❀ Spring5学习大总结
一、了解 Spring 基本介绍、主要思想 IoC/DI
1、了解 Spring 基本介绍
(1) Spring是什么?
Spring 是一个轻量级的 DI/IoC 和 AOP 容器的开源框架,致力于构建致力于构建轻量级的 JavaEE 应用,简化应用开发,本身涵盖了传统应用开发,还拓展到移动端,大数据等领域。
(2) Spring有什么优点?与作用?
① Spring 能帮我们低侵入/低耦合地根据配置文件 创建及组装对象之间的依赖关系。
② Spring 面向切面编程能帮助我们无耦合的实现日志记录,性能统计,安全控制等。
③ Spring 能非常简单的且强大的声明式事务管理(通过配置完成事务,不用修改代码)。
④ Spring 提供了与第三方数据访问框架(如 Hibernate、JPA)无缝集成,且自己也提供了一套 JDBC 模板来方便数据库访问。
⑤ Spring 提供与第三方 Web(如 Struts1/2、JSF)框架 无缝集成,且自己也提供了一套 Spring MVC 框架,来方便 Web 层搭建。
⑥ Spring 能方便的与如 Java Mail、任务调度、缓存框架等技术整合,降低开发难度。
2、主要思想 IoC/DI
✿ Spring 是一个DI容器或IoC容器(DI和IoC 思想差不多)。掌握着创建对象和构建对象之间的依赖的控制权。
● IoC:Inversion of Control(控制反转):
一种设计思想。 其本意是是将原本在程序中手动创建对象的控制权,交由 Spring 框架来管理。
● DI:Dependency Injection(依赖注入):
一种设计思想。具体是指 Spring 创建对象的过程中,将对象依赖属性(常量,对象,集合)通过配置设值给该对象。
二、掌握Spring 基本使用、Spring 获取bean对象的方式、Spring 标签 import的引入配置
1、掌握Spring 基本使用
(1) 依赖jar包:
- spring-beans.jar
- spring-core.jar
- commons-logging.jar
(2) 配置:
-
创建applicationContext.xml 配置文件:
-
配置的约束内容:
<!-- 配置的bean约束内容 --> <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"> <!-- 通过配置的bean元素,告诉Spring的IoC容器,需要管理哪一个类的对象 --> <bean id="hello" class="com.shan.hello.Hello"> <!-- 通过property子元素,设置管理对象的属性的值 --> <property name="password" value="123"/> <property name="username" value="shan"/> </bean> </beans>
(3) 使用:
@Test
void testIoC() throws Exception {
Hello hello = null;
//=========================
//1、加载配置文件:从classpath路径去寻找配置文件,创建资源对象
Resource resource = new ClassPathResource("applicationContext.xml");
//2、创建IoC容器:创建spring的工厂对象(IoC容器对象)
BeanFactory factory = new XmlBeanFactory(resource);
//3、从Ioc容器获取对象:从spring IoC 容器(就是factory 工厂对象)中获取指定名称的对象
hello = (Hello)factory.getBean("hello");
//=========================
hello.printUser();
}
■ 从例子,可以看出,spring不仅帮我们创建对象,还帮我们把对象需要的数据给设置进来(对象的属性依赖)
2、Spring 获取bean对象的方式
-
推荐使用:bean的名称+类型: T getBean(String name, Class
requiredType) 根据bean对象在容器中的 名称+类型 来获取 @Test void testIoC() throws Exception { Hello hello = null; //========================= //1、加载配置文件:从classpath路径去寻找配置文件,创建资源对象 Resource resource = new ClassPathResource("applicationContext.xml"); //2、创建IoC容器:创建spring的工厂对象(IoC容器对象) BeanFactory factory = new XmlBeanFactory(resource); //3、从Ioc容器获取对象:从spring IoC 容器(就是factory 工厂对象)中获取指定名称的对象 //方式(推荐): T getBean(String name, Class<T> requiredType) 根据bean对象在容器中的 名称+类型 来获取 hello = factory.getBean("hello", Hello.class); //========================= hello.printUser(); }
3、Spring 标签 import的引入配置
- 元素:<import resource="com/shan/hello.xml"/> 用于引入spring的配置文件,相当于js中的元素 <javaScript src=""/>
- 推荐resource路径加上
前缀 classpath - 默认情况下,resource 是从 classpath 的跟路径寻找,举例:<import resource="
classpath:com/shan/hello.xml"/>
三、Spring 核心对象 BeanFactory 和 Bean、Spring的配置方式、了解Spring管理bean的原理
1、Spring 核心对象 BeanFactory 和 Bean
-
BeanFactory:是Spring的IoC容器(
容器--管理对象的生命周期),生产 bean 对象的工厂,负责配置,创建和管理 bean。 -
bean:被 Spring IoC 容器管理的对象称之为bean。
2、Spring的配置方式
■ 元数据的配置有三种方式:
□ XML-based configuration (xml配置文件)
