VINS(七)estimator_node 数据对齐 imu预积分 vision
首先通过vins_estimator mode监听几个Topic(频率2000Hz),将imu数据,feature数据,raw_image数据(用于回环检测)通过各自的回调函数封装起来
ros::Subscriber sub_imu = n.subscribe(IMU_TOPIC, 2000, imu_callback, ros::TransportHints().tcpNoDelay()); ros::Subscriber sub_image = n.subscribe("/feature_tracker/feature", 2000, feature_callback); ros::Subscriber sub_raw_image = n.subscribe(IMAGE_TOPIC, 2000, raw_image_callback);
imu_buf.push(imu_msg);
feature_buf.push(feature_msg);
image_buf.push(make_pair(img_ptr->image, img_msg->header.stamp.toSec()));
然后开启处理measurement的线程
std::thread measurement_process{process};
process()函数中,首先将获取的传感器数据imu_buf feature_buf对齐,注意这里只保证了相邻的feature数据之间有完整的imu数据,并不能保证imu和feature数据的精确对齐
// multiple IMU measurements and only one vision(features) measurements std::vector<std::pair<std::vector<sensor_msgs::ImuConstPtr>, sensor_msgs::PointCloudConstPtr>> getMeasurements() { std::vector<std::pair<std::vector<sensor_msgs::ImuConstPtr>, sensor_msgs::PointCloudConstPtr>> measurements; while (true) { if (imu_buf.empty() || feature_buf.empty()) return measurements; // synchronize, if strictly synchronize, should change to ">=" // end up with : imu_buf.front()->header.stamp < feature_buf.front()->header.stamp // 1. should have overlap if (!(imu_buf.back()->header.stamp > feature_buf.front()->header.stamp)) { ROS_WARN("wait for imu, only should happen at the beginning"); sum_of_wait++; return measurements; } // 2. should have complete imu measurements between two feature_buf msg if (!(imu_buf.front()->header.stamp < feature_buf.front()->header.stamp)) { ROS_WARN("throw img, only should happen at the beginning"); feature_buf.pop(); continue; } sensor_msgs::PointCloudConstPtr img_msg = feature_buf.front(); feature_buf.pop(); std::vector<sensor_msgs::ImuConstPtr> IMUs; while (imu_buf.front()->header.stamp <= img_msg->header.stamp) { IMUs.emplace_back(imu_buf.front()); imu_buf.pop(); } measurements.emplace_back(IMUs, img_msg); } return measurements; }
接下来进入对measurements数据的处理:
处理imu数据的接口函数是processIMU()
处理vision数据的借口函数是processImage()
(一)IMU
1. 核心API:
midPointIntegration(_dt, acc_0, gyr_0, _acc_1, _gyr_1, delta_p, delta_q, delta_v, linearized_ba, linearized_bg, result_delta_p, result_delta_q, result_delta_v, result_linearized_ba, result_linearized_bg, 1);
其中,0代表上次测量值,1代表当前测量值,delta_p,delta_q,delta_v代表相对预积分初始参考系的位移,旋转四元数,以及速度(例如,从k帧预积分到k+1帧,则参考系是k帧的imu坐标系)
对应实现的是公式:
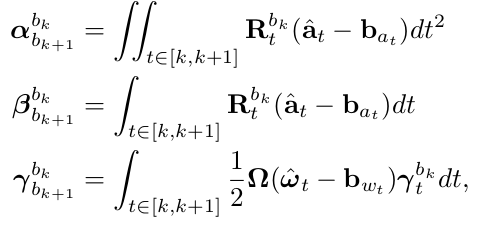
相应的离散实现使用Euler,Mid-point,或者龙格库塔(RK4)数值积分方法。
Euler方法如下:
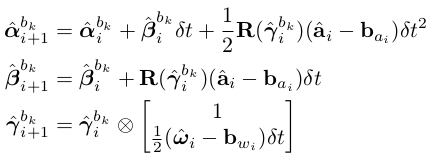
2. 求状态向量对bias的Jacobian,当bias变化较小时,使用Jacobian去更新状态;否则需要以当前imu为参考系,重新预积分,对应repropagation()。同时,需要计算error state model中误差传播方程的系数矩阵F和V:
