Linux Centos安装ElasticSearch、分词器、es-head和Kibana、ingest-attachment
1 前言
Java中比较流行的搜索引擎是Elasticsearch,传统的数据库搜索,使用like’关键字%’,当内容过多时性能会大大降低,所以Elasticsearch就出现了。
下面,记录下Linux下Elasticsearch的安装过程。
2 Linux下安装Elasticsearch
2.1 下载和解压安装包
官网下载地址: https://www.elastic.co/cn/downloads/elasticsearch
选择合适的版本下载,然后上传到Linux中
也可以在Linux命令行,直接执行以下命令进行下载(下载比较慢):
wget https://artifacts.elastic.co/downloads/elasticsearch/elasticsearch-7.13.2-linux-x86_64.tar.gz
执行解压缩命令:
tar -zxvf elasticsearch-7.13.2-linux-x86_64.tar.gz -C /usr/local
2.2 解决es强依赖jdk问题
由于es和jdk是一个强依赖的关系,所以当我们在新版本的ElasticSearch压缩包中包含有自带的jdk,但是当我们的Linux中已经安装了jdk之后,就会发现启动es的时候优先去找的是Linux中已经装好的jdk,此时如果jdk的版本不一致,就会造成jdk不能正常运行,报错如下:
注:如果Linux服务本来没有配置jdk,则会直接使用es目录下默认的jdk,反而不会报错
warning: usage of JAVA_HOME is deprecated, use ES_JAVA_HOME Future versions of Elasticsearch will require Java 11; your Java version from [/usr/local/jdk1.8.0_291/jre] does not meet this requirement. Consider switching to a distribution of Elasticsearch with a bundled JDK. If you are already using a distribution with a bundled JDK, ensure the JAVA_HOME environment variable is not set.
解决办法:
进入bin目录
cd /usr/local/elasticsearch-7.13.2/bin
修改elasticsearch配置
vim ./elasticsearch
############## 添加配置解决jdk版本问题 ############## # 将jdk修改为es中自带jdk的配置目录 export JAVA_HOME=/usr/local/elasticsearch-7.13.2/jdk export PATH=$JAVA_HOME/bin:$PATH if [ -x "$JAVA_HOME/bin/java" ]; then JAVA="/usr/local/elasticsearch-7.13.2/jdk/bin/java" else JAVA=`which java` fi
2.3 解决内存不足问题
由于 elasticsearch 默认分配 jvm空间大小为2g,修改 jvm空间,如果Linux服务器本来配置就很高,可以不用修改。
error: OpenJDK 64-Bit Server VM warning: INFO: os::commit_memory(0x00000000c6a00000, 962592768, 0) failed; error='Not enough space' (errno=12) at org.elasticsearch.tools.launchers.JvmOption.flagsFinal(JvmOption.java:119) at org.elasticsearch.tools.launchers.JvmOption.findFinalOptions(JvmOption.java:81) at org.elasticsearch.tools.launchers.JvmErgonomics.choose(JvmErgonomics.java:38) at org.elasticsearch.tools.launchers.JvmOptionsParser.jvmOptions(JvmOptionsParser.java:13
进入config文件夹开始配置,编辑jvm.options:
vim /usr/local/elasticsearch-7.13.2/config/jvm.options
默认配置如下:
-Xms2g
-Xmx2g
默认的配置占用内存太多了,调小一些:
-Xms256m
-Xmx256m
2.4 创建专用用户启动ES
root用户不能直接启动Elasticsearch,所以需要创建一个专用用户,来启动ES
java.lang.RuntimeException: can not run elasticsearch as root at org.elasticsearch.bootstrap.Bootstrap.initializeNatives(Bootstrap.java:101) at org.elasticsearch.bootstrap.Bootstrap.setup(Bootstrap.java:168) at org.elasticsearch.bootstrap.Bootstrap.init(Bootstrap.java:397) at org.elasticsearch.bootstrap.Elasticsearch.init(Elasticsearch.java:159) at org.elasticsearch.bootstrap.Elasticsearch.execute(Elasticsearch.java:150) at org.elasticsearch.cli.EnvironmentAwareCommand.execute(EnvironmentAwareCommand.java:75) at org.elasticsearch.cli.Command.mainWithoutErrorHandling(Command.java:116) at org.elasticsearch.cli.Command.main(Command.java:79) at org.elasticsearch.bootstrap.Elasticsearch.main(Elasticsearch.java:115) at org.elasticsearch.bootstrap.Elasticsearch.main(Elasticsearch.java:81)