□ Annotation-based configuration (注解)
□ Java-based configuration (基于java-config)
3、了解Spring管理bean的原理
-
底层是:
反射(获取构造器实例对象)+内省机制(设置属性值)
① 通过 Resource 对象加载配置文件
② 解析配置文件,得到指定名称的 bean
③ 解析 bean 元素,id 作为 bean 的名字,class 用于反射得到 bean 的实例
- 注意:此时,bean 类必须存在一个
无参数构造器(且该无参构造器和访问权限无关);
④ 调用 getBean 方法的时候,从容器中返回对象实例;
■ 结论:就是把代码从 JAVA 文件中转移到了 XML 中。
四、使用Spring的测试框架
★相对于传统测试方式,spring测试框架会帮我们关闭对象资源,而使用传统方式,不会正常关闭spring容器。
1、依赖jar包:
- spring-test.jar
- spring-context.jar
- spring-aop.jar
- spring-expression.jar
2、配置文件:
■ SpringTestTest5-context.xml 文件(文件名必须是测试类-context,因为需要跟测试类名对应上):
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!-- 配置bean对象 -->
<bean id="someBean" class="com.shan.spring_test.SomeBean"/>
</beans>
3、测试类:
■ SpringTestTest5 类:
//SpringTest 案例测试
//运行 Spring JUnit5
@SpringJUnitConfig
public class SpringTestTest5 {
//表示自动按照类型 Spring容器中去找到bean对象,并设置给该字段
@Autowired
private SomeBean bean;
@Test
void testIoC() throws Exception {
bean.doWork();
}
}
五、Spring的核心 IoC(基于xml)
1、ApplicationContext 和 BeanFactory 创建对象的区别
-
BeanFactory 在创建Spring容器的时候,并不会立马创建容器中管理的Bean对象,需要等到获取某一个 bean 的时候才会创建该 bean--延迟初始化。(
懒加载) -
ApplicationContext 在启动 Spring 容器的时候就会创建所有的 bean(
在 Web 应用使用Application)
2、常用实例化bean的方式 和 实现FactoryBean接口实例化的方式
(1)实例化bean的方式:
-
构造器实例化(
bean 中有 无参数构造器),标准、常用。<!-- 配置bean对象 --> <bean id="someBean" class="com.shan.spring_test.SomeBean"/>
(2)实现FactoryBean接口实例化的方式:
-
类要实现接口FactoryBean:
public class DogFactory implements FactoryBean<Dog>{ @Override public Dog getObject() throws Exception { Dog dog = new Dog(); return dog; } @Override public Class<?> getObjectType() { return Dog.class; } }<!-- 实现 FactoryBean 接口实例化:实例工厂变种, 如集成 MyBatis 框架使用 --> <bean id="dog" class="com.shan._04_factory_bean.DogFactory"/>
3、 bean作用域scope、初始化init-method和销毁destroy-method
(1) bean作用域scope
缺省和常用的情况是单例 singleton
<bean id="" class="" scope="作用域"/>
-
单例和多例: singleton: 单例(默认的作用域) prototype: 多例
-
在web应用中(request、session、application)
-
globalSession: 一般用于 Porlet 应用环境 , 分布式系统存在全局 session 概念(单点登录)
-
websocket:将一个bean定义定义到WebSocket的生命周期
(2) bean初始化和销毁:
- 属性init-method="该类中初始化方法名" 和 属性destroy-method="该类中销毁方法名"
- 没有使用spring的测试框架的话,就不能正常关闭IoC容器,即销毁bean对象了(可以手动关闭)
<bean id="cat" class="com.shan.lifecycle.Cat" init-method="init" destroy-method="close"/>
六、Spring的核心 DI(基于xml):
1、xml配置注入属性值:
★ 配置与注入:
-
常量类型 配置value--->注入setter方法
-
对象类型 配置ref--->注入setter方法
-
集合类型 配置各自集合对应的元素
- ...--->注入setter方法
1、通过XML配置装配
(1)XML 自动装配(不推荐)通过bean元素的属性 autowire 自动装配
✿(2)setter注入 [ 属性注入(根据类型区分)]
■(
常用) 注入常量value<bean id="person" class="com.shan.di_setter.Person"> <property name="name" value="shan"/> <property name="age" value="22"/> <property name="salary" value="10000"/> </bean>■(
常用) 注入对象ref<bean id="cat" class="com.shan.di_setter2.Cat"> <property name="name" value="kity"/> </bean> <bean id="person" class="com.shan.di_setter2.Person"> <property name="name" value="shan"/> <property name="age" value="22"/> <property name="cat" ref="cat"/> </bean>■ 注入集合
