python 机器学习多项式回归
现实世界的曲线关系都是通过增加多项式实现的,现在解决多项式回归问题
住房价格样本
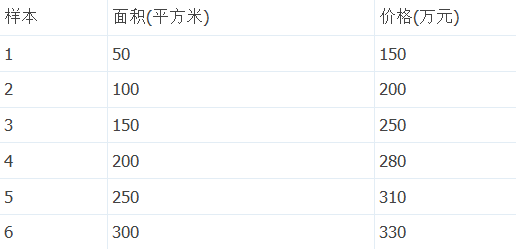
样本图像
import matplotlib.font_manager as fm import matplotlib.pyplot as plt myfont = fm.FontProperties(fname='C:\Windows\Fonts\simsun.ttc') # plt.figure() # 实例化作图变量 plt.title('房价面积价格样本', fontproperties = myfont) # 图像标题 plt.xlabel('面积(平方米)', fontproperties = myfont) # x轴文本 plt.ylabel('价格(万元)', fontproperties = myfont) # y轴文本 # plt.axis([30, 400, 100, 400]) plt.grid(True) # 是否绘制网格线 X = [[50], [100], [150], [200], [250], [300]] y = [[150], [200], [250], [280], [310], [330]] X_test = [[250], [300]] # 用来做最终效果测试 y_test = [[310], [330]] # 用来做最终效果测试 # plt.plot(X, y, 'b.')#点 # plt.plot(X, y, 'b-')#线 plt.scatter(X, y, marker='*',color='blue',label='房价面积价格样本') plt.show()
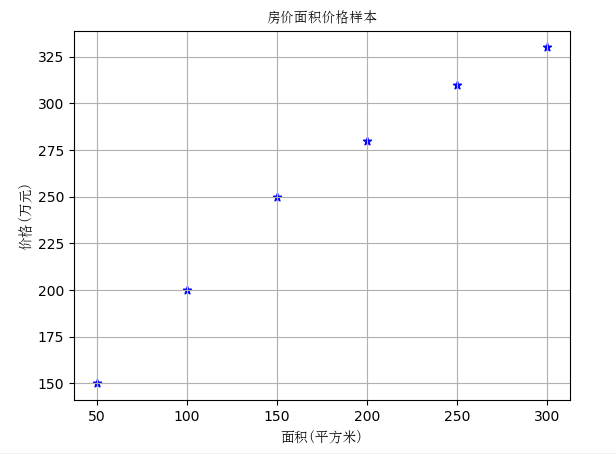
用线性回归
添加以下代码
model = LinearRegression() model.fit(X, y) print('一元线性回归 r-squared', model.score(X_test, y_test)) X2 = [[30], [400]] y2 = model.predict(X2) plt.plot(X2, y2, 'g-') plt.show()

实际情况是,如果房屋面积一味的增加,房价并不会线性增长,因此线性关系已经无法描述真实的房价问题
采用多项式回归
首先我们用二次多项式
# 实例化一个二次多项式特征实例 quadratic_featurizer = PolynomialFeatures(degree=2) # 用二次多项式对样本X值做变换 X_train_quadratic = quadratic_featurizer.fit_transform(X) # 创建一个线性回归实例 regressor_model = LinearRegression() # 以多项式变换后的x值为输入,代入线性回归模型做训练 regressor_model.fit(X_train_quadratic, y) # 设计x轴一系列点作为画图的x点集 xx = np.linspace(30, 400, 100) # 把训练好X值的多项式特征实例应用到一系列点上,形成矩阵 xx_quadratic = quadratic_featurizer.transform(xx.reshape(xx.shape[0], 1)) yy_predict = regressor_model.predict(xx_quadratic) # 用训练好的模型作图 plt.plot(xx, yy_predict, 'r-') X_test_quadratic = quadratic_featurizer.transform(X_test) print('二次回归 r-squared', regressor_model.score(X_test_quadratic, y_test)) # # plt.show() # 展示图像
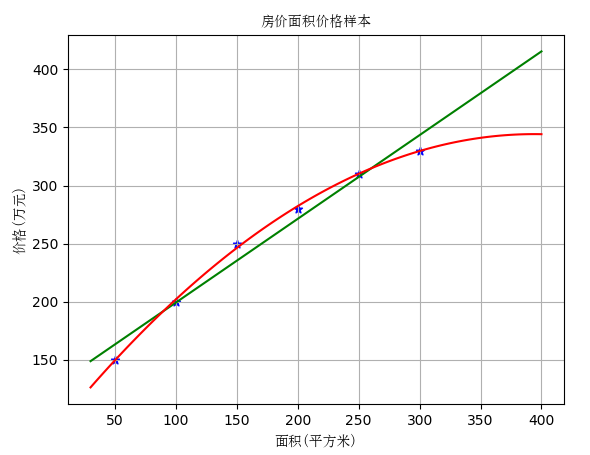
继续三次回归
cubic_featurizer = PolynomialFeatures(degree=3) X_train_cubic = cubic_featurizer.fit_transform(X) regressor_cubic = LinearRegression() regressor_cubic.fit(X_train_cubic, y) xx_cubic = cubic_featurizer.transform(xx.reshape(xx.shape[0], 1)) plt.plot(xx, regressor_cubic.predict(xx_cubic)) X_test_cubic = cubic_featurizer.transform(X_test) print('三次回归 r-squared', regressor_cubic.score(X_test_cubic, y_test)) plt.show() # 展示图像
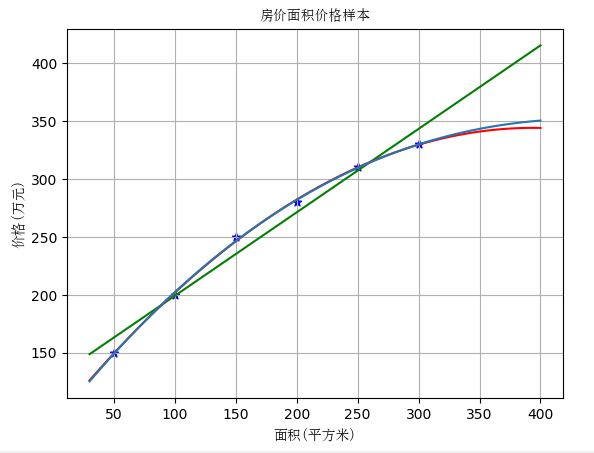
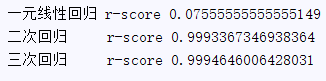
可以看到三次回归比二次回归效果又好了一些,但是不是很明显。所以二次回归更可能是最适合的回归模型,三次回归可能有过拟合现象
参考:http://www.aboutyun.com/thread-19073-1-1.html



