
HttpRequestMessage request,
HttpControllerDescriptor controllerDescriptor,
IHttpController controller)
{
Contract.Assert(request != null);
Contract.Assert(controllerDescriptor != null);
Contract.Assert(controller != null);
HttpConfiguration controllerConfiguration = controllerDescriptor.Configuration;
HttpConfiguration requestConfig = request.GetConfiguration();
if (requestConfig == null)
{
request.SetConfiguration(controllerConfiguration);
}
else
{
if (requestConfig != controllerConfiguration)
{
request.SetConfiguration(controllerConfiguration);
}
}
HttpRequestContext requestContext = request.GetRequestContext();
if (requestContext == null)
{
requestContext = new RequestBackedHttpRequestContext(request)
{
Configuration = controllerConfiguration,
};
request.SetRequestContext(requestContext);
}
return new HttpControllerContext(requestContext, request, controllerDescriptor, controller);
}
private static HttpConfiguration EnsureNonNull(HttpConfiguration configuration)
{
if (configuration == null)
{
throw Error.ArgumentNull("configuration");
}
return configuration;
}
}