、 - 、
、 <bean id="person" class="com.shan.di_setter3.Person"> <!-- set类型 --> <property name="set"> <set> <value>set1</value> <value>set2</value> </set> </property> <!-- list类型 --> <property name="list"> <list> <value>list1</value> </list> </property> <!-- array类型 --> <property name="array"> <array> <value>array1</value> </array> </property> <!-- map类型(字典类型) --> <property name="map"> <map> <entry key="key1" value="value1"/> </map> </property> <!-- properties类型(特殊的map类型【key和value都是字符串】) --> <property name="prop"> <value> p1=v1 p2=v2 </value> </property> </bean>
2、bean元素继承 (本质是xml配置内容的拷贝)
-
通过abstract属性进行抽取
-
通过parent属性进行引入

3、属性注入应用---配置数据库连接池
-
动态加载配置文件(db.properties---数据库连接的配置信息)
-
<context:property-placeholder/>
-
使用 ${} 动态引入属性值
(1) 配置数据库连接池
<!-- 配置数据库连接池 -->
<bean id="dataSource" class="com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource" init-method="init" destroy-method="close">
<property name="driverClassName" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"/>
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/springdemo?useSSL=false"/>
<property name="username" value="root"/>
<property name="password" value="admin"/>
<property name="initialSize" value="2"/>
</bean>
(2) db.properties---数据库连接的配置信息
(3) property place holder
● 要是使用标签Context,需要先引入Context的约束(在beans的基础进行修改即可):

● context:property-placeholder 属性占位符
<!-- 从classpath的根路径 加载db.properties -->
<context:property-placeholder location="classpath:db.properties"/>
● 使用 ${} 动态引入属性值
<!-- 配置数据库连接池 -->
<bean id="dataSource" class="com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource" init-method="init" destroy-method="close">
<property name="driverClassName" value="${jdbc.driverClassName}"/>
<property name="url" value="${jdbc.url}"/>
<property name="username" value="${jdbc.username}"/>
<property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}"/>
<property name="initialSize" value="${jdbc.initialSize}"/>
</bean>
七、Spring使用注解配置
1、注解三要素:注解本身、被贴、第三方程序(赋予注解的特殊功能)
★ 对于IoC注解、DI注解:他们的第三方程序是他们对应的解析器。
IoC注解:组件扫描器 <context:component-scan base-package=""/>
DI注解:注解配置 <context:annotation-config/>
2、DI 注解:@Autowired、@Resource、@Value
- value注解的威力:结合动态properties配置文件引入值变量 例如:@Value("${service.port}")
(1) 通过注解注入属性值
★ 配置与注入:
-
常量类型 配置value--->注入@Value
-
对象类型 配置ref--->注入@Autowired/@Resource
(2) IoC 注解:@Component、@Scope、@PostConstruct、@PreDestroy
★ 使用注解@Component(配置Bean)
//相当于 <bean id="dataSource" class="com.shan.ioc.MyDataSource"/>
@Component("dataSource")
public class MyDataSource {
}
★ bean组件版型:
@Component 泛指组件
@Repository 持久层
@Service 业务层
@Controller 控制层
★ 作用域注解、初始化和销毁注解:@Scope、@PostConstruct、@PreDestroy
八、Spring AOP
1、了解AOP思想[面向切面编程的思想]、AOP思想的原理
(1) 面向切面编程的思想:
利用一种称为"横切"的技术,剖开封装的对象内部,并将那些影响了多个类的公共行为封装到一个可重用模块,并将其命名为"Aspect",即切面。
-
切面:
把一个个的横切关注点放到某个模块中去,称之为切面。 -
那么每一个的切面都能影响业务的某一种功能,
切面的目的就是功能增强,如日志切面就是一个横切关注点,应用中许多方法需要做日志记录的只需要插入日志的切面即可.