创建用户
useradd user-es
创建所属组:
chown user-es:user-es -R /usr/local/elasticsearch-7.13.2
切换到user-es用户
su user-es
进入bin目录
cd /usr/local/elasticsearch-7.13.2/bin
启动elasticsearch
./elasticsearch
如果出现如下错误信息(最大文件数太小、线程太小、内存太低):
2.5 修改ES核心配置信息
执行命令修改elasticsearch.yml文件内容
vim /usr/local/elasticsearch-7.13.2/config/elasticsearch.yml
修改数据和日志目录
这里可以不用修改,如果不修改,默认放在elasticsearch根目录下
# 数据目录位置
path.data: /home/新用户名称/elasticsearch/data
# 日志目录位置
path.logs: /home/新用户名称/elasticsearch/logs
修改绑定的ip允许远程访问
#默认只允许本机访问,修改为0.0.0.0后则可以远程访问 # 绑定到0.0.0.0,允许任何ip来访问 network.host: 0.0.0.0
初始化节点名称
cluster.name: elasticsearch node.name: es-node0 cluster.initial_master_nodes: ["es-node0"]
修改端口号(非必须)
http.port: 19200
2.6 vm.max_map_count [65530] is too low问题
上面几个步骤依然没启动成功,继续解决问题:
ERROR: [1] bootstrap checks failed. You must address the points described in the following [1] lines before starting Elasticsearch. bootstrap check failure [1] of [1]: max virtual memory areas vm.max_map_count [65530] is too low, increase to at least [262144]
elasticsearch用户拥有的内存权限太小,至少需要262144,解决办法:
在 /etc/sysctl.conf 文件最后添加如下内容,即可永久修改
切换到root用户
执行命令:
su root
执行命令
vim /etc/sysctl.conf
添加如下内容
vm.max_map_count=262144
保存退出,刷新配置文件
sysctl -p
切换user-es用户,继续启动
su user-es
启动es服务
/usr/local/elasticsearch-7.13.2/bin/elasticsearch
启动成功后,可以通过http://127.0.0.1:19200/访问,如果出现以下内容,说明ES安装成功:
{ "name": "es-node0", "cluster_name": "elasticsearch", "cluster_uuid": "ROwqoHBNQmebLiJ6fhg9Bg", "version": { "number": "7.15.0", "build_flavor": "default", "build_type": "tar", "build_hash": "79d65f6e357953a5b3cbcc5e2c7c21073d89aa29", "build_date": "2021-09-16T03:05:29.143308416Z", "build_snapshot": false, "lucene_version": "8.9.0", "minimum_wire_compatibility_version": "6.8.0", "minimum_index_compatibility_version": "6.0.0-beta1" }, "tagline": "You Know, for Search" }
2.7 可能遇到的max file descriptors [4096]问题
[1]: max file descriptors [4096] for elasticsearch process is too low, increase to at least [65535]
切换到root用户,执行命令:
vi /etc/security/limits.conf
添加如下内容:
* soft nofile 65536 * hard nofile 131072 * soft nproc 2048 * hard nproc 4096
然后重启linux
2.8 ES服务的启动与停止
前台运行,Ctrl + C 则程序终止
/usr/local/elasticsearch-7.13.2/bin/elasticsearch
后台运行
/usr/local/elasticsearch-7.13.2/bin/elasticsearch -d
出现started时启动完成
关闭ES服务
kill pid
说明:
Elasticsearch端口9300、9200,其中:
9300是tcp通讯端口,集群ES节点之间通讯使用,9200是http协议的RESTful接口
2.9 为Elasticsearch设置登录密码
ES7.x以后的版本将安全认证功能免费开放了,并将X-pack插件集成了到了开源的ElasticSearch版本中。下面将介绍如何利用X-pack给ElasticSearch相关组件设置用户名和密码。
编辑配置文件
vim /usr/local/elasticsearch-7.13.2/config/elasticsearch.yml
在 elasticsearch.yml 末尾,加入以下内容:
xpack.security.enabled: true xpack.security.transport.ssl.enabled: true
编辑内容后重启Elasticsearch服务(必须操作)
设置用户名和密码
/usr/local/elasticsearch-7.13.2/bin/elasticsearch-setup-passwords interactive
这里依次设置elastic、kibana、logstash等的访问密码,test123