// pre-integration // time interval of two imu; last and current imu measurements; p,q,v relate to local frame; ba and bg; propagated p,q,v,ba,bg; // whether to update Jacobian and calculate F,V void midPointIntegration(double _dt, const Eigen::Vector3d &_acc_0, const Eigen::Vector3d &_gyr_0, const Eigen::Vector3d &_acc_1, const Eigen::Vector3d &_gyr_1, const Eigen::Vector3d &delta_p, const Eigen::Quaterniond &delta_q, const Eigen::Vector3d &delta_v, const Eigen::Vector3d &linearized_ba, const Eigen::Vector3d &linearized_bg, Eigen::Vector3d &result_delta_p, Eigen::Quaterniond &result_delta_q, Eigen::Vector3d &result_delta_v, Eigen::Vector3d &result_linearized_ba, Eigen::Vector3d &result_linearized_bg, bool update_jacobian) { //ROS_INFO("midpoint integration"); // mid-point integration with bias = 0 Vector3d un_acc_0 = delta_q * (_acc_0 - linearized_ba); Vector3d un_gyr = 0.5 * (_gyr_0 + _gyr_1) - linearized_bg; result_delta_q = delta_q * Quaterniond(1, un_gyr(0) * _dt / 2, un_gyr(1) * _dt / 2, un_gyr(2) * _dt / 2); Vector3d un_acc_1 = result_delta_q * (_acc_1 - linearized_ba); Vector3d un_acc = 0.5 * (un_acc_0 + un_acc_1); result_delta_p = delta_p + delta_v * _dt + 0.5 * un_acc * _dt * _dt; result_delta_v = delta_v + un_acc * _dt; // ba and bg donot change result_linearized_ba = linearized_ba; result_linearized_bg = linearized_bg; // jacobian to bias, used when the bias changes slightly and no need of repropagation if(update_jacobian) { // same as un_gyr, gyrometer reference to the local frame bk Vector3d w_x = 0.5 * (_gyr_0 + _gyr_1) - linearized_bg; // last acceleration measurement Vector3d a_0_x = _acc_0 - linearized_ba; // current acceleration measurement Vector3d a_1_x = _acc_1 - linearized_ba; // used for cross-product // pay attention to derivation of matrix product Matrix3d R_w_x, R_a_0_x, R_a_1_x; R_w_x<<0, -w_x(2), w_x(1), w_x(2), 0, -w_x(0), -w_x(1), w_x(0), 0; R_a_0_x<<0, -a_0_x(2), a_0_x(1), a_0_x(2), 0, -a_0_x(0), -a_0_x(1), a_0_x(0), 0; R_a_1_x<<0, -a_1_x(2), a_1_x(1), a_1_x(2), 0, -a_1_x(0), -a_1_x(1), a_1_x(0), 0; // error state model // should use discrete format and mid-point approximation MatrixXd F = MatrixXd::Zero(15, 15); F.block<3, 3>(0, 0) = Matrix3d::Identity(); F.block<3, 3>(0, 3) = -0.25 * delta_q.toRotationMatrix() * R_a_0_x * _dt * _dt + -0.25 * result_delta_q.toRotationMatrix() * R_a_1_x * (Matrix3d::Identity() - R_w_x * _dt) * _dt * _dt; F.block<3, 3>(0, 6) = MatrixXd::Identity(3,3) * _dt; F.block<3, 3>(0, 9) = -0.25 * (delta_q.toRotationMatrix() + result_delta_q.toRotationMatrix()) * _dt * _dt; F.block<3, 3>(0, 12) = -0.25 * result_delta_q.toRotationMatrix() * R_a_1_x * _dt * _dt * -_dt; F.block<3, 3>(3, 3) = Matrix3d::Identity() - R_w_x * _dt; F.block<3, 3>(3, 12) = -1.0 * MatrixXd::Identity(3,3) * _dt; F.block<3, 3>(6, 3) = -0.5 * delta_q.toRotationMatrix() * R_a_0_x * _dt + -0.5 * result_delta_q.toRotationMatrix() * R_a_1_x * (Matrix3d::Identity() - R_w_x * _dt) * _dt; F.block<3, 3>(6, 6) = Matrix3d::Identity(); F.block<3, 3>(6, 9) = -0.5 * (delta_q.toRotationMatrix() + result_delta_q.toRotationMatrix()) * _dt; F.block<3, 3>(6, 12) = -0.5 * result_delta_q.toRotationMatrix() * R_a_1_x * _dt * -_dt; F.block<3, 3>(9, 9) = Matrix3d::Identity(); F.block<3, 3>(12, 12) = Matrix3d::Identity(); MatrixXd V = MatrixXd::Zero(15,18); V.block<3, 3>(0, 0) = 0.25 * delta_q.toRotationMatrix() * _dt * _dt; V.block<3, 3>(0, 3) = 0.25 * -result_delta_q.toRotationMatrix() * R_a_1_x * _dt * _dt * 0.5 * _dt; V.block<3, 3>(0, 6) = 0.25 * result_delta_q.toRotationMatrix() * _dt * _dt; V.block<3, 3>(0, 9) = V.block<3, 3>(0, 3); V.block<3, 3>(3, 3) = 0.5 * MatrixXd::Identity(3,3) * _dt; V.block<3, 3>(3, 9) = 0.5 * MatrixXd::Identity(3,3) * _dt; V.block<3, 3>(6, 0) = 0.5 * delta_q.toRotationMatrix() * _dt; V.block<3, 3>(6, 3) = 0.5 * -result_delta_q.toRotationMatrix() * R_a_1_x * _dt * 0.5 * _dt; V.block<3, 3>(6, 6) = 0.5 * result_delta_q.toRotationMatrix() * _dt; V.block<3, 3>(6, 9) = V.block<3, 3>(6, 3); V.block<3, 3>(9, 12) = MatrixXd::Identity(3,3) * _dt; V.block<3, 3>(12, 15) = MatrixXd::Identity(3,3) * _dt; //step_jacobian = F; //step_V = V; jacobian = F * jacobian; covariance = F * covariance * F.transpose() + V * noise * V.transpose(); } }
(二)Vision
首先判断该帧是否关键帧:
if (f_manager.addFeatureCheckParallax(frame_count, image)) marginalization_flag = MARGIN_OLD; else marginalization_flag = MARGIN_SECOND_NEW;
关键帧的判断依据是rotation-compensated过后的parallax足够大,并且tracking上的feature足够多;关键帧会保留在当前Sliding Window中,marginalize掉Sliding Window中最旧的状态,如果是非关键帧则优先marginalize掉。
1. 标定外参旋转矩阵
initial_ex_rotation.CalibrationExRotation(corres, pre_integrations[frame_count]->delta_q, calib_ric)
其中
pre_integrations[frame_count]->delta_q
是使用imu pre-integration获取的旋转矩阵,会和视觉跟踪求解fundamentalMatrix分解后获得的旋转矩阵构建约束方程,从而标定出外参旋转矩阵。
2. 线性初始化
if (solver_flag == INITIAL) { if (frame_count == WINDOW_SIZE) { bool result = false; if( ESTIMATE_EXTRINSIC != 2 && (header.stamp.toSec() - initial_timestamp) > 0.1) { result = initialStructure(); initial_timestamp = header.stamp.toSec(); } if(result) { solver_flag = NON_LINEAR; solveOdometry(); slideWindow(); f_manager.removeFailures(); ROS_INFO("Initialization finish!"); last_R = Rs[WINDOW_SIZE]; last_P = Ps[WINDOW_SIZE]; last_R0 = Rs[0]; last_P0 = Ps[0]; } else slideWindow(); } else frame_count++; }
3. 非线性优化
else { TicToc t_solve; solveOdometry(); ROS_DEBUG("solver costs: %fms", t_solve.toc()); if (failureDetection()) { ROS_WARN("failure detection!"); failure_occur = 1; clearState(); setParameter(); ROS_WARN("system reboot!"); return; } TicToc t_margin; slideWindow(); f_manager.removeFailures(); ROS_DEBUG("marginalization costs: %fms", t_margin.toc()); // prepare output of VINS key_poses.clear(); for (int i = 0; i <= WINDOW_SIZE; i++) key_poses.push_back(Ps[i]); last_R = Rs[WINDOW_SIZE]; last_P = Ps[WINDOW_SIZE]; last_R0 = Rs[0]; last_P0 = Ps[0]; }
主要的初始化,非线性优化的api均在这里,因此放在后面去说明。