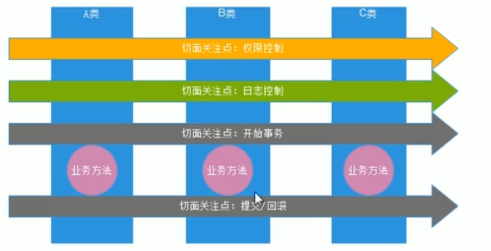
(2) AOP思想的原理:动态代理
2、Pointcot语法
- 找到具体的某个方法--
哪个包.哪个类.哪个方法
execution(<修饰符>? <返回类型> <声明类型>? <方法名>(<参数>) <异常>)
-
切入点表达式中的通配符(
看具体的方法,先从方法名位置开始看):*:匹配任何部分,但是只能表示一个单词。
..:可用于全限定名中和方法参数中,分别表示子包和 0 到 N 个参数。
3、AOP 开发:
(1) 依赖jar包:
- spring-aop.jar
- com.springsource.org.aopalliance.jar [spring5的spring-aop.jar已经包含]
- com.springsource.org.aspectj.weaver.jar
(2) 配置:
-
引入AOP的约束:

-
AOP的3W-what、where、when
<!-- AOP 配置:在什么地点、什么时机、做什么 -->
<!-- 1、what:做什么增强 -->
<bean id="transactionManager" class="com.shan.tx.TransactionManager"/>
<aop:config proxy-target-class="false"> <!-- 属性proxy-target-class配置是否使用真实对象 -->
<!-- 配置AOP切面 -->
<aop:aspect ref="transactionManager"> <!-- 关联what -->
<!-- 2、where:在哪些包中的哪些类中的哪些方法上做增强 -->
<aop:pointcut id="txPoint" expression="execution(* com.shan.service..*Service*.*(..))"/>
<!-- 3、when:在方法执行的什么时机做增强 --><!-- 关联where -->
<aop:before method="open" pointcut-ref="txPoint"/>
<aop:after-returning method="commit" pointcut-ref="txPoint"/>
<aop:after-throwing method="rollback" pointcut-ref="txPoint"/>
<aop:after method="close" pointcut-ref="txPoint"/>
<aop:around method="aroundMethod" pointcut-ref="txPoint"/>
</aop:aspect>
</aop:config>
4、AOP增强的分类
■ 根据被增强的方法的执行时机分为:前置增强、后置增强、异常增强、最终增强、环绕增强
- 前置增强:权限控制、日志记录等 [被增强的方法执行之前]
- 后置增强:提交事务、统计分析数据结果等 [被增强的方法正常执行之后(中途没有异常)]
- 最终增强:回滚事务、记录日志异常信息等 [被增强的方法出现异常]
- 最终增强:释放资源等 [finally最后操作]
- 环绕增强:缓存、性能日志、权限、事务管理等 [可以自定义在被增强方法的什么时机执行(返回一个Object,参数processdingJoinpoint)]
5、获取被增强方法的信息, 并且可以传递给增强方法【参数Joinpoint类】
-
Joinpoint类连接点,访问被增强方法的真实对象,代理对象,方法参数等 -
可以作为前置、后置、异常、最终增强方法的参数,
第一个参数//可以作为前置、后置、异常、最终增强方法的参数,**`第一个参数`** public void open(JoinPoint jp) { System.out.println("开启事务~"); System.out.println("代理对象:" +jp.getThis().getClass()); System.out.println("目标对象:" +jp.getTarget().getClass()); System.out.println("被增强方法的参数:" +Arrays.toString(jp.getArgs())); System.out.println("连接点方法的签名:" +jp.getSignature()); System.out.println("当前连接点的类型:" +jp.getKind()); }
5-2、环绕增强方法调用真实对象的方法【参数processdingJoinpoint】
-
参数processdingJoinpoint:是JointPoin 的子类,只能用于环绕增强,
作为第一个参数还可以调用真实对象中被增强的方法。
//调用真实对象的方法 ret = pjp.proceed();
public Object aroundMethod(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp) {
Object ret = null;
System.out.println("开启事务~");
