数据结构与算法系列(一)数组实现
数据结构与算法系列(一)数组实现
注:这是一个新的系列,主要是由于数据结构与算法是程序员以后立身的根本,我以前在大学也学过,但是很快就忘记了,现在想把它捡起来,通过写一个系列文章,加深自己的理解,其实我写这个系列主要是想先通过预热,然后去刷leetcode。刷算法本身是想锻炼自己写程序的思维,不想因为每天写业务代码,导致自己思维僵化,此系列会与springboot系列同时更新,立个falg。
java实现数组
说明:
数组是一段拥有连续的存储相同类型的结构,并且是一种线性结构,因为是线性结构,所以数组中每一个数据,都有前和后,但是注意,不包括开始数据(首)和末数据。- 数组有一个非常重要的特性,那就是
随机访问
1.定义数组
数组有两个基本变量:
- 数组长度:含义是表示数组本身大小
- 数组存储具体数据的连续空间
// 数组申请空间的长度
private int size = 0;
// 数组实际长度
private int count;
// 数组实际存储
private int array[];
2.基本方法:构造方法 增 删 查 改
构造方法
/**
* 构造方法-初始化
* @param capacity 数组初始化长度
*/
public MyArray(int capacity) {
this.size = capacity;
this.array = new int[capacity];
this.count = 0;
}
// 使用构造方法,初始化空间大小
MyArray myArray = new MyArray(6);
新增
注:新增本质上就是在连续的空间插入新的数据,我目前已知两种
- 第一种,就是先将从数组的尾部位置开始依次将数据向后移动一位,将index所指向的位置腾出来,方便插入新的数据。如图所示,先后依次移动
55 44 33,这样,位置就空出来,切忌不能先移动33,如果先移动33,则33会直接覆盖掉44。代码如下

- 第二种,就是直接将指定index位置的数据直接取出,放到数组的末尾,这样就避免了数组的整体移动,当数据量很大的时候,可以考虑这种做法。
/**
* 根据索引在指定位置插入数据
* @param index 索引
* @param value 带插入的值
*/
protected boolean myArrayInsert(int index,int value){
// 判断数组是否还有空余空间
if (count == size){
System.out.println("没有可插入的空间");
return false;
}
// 判断是否越界
if (index < 0 || index >= size){
System.out.println("数组越界异常");
return false;
}
// 循环,从插入的位置开始依次将数据向后移动,将index所指向的位置腾出来,方便插入新的数据
for (int i = count; i > index; i--) {
array[i] = array[i-1];
}
array[index] = value;
count ++ ;
System.out.println("插入成功");
return true;
}
删除:同新增,依然有两种方法
- 第一种:index索引删除的位置开始,后面的元素依次向前移动一位,将前面的覆盖掉就行了。但是依然需要移动索引之后的每一个元素。
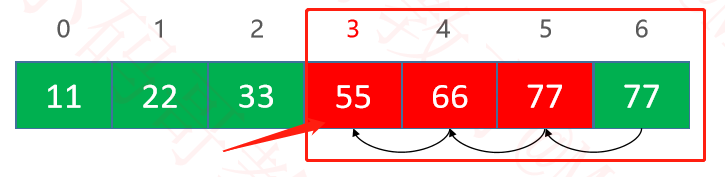
- 第二种:最简单的就是,直接将数组的最后一位元素放入
index的位置,这样就减少了数据的移动
/**
* 删除指定位置的数
* @param index 索引
*/
protected boolean myArrayDel(int index){
if (index < 0 || index >= count){
System.out.println("索引越界");
return false;
}
for (int i = index; i < count - 1; i++) {
array[i] = array[i + 1];
}
count --;
System.out.println("删除成功");
return true;
}
查询:返回查询成功之后数据的索引值
/**
* 数组查询
* @param value 待查询的值
* @return 返回该值对应的索引
*/
protected int myArrayFind(int value){
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
if (array[i] == value){
System.out.println("查询成功");
return i;
}
}
System.out.println("查询不成功,该数不存在");
return -1;
}
修改
/**
* 修改替换指定位置的数据
* @param index 指定位置索引
* @param value 值
* @return 是否修改成功
*/
protected boolean myArrayModify(int index,int value){
if (index < 0 || index >= count){
System.out.println("索引越界");
return false;
}
array[index] = value;
return true;
}
打印输出:为了方便查询效果,提供打印方法
/**
* 数组打印
*
*/
protected void printAll(){
System.out.println("当前数组实际长度:" + count);
System.out.println("申请的数组空间大小:" + size);
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
System.out.println("位置:" + i + "----" + array[i]);
}
}
测试
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyArray myArray = new MyArray(6);
myArray.myArrayInsert(0,0);
myArray.myArrayInsert(1,1);
myArray.myArrayInsert(2,2);
myArray.myArrayInsert(3,3);
myArray.myArrayInsert(4,4);
myArray.myArrayInsert(5,5);
// 新增
myArray.myArrayInsert(2,3);
// 删除
myArray.myArrayDel(0);
// 查询
int i = myArray.myArrayFind(4);
System.out.println("对应的索引位置:" + i);
// 修改
myArray.myArrayModify(1,9);
myArray.printAll();
}
注:以上就是数组的基本操作了,属于个人理解,可能略显浅显,有错误的地方欢迎指正与交流。
希望自己能一直保持初衷,文章一直写下去,和大家一起成长
本系列代码github地址:https://github.com/shanggushenlong/Data_Structures_and_Algorithms_Java