设置了访问密码,再次访问ES时,需要输入密码

好啦,单机版Elasticsearch服务终于安装好了,还是有点麻烦哦~
elasticsearch.yml配置全览
# ======================== Elasticsearch Configuration ========================= # # NOTE: Elasticsearch comes with reasonable defaults for most settings. # Before you set out to tweak and tune the configuration, make sure you # understand what are you trying to accomplish and the consequences. # # The primary way of configuring a node is via this file. This template lists # the most important settings you may want to configure for a production cluster. # # Please consult the documentation for further information on configuration options: # https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/index.html # # ---------------------------------- Cluster ----------------------------------- # # Use a descriptive name for your cluster: # #cluster.name: my-application # # ------------------------------------ Node ------------------------------------ # # Use a descriptive name for the node: # #node.name: node-1 # # Add custom attributes to the node: # #node.attr.rack: r1 # # ----------------------------------- Paths ------------------------------------ # # Path to directory where to store the data (separate multiple locations by comma): # #path.data: /path/to/data # # Path to log files: # #path.logs: /path/to/logs # # ----------------------------------- Memory ----------------------------------- # # Lock the memory on startup: # #bootstrap.memory_lock: true # # Make sure that the heap size is set to about half the memory available # on the system and that the owner of the process is allowed to use this # limit. # # Elasticsearch performs poorly when the system is swapping the memory. # # ---------------------------------- Network ----------------------------------- # # By default Elasticsearch is only accessible on localhost. Set a different # address here to expose this node on the network: # #network.host: 192.168.0.1 network.host: 0.0.0.0 # # By default Elasticsearch listens for HTTP traffic on the first free port it # finds starting at 9200. Set a specific HTTP port here: # http.port: 9200 # # For more information, consult the network module documentation. # # --------------------------------- Discovery ---------------------------------- # cluster.name: elasticsearch node.name: es-node0 cluster.initial_master_nodes: ["es-node0"] # Pass an initial list of hosts to perform discovery when this node is started: # The default list of hosts is ["127.0.0.1", "[::1]"] # #discovery.seed_hosts: ["host1", "host2"] # # Bootstrap the cluster using an initial set of master-eligible nodes: # #cluster.initial_master_nodes: ["node-1", "node-2"] # # For more information, consult the discovery and cluster formation module documentation. # # ---------------------------------- Various ----------------------------------- # # Require explicit names when deleting indices: # #action.destructive_requires_name: true ingest.geoip.downloader.enabled: false xpack.security.enabled: true xpack.security.transport.ssl.enabled: true http.cors.enabled: true http.cors.allow-origin: "*" http.cors.allow-headers: Authorization,X-Requested-With,Content-Type,Content-Length
3 安装elasticsearch-head插件
ealsticsearch只是后端提供各种resulful api,那么怎么直观的看它的信息呢?
elasticsearch-head是一款专门针对于elasticsearch的客户端工具,用来展示数据。
elasticsearch-head是基于JavaScript语言编写的,可以使用npm部署
npm是Nodejs下的包管理器。
3.1 安装node环境
如果Linux服务已经安装过node环境,这个步骤可以跳过,没有node环境的,可以安装node环境,参考《Linux系统安装Nodejs的详细教程 - 夏威夷8080 - 博客园》。
npm环境准备好了之后,开始安装elasticsearch-head
3.2 安装elasticsearch-head
3.2.1 下载elasticsearch-head安装包
下载地址: https://github.com/mobz/elasticsearch-head