try {
ret = pjp.proceed();//调用真实对象的方法
System.out.println("调用真实对象的方法...~");
System.out.println("提交事务~");
} catch (Throwable e) {
System.out.println("回滚事务~,错误信息:" + e.getMessage());
}finally {
System.out.println("关闭资源~");
}
return ret;
}
6、使用注解配置AOP
(1) AOP注解的解析器【第三方程序,赋予注解的特殊功能】:
- 使用cglib注解:配置属性proxy-target-class="true"
<!-- what -->
<bean id="txManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"></property>
</bean>
<!-- AOP注解的解析器 -->
<aop:aspectj-autoproxy/>
(2) 使用注解@Aspect(配置一个AOP切面)
- @Pointcut (
配置where) - @Before、@AfterReturning、@AfterThrowing、@After、@Around(
配置when)
@Component@Aspect //配置一个AOP切面
public class TransactionManager {
//where
//xml:<aop:pointcut id="txPoint" expression="execution(* com.shan.service..*Service*.*(..))"/>
@Pointcut("execution(* com.shan.service..*Service*.*(..))")
public void txPoint() {
}
//@Before("txPoint()")
public void open(JoinPoint jp) {
System.out.println("开启事务~");
}
//@AfterReturning("txPoint()")
public void commit() {
System.out.println("提交事务~");
}
//@AfterThrowing(value="txPoint()", throwing="ex")
public void rollback(Throwable ex) {
System.out.println("回滚事务~,异常信息:" +ex.getMessage());
}
//@After("txPoint()")
public void close() {
System.out.println("关闭资源~");
}
@Around("txPoint()")
public Object aroundMethod(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp) {
Object ret = null;
System.out.println("开启事务~");
try {
ret = pjp.proceed();//调用真实对象的方法
System.out.println("调用真实对象的方法...~");
System.out.println("提交事务~");
} catch (Throwable e) {
System.out.println("回滚事务~,错误信息:" + e.getMessage());
}finally {
System.out.println("关闭资源~");
}
return ret;
}
}
九、Spring DAO
1、模板类和基类:
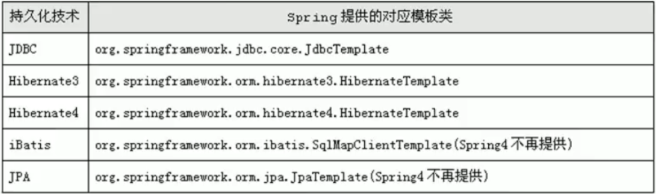

2、pring JDBC 【JDBCTemplate 模板类】
(1) 依赖jar包:
- mysql-connector-java.jar 【还可以使用德鲁伊连接池:druid.jar】
- spring-jdbc.jar
- spring-tx.jar
(2) 总结JdbcTemplate模板类-处理CRUD 操作
//DML操作:
public update(String sql, Object...args)
参数:sql ?占位符对应的参数
返回:受影响的行数
//DQL 操作:
public <T>List<T> query(String sql, Object...args, RowMapper<T> rowMapper)
参数:sql ?占位符对应的参数 结果集处理器
返回:多行结果集封装的list
3、模板类JdbcTemplate的问题与解决NameParameterJdbcTemplate
(1) 问题:
● 在模板类JdbcTemplate中使用的占位符 ?【顺序占位符】,需要数第几个,然后写对应的参数,参数多了麻烦
● 面对集合查询 in查询时(不确定参数个数), select * from employee where id in .....
