转自:https://blog.csdn.net/huangjinjin520/article/details/89740672
Spring Cloud将服务注册到了Eureka上,可以从Eureka的UI界面中,看到有哪些服务已经注册到了Eureka Server上;但是如果想查看当前服务提供了哪些RESTful接口方法的话,就无法从Eureka Server获取了,而传统的方法是梳理一个接口文档来供开发人员之间来进行交流。这种情况下经常会造成文档和代码的不一致性,比如说代码改了,但是接口文档还没来得及修改等问题,而Swagger2则给我们提供了一套完美的解决方案,下面来看看Swagger2是如何来解决这个问题的。
1、 新建项目sc-swagger2,对应的pom.xml文件
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>spring-cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>sc-swagger2</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<packaging>jar</packaging>
<name>sc-swagger2</name>
<url>http://maven.apache.org</url>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.0.4.RELEASE</version>
</parent>
<dependencyManagement>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-dependencies</artifactId>
<version>Finchley.RELEASE</version>
<type>pom</type>
<scope>import</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</dependencyManagement>
<properties>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
<maven.compiler.source>1.8</maven.compiler.source>
<maven.compiler.target>1.8</maven.compiler.target>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.springfox</groupId>
<artifactId>springfox-swagger2</artifactId>
<version>2.9.2</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.springfox</groupId>
<artifactId>springfox-swagger-ui</artifactId>
<version>2.9.2</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</project>
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
2、 新建springboot启动类
package sc.swagger2;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
@SpringBootApplication
public class Swagger2Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Swagger2Application.class, args);
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
3、 新建Swagger2配置类
package sc.swagger2.config;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import springfox.documentation.builders.ApiInfoBuilder;
import springfox.documentation.builders.PathSelectors;
import springfox.documentation.builders.RequestHandlerSelectors;
import springfox.documentation.service.ApiInfo;
import springfox.documentation.service.Contact;
import springfox.documentation.spi.DocumentationType;
import springfox.documentation.spring.web.plugins.Docket;
import springfox.documentation.swagger2.annotations.EnableSwagger2;
@Configuration
@EnableSwagger2
public class Swagger2Config {
@Bean
public Docket createRestApi() {
return new Docket(DocumentationType.SWAGGER_2)
.apiInfo(apiInfo())
.select()
.apis(RequestHandlerSelectors.basePackage("sc.swagger2"))
.paths(PathSelectors.any())
.build();
}
private ApiInfo apiInfo() {
return new ApiInfoBuilder()
.title("Spring Boot中使用Swagger2构建RESTful APIs")
.description("更多Spring Boot相关文章请关注: JAVA乐园 公众号")
.termsOfServiceUrl("https://edu.csdn.net/lecturer/995")
.contact(new Contact("huangjinjin", //
"https://edu.csdn.net/lecturer/995",//
"happyhuangjinjin@sina.com"))
.version("1.0")
.build();
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
4、 新建一个模拟的Controller
package sc.swagger2.controller;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.DeleteMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PutMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
import io.swagger.annotations.Api;
import io.swagger.annotations.ApiImplicitParam;
import io.swagger.annotations.ApiImplicitParams;
import io.swagger.annotations.ApiOperation;
import io.swagger.annotations.ApiResponse;
import io.swagger.annotations.ApiResponses;
import sc.swagger2.model.User;
@Api(value="用户管理")
@Controller
public class UserController {
@ApiResponses({ @ApiResponse(code = 000000, message = "操作成功"),
@ApiResponse(code = 000001, message = "服务器内部异常") })
@GetMapping(value = "/feign/user/getUser/{id}")
@ResponseBody
@ApiOperation(value = "获取根据Id用户信息",response = User.class)
@ApiImplicitParam(name = "id", value = "用户ID", required = true, dataType = "Long",example="100")
public Map<String, Object> getUser(@PathVariable Long id) {
Map<String, Object> result = new HashMap<String, Object>();
result.put("code", "000000");
result.put("msg", "success");
User u = new User();
u.setId(1L);
u.setAge(23);
u.setUserName("huangjinjin");
u.setPosition("cto");
result.put("body", u);
return result;
}
@ApiResponses({ @ApiResponse(code = 000000, message = "操作成功"),
