单链表的合并
要求:讲两个有序链表合并成一个有序链表,结果链表仍使用原来两个链表的存储空间,不占用其他存储空间,表中允许有重复的数据。
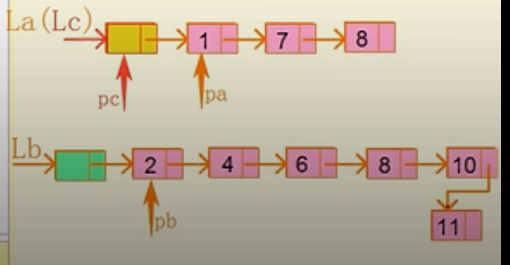
算法:(1)指针pa和pb初始化,分别指向连个链表La和Lb的第一个节点
(2)Lc的结点取值为La的头结点
(3)指针pc初始化,指向Lc的头结点
(4)当指针Pa和Pb均未达到相应表尾时,则依次比较pa和pb所指向元素大小,从La或Lb中取出较小的结点插入到c的最后
(5)将非空表的剩余段插入到pc所指结点之后,并释放Lb的头结点
如图:这是算法1-3步之后结果
程序:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#define OK 1
#define ERROR 0
#define OVERFLOW 0
typedef struct LNode{
int data;
struct LNode *next;
}LNode,*LinkList;
//建立一个空链表
int InitList_L(LinkList &L){
L=(LinkList)malloc(sizeof(LNode));
if(!L){
exit(OVERFLOW);
}
L->next=NULL;
return OK;
}
int CreateList_L(LinkList &L,int n){
LinkList p,q;
int i;
printf("Input the datas in increasing order:");
q=L;
for(i=0;i<n;i++){
p=(LinkList)malloc(sizeof(LNode));
scanf("%d",&p->data);
p->next=q->next;
// p->next=L->next;
q->next=p;
q=p;
}
return OK;
}
int MergeList_L(LinkList &La,LinkList &Lb,LinkList &Lc){
LinkList pa,pb,pc;
pa=La->next;//初始化pa的初值指向表La的第一个结点
pb=Lb->next;
Lc=pc=La;//用La的头结点作为Lc的头结点,pc的初值指向Lc的头结点
while(pa && pb){ //当两个表非空,依次取出两表中较小的结点插入到Lc表的最后
if(pa->data<=pb->data){
pc->next=pa;pc=pa;pa=pa->next;
}else{
pc->next=pb;pc=pb;pb=pb->next;
}
}
pc->next=pa?pa:pb;//插入剩余结点
free(Lb);
return OK;
}
int TraverseList_L(LinkList L){
LinkList p;
p=L->next;
while(p){
printf("%d",p->data);
p=p->next;
}
return OK;
}
main(){
int n;
LinkList La,Lb,Lc;
InitList_L(La);
InitList_L(Lb);
printf("Input the length of the list La:");
scanf("%d",&n);
CreateList_L(La,n);
printf("Input the length of the list Lb:");
scanf("%d",&n);
CreateList_L(Lb,n);
MergeList_L(La,Lb,Lc);
printf("Output the data in Lc:");
TraverseList_L(Lc);
printf("\n");
}
结果:
android@android-Latitude-E4300:~/work/c/danlianbiao$ ./mergelist
Input the length of the list La:3
Input the datas in increasing order:1 3 5
Input the length of the list Lb:4
Input the datas in increasing order:2 4 6 8
Output the data in Lc:1234568



