【java多线程】ConCurrent并发包 - Lock详解
完整的锁解释:https://www.cnblogs.com/shangxiaofei/articles/16361990.html
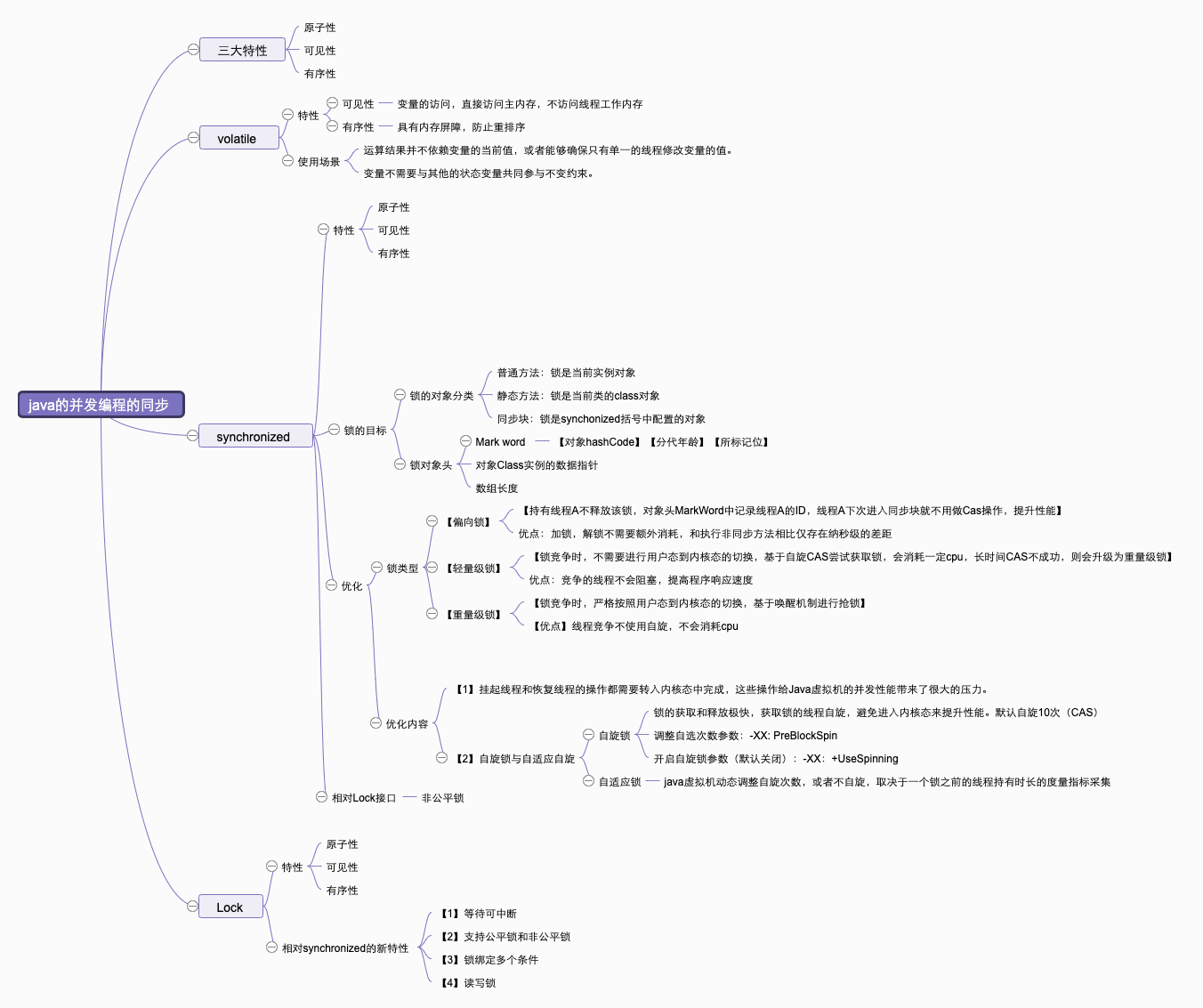
synchronized的缺陷
我们知道,可以利用synchronized关键字来实现共享资源的互斥访问。 Java 5在java.util.concurrent.locks包下提供了另一种来实现线程的同步访问,那就是Lock。既然有了synchronized来 实现线程同步,Java为什么还需要提供Lock呢?
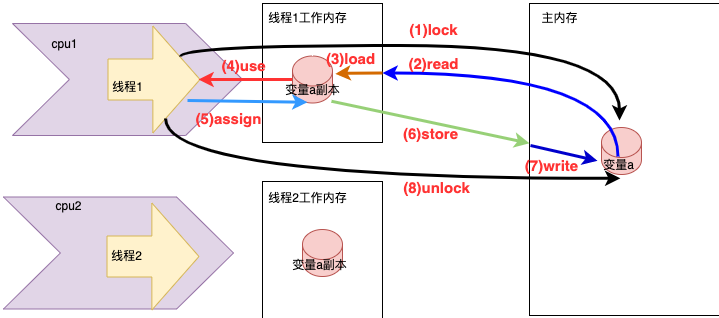
synchronized是Java的一个关键字,当我们使用synchronized来修饰方法或代码块时,线程必须先获得对应的锁才能执行该段代码。而其他线程只能一直等待,直到当前线程释放锁并获得对应的锁才能进入该段代码。这里获取锁的线程释放锁只会有两种情况:
- 获取锁的线程执行完该段代码,线程会释放占有的锁;
- 线程执行发生异常,此时JVM会让线程自动释放锁。
那么如果这个占有锁的线程由于等待IO或其他原因(比如调用sleep方法)被阻塞,但是还没有释放锁,那么其他线程只能干巴巴的等着,试想这多么影响程序的执行效率。
当多个线程同时读写文件是,我们知道读操作和写操作会发生冲突,写操作和写操作 也会发生冲突,但是读操作和读操作之间不会冲突。synchronized关键字对一段代码加锁,所有的线程必须先获得对应的锁才有该代码段的执行权限。 如果多个线程同时进行读操作时,使用synchronized关键字会导致在任何时刻只有一个线程读,其他线程等待,大大降低执行效率。
Lock可以对以上种种情况作优化,提供更好的执行效率。另外,Lock方便了 对锁的管理,可以自由的加锁和释放锁,还可以判断有没有成功获取锁。但是在使用Lock时要注意,Lock需要开发者手动去释放锁,如果没有主动释放锁, 就要可能导致死锁出现。建议在finally语句块中释放Lock锁。
concurrent.locks包下常用类
1. Lock
首先要说明的是Lock,它是一个接口:

public interface Lock { void lock(); void lockInterruptibly() throws InterruptedException; boolean tryLock(); boolean tryLock(long time, TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException; void unlock(); Condition newCondition(); }
- lock()方法用来获取锁。
- tryLock()尝试获取锁,如果成功则返回true,失败返回false(其他线程已占有锁)。这个方法会立即返回,在拿不到锁时也不会等待。
- tryLock(long time, TimeUnit unit)方法和tryLock()方法类似,只不过在拿不到锁时等待一定的时间,如果超过等待时间还拿不到锁就返回false。
- lockInterruptibly() 方法比较特殊,当通过这个方法获取锁时,如果该线程正在等待获取锁,则它能够响应中断。也就是说,当两个线程同时通过 lockInterruptibly()获取某个锁时,假如线程A获得了锁,而线程B仍在等待获取锁,那么对线程B调用interrupt()方法可以中 断B的等待过程。

// lock()的使用 Lock lock = ...; lock.lock(); try{ //处理任务 }catch(Exception ex){ }finally{ lock.unlock(); //释放锁 }

// tryLock()的使用 Lock lock = ...; if(lock.tryLock()) { try{ //处理任务 }catch(Exception ex){ }finally{ lock.unlock(); //释放锁 } }else { //如果不能获取锁,则直接做其他事情 }

// lockInterruptibly()的使用 public void method() throws InterruptedException { lock.lockInterruptibly(); try { //..... } finally { lock.unlock(); } }
使用synchronized关键字,当线程处于等待锁的状态时,是无法被中断的,只能一直等待。
2.ReentrantLock
ReentrantLock是可重入锁。如果所具备可重入性,则称为可重入锁,synchronized可ReentrantLock都是可重入锁。可重入锁也叫递归锁,当一个线程已经获得该代码块的锁时,再次进入该代码块不必重新申请锁,可以直接执行。
例1, lock()的使用方法:

public class Test { private ArrayList<Integer> arrayList = new ArrayList<Integer>(); private Lock lock = new ReentrantLock(); //注意这个地方 public static void main(String[] args) { final Test test = new Test(); new Thread(){ public void run() { test.insert(Thread.currentThread()); }; }.start(); new Thread(){ public void run() { test.insert(Thread.currentThread()); }; }.start(); } public void insert(Thread thread) { lock.lock(); try { System.out.println(thread.getName()+"得到了锁"); for(int i=0;i<5;i++) { arrayList.add(i); } } catch (Exception e) { // TODO: handle exception }finally { System.out.println(thread.getName()+"释放了锁"); lock.unlock(); } } }
例2, lockInterruptibly()响应中断的使用方法:

public class Test { private Lock lock = new ReentrantLock(); public static void main(String[] args) { Test test = new Test(); MyThread thread1 = new MyThread(test); MyThread thread2 = new MyThread(test); thread1.start(); thread2.start(); try { Thread.sleep(2000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } thread2.interrupt(); } public void insert(Thread thread) throws InterruptedException{ lock.lockInterruptibly(); //注意,如果需要正确中断等待锁的线程,必须将获取锁放在外面,然后将InterruptedException抛出 try { System.out.println(thread.getName()+"得到了锁"); long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); for( ; ;) { if(System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime >= Integer.MAX_VALUE) break; //插入数据 } } finally { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"执行finally"); lock.unlock(); System.out.println(thread.getName()+"释放了锁"); } } } class MyThread extends Thread { private Test test = null; public MyThread(Test test) { this.test = test; } @Override public void run() { try { test.insert(Thread.currentThread()); } catch (InterruptedException e) { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"被中断"); } } }
3. ReadWriteLock
ReadWriteLock也是一个接口,它只定义了两个方法:

public interface ReadWriteLock { /** * Returns the lock used for reading. */ Lock readLock(); /** * Returns the lock used for writing. */ Lock writeLock(); }
readLock()用来获取读锁,writeLock()用来获取写锁。也就是将文件的读写操作分开,分成两个锁来分配给线程,从而使多个线程可以同时进行读操作。ReentrantReadWriteLock是它的实现类。

public class Test { private ReentrantReadWriteLock rwl = new ReentrantReadWriteLock(); public static void main(String[] args) { final Test test = new Test(); new Thread(){ public void run() { test.get(Thread.currentThread()); }; }.start(); new Thread(){ public void run() { test.get(Thread.currentThread()); }; }.start(); } public void get(Thread thread) { rwl.readLock().lock(); try { long start = System.currentTimeMillis(); while(System.currentTimeMillis() - start <= 1) { System.out.println(thread.getName()+"正在进行读操作"); } System.out.println(thread.getName()+"读操作完毕"); } finally { rwl.readLock().unlock(); } } }
==================华丽的分割线=======================
synchronized和Lock的总结