@ApiResponse(code = 000001, message = "服务器内部异常") })
@RequestMapping(value = "/feign/user/listUser", method = RequestMethod.GET)
@ResponseBody
@ApiOperation(value = "获取用户列表")
public Map<String, Object> listUser() {
Map<String, Object> result = new HashMap<String, Object>();
result.put("code", "000000");
result.put("msg", "success");
User u = new User();
u.setId(1L);
u.setAge(23);
u.setUserName("huangjinjin");
u.setPosition("cto");
List<User> list = new ArrayList<User>();
list.add(u);
result.put("body", list);
return result;
}
@ApiResponses({ @ApiResponse(code = 000000, message = "操作成功"),
@ApiResponse(code = 000001, message = "服务器内部异常") })
@PostMapping(value = "/feign/user/addUser")
@ResponseBody
@ApiOperation(value = "添加用户", notes = "根据User对象创建用户")
@ApiImplicitParams({ @ApiImplicitParam(name = "userName", value = "用户名", required = true, dataType = "String"),
@ApiImplicitParam(name = "age", value = "年龄", required = true, dataType = "String"),
@ApiImplicitParam(name = "position", value = "职位", required = true, dataType = "String"),
@ApiImplicitParam(name = "id", value = "用户ID", required = false, dataType = "Long",example="100")})
public Map<String, Object> addUser(User user) {
Map<String, Object> result = new HashMap<String, Object>();
result.put("code", "000000");
result.put("msg", "success");
result.put("body", 1);
return result;
}
@ApiResponses({ @ApiResponse(code = 000000, message = "操作成功"),
@ApiResponse(code = 000001, message = "服务器内部异常") })
@ApiOperation(value = "更新用户")
@PutMapping(value = "/feign/user/updateUser")
@ResponseBody
@ApiImplicitParams({ @ApiImplicitParam(name = "userName", value = "用户名", required = true, dataType = "String"),
@ApiImplicitParam(name = "age", value = "年龄", required = true, dataType = "String"),
@ApiImplicitParam(name = "position", value = "职位", required = true, dataType = "String"),
@ApiImplicitParam(name = "id", value = "用户ID", required = true, dataType = "Long", example="100")})
public Map<String, Object> updateUser(User user) {
Map<String, Object> result = new HashMap<String, Object>();
result.put("code", "000000");
result.put("msg", "success");
result.put("body", 1);
return result;
}
@ApiResponses({ @ApiResponse(code = 000000, message = "操作成功"),
@ApiResponse(code = 000001, message = "服务器内部异常") })
@DeleteMapping(value = "/feign/user/deleteUser/{id}")
@ResponseBody
@ApiOperation(value = "删除用户")
@ApiImplicitParam(name = "id", value = "用户ID", required = true, dataType = "Long",example="100")
public Map<String, Object> deleteUser(@PathVariable Long id) {
Map<String, Object> result = new HashMap<String, Object>();
result.put("code", "000000");
result.put("msg", "success");
result.put("body", 1);
return result;
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
5、 新建User模型类
package sc.swagger2.model;
import java.io.Serializable;
import io.swagger.annotations.ApiModel;
import io.swagger.annotations.ApiModelProperty;
@ApiModel
public class User implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 4639927446947303736L;
@ApiModelProperty(name="id", dataType="Long", value="主键ID")
private Long id;
@ApiModelProperty(name="userName", dataType="String", value="姓名", required=true)
private String userName;
@ApiModelProperty(name="age", dataType="String", value="年龄", required=true)
private Integer age;
@ApiModelProperty(name="position", dataType="String", value="职位")
private String position;
public String getUserName() {
return userName;
}
public void setUserName(String userName) {
this.userName = userName;
}
public Integer getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(Integer age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String getPosition() {
return position;
}
public void setPosition(String position) {
this.position = position;
}
public Long getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Long id) {
this.id = id;
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
6、 启动sc-swagger2项目,并验证是否启动成功
方式一:查看日志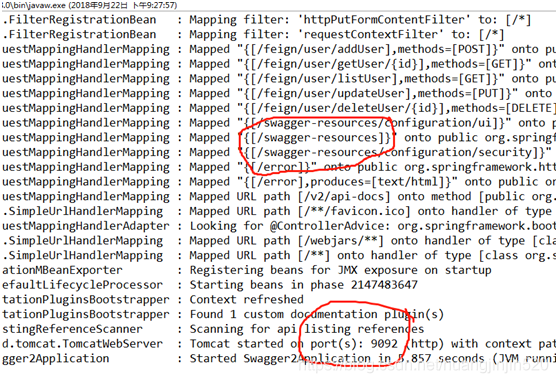
方式二:访问地址
http://127.0.0.1:9092/swagger-ui.html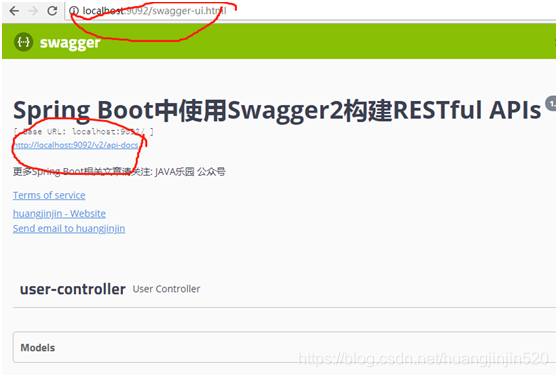
或者访问http://localhost:9092/v2/api-docs
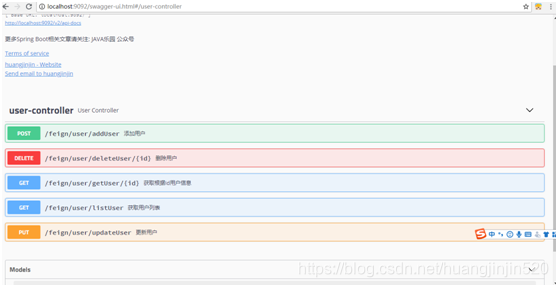
7、 在界面http://127.0.0.1:9092/swagger-ui.html点击【user-controller】可以看到所有的接口,同时也可以在界面上进行接口调用调试



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号