字典树
字典树
字典树的样子:
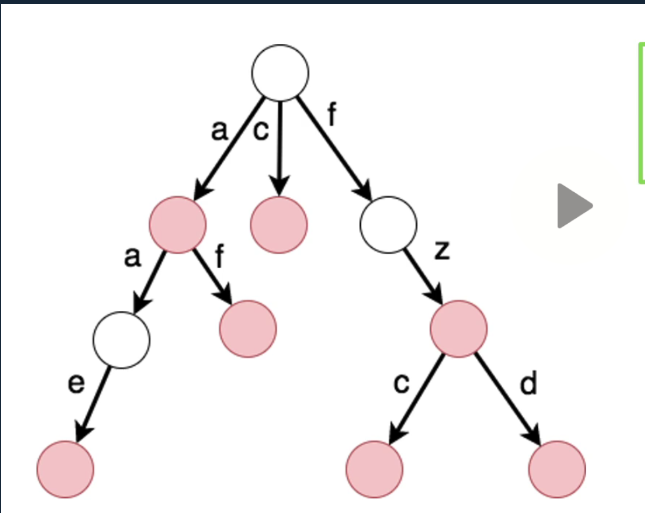
需要注意到,这颗字典树的字符是存储在树枝上而不是节点上,每经过一个根那么寻找的字符后面就加上这个字母。同时结点的作用是标记遍历到这个结点所形成的字符串是否存在。 每当你存储一个字符串,那么最后一个字符所在根的下一个结点就是被标记的,每当遍历到这个节点时得到的字符串就是其中一个存在的字符串,对应上图中有颜色的结点。
就上面的树,查询找出的字符串分别有
aae,af,c,fzc,fzd。你会发现用深度优先遍历出来的字符串就是按照字典序的方式从小到大排列。
代码演示:
using namespace std;
#define base 26
class Node {
public:
int flag = 0;
Node** pnext;
int* a;
Node() {
flag = 0;
pnext = new Node*[base];
memset(pnext, 0, sizeof(Node*) * base);
}
};
class trie {
private:
int h = 0;
static Node* root;
public:
trie() {
root = new Node();
}
void insert(char* str) {
Node* p = root;
for (int i = 0; str[i]; i++) {
if (!p->pnext[str[i] - 'a'])p->pnext[str[i] - 'a'] = new Node();
p = p->pnext[str[i] - 'a'];
}
p->flag = 1;
return;
}
bool find_str(char* str,int h = 0) {
Node* p = this->root;
for (int i = 0; str[i]; i++) {
p = p->pnext[str[i] - 'a'];
if (!p)return 0;
}
return p->flag;
}
void clear(Node* root = root) {
if (!root)return;
for (int i = 0; i < base; i++) {
clear(root->pnext[i]);
}
free(root);
return;
}
};
Node* trie::root;
竞赛版
using namespace std;
#define base 26
#define MAX_N 100000
//将所有结点物理上时平行的,逻辑上是层次的
class Node {
public:
int pnext[base] = { 0 };
//用数字的形式代替具体的地址,有效的降低内存和运行时间。
int flag = 0;
Node(){}
};
class trie {
private:
int h = 0;
int root = 0;
int node_cnt = 1;
Node* tree = new Node[MAX_N];
public:
int get_node() {
return node_cnt++;
/*每有一个结点插进来就加一,防止将结点放在相同的地址,
*因为结点在物理上是平行的。
*/
}
void insert(char* str) {
int p = root;
for (int i = 0; str[i]; i++) {
int ind = str[i] - 'a';
if (tree[p].pnext[ind] == 0)tree[p].pnext[ind] = get_node();
p = tree[p].pnext[ind];
}
tree[p].flag = 1;
return;
}
bool find_str(char* str) {
int p = root;
for (int i = 0; str[i]; i++) {
int ind = str[i] - 'a';
if (tree[p].pnext[ind] == 0)return 0;
p = tree[p].pnext[ind];
}
return tree[p].flag;
}
void clear() {
delete[] tree;
}
};





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 开发者必知的日志记录最佳实践
· SQL Server 2025 AI相关能力初探
· Linux系列:如何用 C#调用 C方法造成内存泄露
· AI与.NET技术实操系列(二):开始使用ML.NET
· 记一次.NET内存居高不下排查解决与启示
· 被坑几百块钱后,我竟然真的恢复了删除的微信聊天记录!
· 没有Manus邀请码?试试免邀请码的MGX或者开源的OpenManus吧
· 【自荐】一款简洁、开源的在线白板工具 Drawnix
· 园子的第一款AI主题卫衣上架——"HELLO! HOW CAN I ASSIST YOU TODAY
· Docker 太简单,K8s 太复杂?w7panel 让容器管理更轻松!