- in 后边不知道该怎么写,是应该写一个?还是(多少个?,都是不确定的)
(2) 解决:使用NameParameterJdbcTemplate
-
命名的参数JdbcTemplate模板,其实就是在JdbcTemplate外面套一层。
-
允许使用 xx 来给占位参数起名称,我们需要给名称xx的位置设置参数。
□ 举例:
public int countOfActorsByFirstName(String firstName) {
String sql = "select count(*) from T_ACTOR where first_name = :first_name";
Map<String, String> namedParameters = Collections.singletonMap("first_name", firstName);
return this.namedParameterJdbcTemplate.queryForObject(sql, namedParameters, Integer.class);
}
十、Spring ORM --- 集成mybatis框架
十一、Spring tx
1、Spring 的事务管理主要包括 3 个 api:
- PlatformTransactionManager:根据 TransactionDefinition 提供的事务属性配置信息,
创建事务。 - TransactionDefinition:
封装事务的隔离级别和超时时间,是否为只读事务和事务的隔离级别和传播规则等事务属性. - TransactionStatus:
封装了事务的具体运行状态。如是否是新开启事务,是否已经提交事务,设置当前事务为rollback-only.
✿ 记:常用的事务管理器:
-
JDBC/MyBatis:DataSourceTransactionManager
-
Hibernate: HibernateTransactionManager
2、事务传播规则 TransactionDefinition 和 常用的情况
(1) 事务传播规则:
在一个事务方法中,调用了其他事务的方法,此时事务该如何传递,按照什么规则传播.
(2) 常用的情况:
■ 情况一:需要尊重/遵从当前事务
- REQUIRED:(
常用)必须存在一个事务,如果当前存在一个事务,则加入到该事务中,否则,新建一个事务.
■ 情况二:不遵从当前事务的
- REQUIRES_NEW:(
常用)不管当前是否存在事务,都会新开启一个事务.必须是一个新的事务.
■ 情况三:寄生事务(外部事务/内部事务/嵌套事务)
- NESTED:寄生事务,如果当前存在事务,则在内部事务内执行.如果当前不存在事务,则创建一个新的事务.
3、事务配置(基于xml和注解)
(1) 基于xml:事务增强—本质就是AOP增强what、when、where
<!-- ===============好比是AOP,事务增强================================== -->
<!-- 1、what:配置jdbc事务管理器 -->
<bean id="txManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/>
</bean>
<!-- 2:when:配置事务管理器增强(环绕增强) --><!-- 关联what -->
<tx:advice id="txAdvice" transaction-manager="txManager">
<tx:attributes>
<tx:method name="trans"/>
</tx:attributes>
</tx:advice>
<!-- 3、where:配置切面 --><!-- 关联when -->
<aop:config>
<aop:pointcut id="txPc" expression="execution(* com.shan.service.*Service.*(..))" />
<aop:advisor advice-ref="txAdvice" pointcut-ref="txPc"/>
</aop:config>
(2) 使用注解配置jdbc事务:tx注解解析器、@Transactional
-
注解:@Transactional
-
注解属性:name、propagation、isolation、timeout、read-only、rollback-for、no-rollback-for
■ 注解第三方解析:
<bean id="txManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager"> <property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"></property> </bean> <!-- tx注解解析器 --> <tx:annotation-driven transaction-manager="txManager"/>■ 注解@Transactional使用:
@Service@Transactional public class AccountServiceImpl implements IAccountService{ @Autowired private IAccountDAO dao; @Override public void trans(Long outId, Long inId, int money) { dao.transOut(outId, money); int a = 1/0; //算术异常 dao.transIn(inId, money); } //若是有查询方法,可以再贴注解@Transactional添加注解属性 @Transactional(readOnly = true) public void listXX() { } }
(3) 事务配置(基于注解+Java Config 配置)
-
注解:
配置
配置创建bean对象
IoC注解解析器
事务注解解析器
@Transactional 配置jdbc事务
@PropertySource 配置引入的属性文件资源
泛指组件
持久层
业务层
控制层
@Value 配置注入属性值
@Autowired 配置注入属性值
本文来自博客园,作者:一乐乐,转载请注明原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/shan333/p/15974254.html



【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· TypeScript + Deepseek 打造卜卦网站:技术与玄学的结合
· 阿里巴巴 QwQ-32B真的超越了 DeepSeek R-1吗?
· 【译】Visual Studio 中新的强大生产力特性
· 【设计模式】告别冗长if-else语句:使用策略模式优化代码结构
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语 ── 封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义