3.2.2 解压zip包
执行命令:
unzip elasticsearch-head-5.0.0.zip
把安装包移动到/usr/local下:
mv elasticsearch-head-5.0.0 /usr/local/
3.2.3 npm install
进入安装目录
cd /usr/local/elasticsearch-head-5.0.0
执行命令安装
npm install
注:如果执行失败,可以cnpm install,使用cnpm之前需要安装cnpm,通过如下命令安装
npm install -g cnpm --registry=https://registry.npm.taobao.org
显示所有使用帮助信息
npm -l
每个项目的根目录下面,一般都有一个package.json文件,定义了这个项目所需要的各种模块,以及项目的配置信息(比如名称、版本、许可证等元数据)
npm install命令根据这个配置文件,自动下载所需的模块,也就是配置项目所需的运行和开发环境。
3.2.4 启动elasticsearch-head服务
启动服务
npm run start 或者 npm run-script start
可以后台启动
nohup npm run-script start &
出现下图,说明启动elasticsearch-head服务成功:

3.2.5 访问elasticsearch-head服务
然后访问: http://localhost:9100/
elasticsearch-head服务访问成功:

3.2.6 使用Head插件访问elasticsearch
访问失败,要允许跨域,需要修改elasticsearch.yml文件,添加如下内容:
http.cors.enabled: true http.cors.allow-origin: "*"
出现以下界面,说明访问成功:

3.2.7 ES开启安全密码认证后,es-head连接方式
在web界面访问时,该框由原来的 http://172.16.3.227:9100替换为 http://172.16.3.227:9100/?auth_user=elastic&auth_password=123456

4. ES ik分词器的下载和安装,测试
之前我们创建索引,查询数据,都是使用的默认的分词器,分词效果不太理想,会把text的字段分成一个一个汉字,然后搜索的时候也会把搜索的句子进行分词,所以这里就需要更加智能的分词器IK分词器了。
4.1 下载ik分词器
下载地址:https://github.com/medcl/elasticsearch-analysis-ik/releases ,这里你需要根据你的Es的版本来下载对应版本的IK,这里我使用的是6.3.2的ES,所以就下载ik-6.3.2.zip的文件。

4.2 解压
在es的安装目录/plugin/下创建ik目录,然后将文件复制到 ik下面即可,完成之后效果如下:

到这里已经完成了,不需要去elasticSearch的 elasticsearch.yml 文件去配置。
4.3 重启ElasticSearch
4.4 测试效果
#插入测试数据 PUT book/analyze/1 { "text": "我是中国人" } 未使用ik分词器的时候测试分词效果: POST book/_analyze { "text": "我是中国人" } //结果是: { "tokens": [ { "token": "我", "start_offset": 0, "end_offset": 1, "type": "<IDEOGRAPHIC>", "position": 0 }, { "token": "是", "start_offset": 1, "end_offset": 2, "type": "<IDEOGRAPHIC>", "position": 1 }, { "token": "中", "start_offset": 2, "end_offset": 3, "type": "<IDEOGRAPHIC>", "position": 2 }, { "token": "国", "start_offset": 3, "end_offset": 4, "type": "<IDEOGRAPHIC>", "position": 3 }, { "token": "人", "start_offset": 4, "end_offset": 5, "type": "<IDEOGRAPHIC>", "position": 4 } ] }
使用IK分词器之后,结果如下:
POST book_v6/_analyze { "analyzer": "ik_max_word", "text": "我是中国人" } //结果如下: { "tokens": [ { "token": "我", "start_offset": 0, "end_offset": 1, "type": "CN_CHAR", "position": 0 }, { "token": "是", "start_offset": 1, "end_offset": 2, "type": "CN_CHAR", "position": 1 }, { "token": "中国人", "start_offset": 2, "end_offset": 5, "type": "CN_WORD", "position": 2 }, { "token": "中国", "start_offset": 2, "end_offset": 4, "type": "CN_WORD", "position": 3 }, { "token": "国人", "start_offset": 3, "end_offset": 5, "type": "CN_WORD", "position": 4 } ] }
对于上面两个分词效果的解释:
1. 如果未安装ik分词器,那么,你如果写 "analyzer": "ik_max_word",那么程序就会报错,因为你没有安装ik分词器
2. 如果你安装了ik分词器之后,你不指定分词器,不加上 "analyzer": "ik_max_word" 这句话,那么其分词效果跟你没有安装ik分词器是一致的,也是分词成每个汉字。
4.5 创建指定分词器的索引
索引创建之后就可以使用ik进行分词了,当你使用ES搜索的时候也会使用ik对搜索语句进行分词,进行匹配。
PUT book_v5 { "settings":{ "number_of_shards": "6", "number_of_replicas": "1", //指定分词器 "analysis":{ "analyzer":{ "ik":{ "tokenizer":"ik_max_word" } } } }, "mappings":{ "novel":{ "properties":{ "author":{ "type":"text" }, "wordCount":{ "type":"integer" }, "publishDate":{ "type":"date", "format":"yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss || yyyy-MM-dd" }, "briefIntroduction":{ "type":"text" }, "bookName":{ "type":"text" } } } } }
关于ik分词器的分词类型(可以根据需求进行选择):
ik_max_word:会将文本做最细粒度的拆分,比如会将“中华人民共和国国歌”拆分为“中华人民共和国,中华人民,中华,华人,人民共和国,人民,人,民,共和国,共和,和,国国,国歌”,会穷尽各种可能的组合;
ik_smart:会做最粗粒度的拆分,比如会将“中华人民共和国国歌”拆分为“中华人民共和国,国歌”。如下:
POST book_v6/_analyze { "analyzer": "ik_smart", "text": "我是中国人" } //结果 { "tokens": [ { "token": "我", "start_offset": 0, "end_offset": 1, "type": "CN_CHAR", "position": 0 }, { "token": "是", "start_offset": 1, "end_offset": 2, "type": "CN_CHAR", "position": 1 }, { "token": "中国人", "start_offset": 2, "end_offset": 5, "type": "CN_WORD", "position": 2 } ] }
5 安装Kibana
Kibana是一个基于Node.js的Elasticsearch索引库数据统计工具,可以利用Elasticsearch的聚合功能,生成各种图表,如柱形图,线状图,饼图等。而且还提供了操作Elasticsearch索引数据的控制台,并且提供了一定的API提示,非常有利于我们学习Elasticsearch的语法。
5.1 下载Kibana
需要选择和es版本一致的版本的kibana下载,下载地址:https://www.elastic.co/downloads/past-releases#kibana

5.2 解压
tar -zxvf kibana-7.17.3-linux-x86_64.tar.gz -C /usr/local
5.3 修改配置文件
cd /usr/local/ vi kibana-7.17.3/config/kibana.yml
配置参数如下:
#配置端口号 server.port: 5601 #配置网络访问地址 server.host: "0.0.0.0" server.publicBaseUrl: "http://116.205.230.143:5601" #配置es链接地址(es集群,可以用逗号分隔) elasticsearch.hosts: ["http://116.205.230.143:9200"] #配置中文语言界面 i18n.locale: "zh-CN"
5.4 分配普通用户权限
注意:必须使用普通用户启动服务,Kibana如果用root用户启动也会报错跟ElasticSearch一样,需要换成非root用户启动。这里把权限加上即可
chown -R elasticsearch:elasticsearch /usr/local/kibana-7.17.3-linux-x86_64/
5.5 启动kibana
#切换用户 su elasticsearch #进入bin目录 cd /usr/local/kibana-7.17.3-linux-x86_64/bin/ #直接启动 ./kibana #后台启动 nohup ./kibana & nohup ./kibana > kibana.log 2>&1 & #允许root用户去启动,没试过这个命令不知道行不行 ./kibana --allow-root
注意:防火墙开启5601端口
5.6 kibana关闭
在使用ps命令ps -ef|grep kibana 和 ps -ef|grep 5601 查看进程的时候都找不到。所以我们可以尝试 使用下面的命令找到kibana进程:
fuser -n tcp 5601 kill -9 端口 # 或者下面的命令 ps -ef | grep node netstat -anltp | grep 5601 netstat -tunlp | grep 5601
启动后的效果:



警告1:
#! Elasticsearch built-in security features are not enabled. Without authentication, your cluster could be accessible to anyone. See https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/7.17/security-minimal-setup.html to enable security. 意思是未启用 Elasticsearch 内置的安全功能,即没有开启身份验证的功能。 如果没有身份验证,任何人都可以访问您的集群。下面会详细介绍开启 Elasticsearch 自带的身份验证功能,如果你不想看到报错警告则在ES的elasticsearch.yml加入这个参数:xpack.security.enabled: false
警告2:
#! this request accesses system indices: [.apm-agent-configuration, .apm-custom-link, .kibana_7.17.3_001, .kibana_task_manager_7.17.3_001, .tasks], but in a future major version, direct access to system indices will be prevented by default 说我们访问了系统索引,所以我们尽量别访问系统的索引,从上面响应的时间来看,响应的36699ms,太久了。在后面ES的主要版本中,会默认禁止直接访问系统索引。只要我们不访问系统索引应该就不会出现这个警告。

5.7 Kibana 配置 xpack
截止到目前Elasticsearch的部分已经修改完毕,下面修改kibana配置以便于让其和Elasticsearch完成连接。
修改kibana的配置文件config/kibana.yml:
cd /usr/local/kibana-7.17.3-linux-x86_64/ vi config/kibana.yml
在配置文件中添加下面内容:
elasticsearch.username: "kibana" elasticsearch.password: "之前设置的密码"
重启Kibana
注:kibana 使用ps -ef|grep kibana是查不到进程的,因为其实运行在node里面。但是我们也不能关闭所有node里面的软件,所以我们需要查询kibana监听端口5601的进程。使用下面命令关闭kibana
fuser -n tcp 5601 kill -9 端口 # 或者下面的命令 ps -ef | grep node netstat -anltp | grep 5601 netstat -tunlp | grep 5601
然后重启Kibana
#切换用户 su elasticsearch #进入bin目录 cd /usr/local/kibana-7.17.3-linux-x86_64/bin/ #直接启动 ./kibana #后台启动 nohup ./kibana & nohup ./kibana > kibana.log 2>&1 &
此时访问kibana(http://localhost:5601)会提示需要输入账号密码。注意此时需要输入的是elastic的用户密码。

5.8 kibana.yml配置全览
# Kibana is served by a back end server. This setting specifies the port to use. server.port: 5601 # Specifies the address to which the Kibana server will bind. IP addresses and host names are both valid values. # The default is 'localhost', which usually means remote machines will not be able to connect. # To allow connections from remote users, set this parameter to a non-loopback address. server.host: "0.0.0.0" # Enables you to specify a path to mount Kibana at if you are running behind a proxy. # Use the `server.rewriteBasePath` setting to tell Kibana if it should remove the basePath # from requests it receives, and to prevent a deprecation warning at startup. # This setting cannot end in a slash. #server.basePath: "" # Specifies whether Kibana should rewrite requests that are prefixed with # `server.basePath` or require that they are rewritten by your reverse proxy. # This setting was effectively always `false` before Kibana 6.3 and will # default to `true` starting in Kibana 7.0. #server.rewriteBasePath: false # Specifies the public URL at which Kibana is available for end users. If # `server.basePath` is configured this URL should end with the same basePath. server.publicBaseUrl: "http://203.34.56.93:5601" # The maximum payload size in bytes for incoming server requests. #server.maxPayload: 1048576 # The Kibana server's name. This is used for display purposes. #server.name: "your-hostname" # The URLs of the Elasticsearch instances to use for all your queries. elasticsearch.hosts: ["http://203.34.56.93:9200"] # Kibana uses an index in Elasticsearch to store saved searches, visualizations and # dashboards. Kibana creates a new index if the index doesn't already exist. #kibana.index: ".kibana" # The default application to load. #kibana.defaultAppId: "home" # If your Elasticsearch is protected with basic authentication, these settings provide # the username and password that the Kibana server uses to perform maintenance on the Kibana # index at startup. Your Kibana users still need to authenticate with Elasticsearch, which # is proxied through the Kibana server. elasticsearch.username: "elastic" elasticsearch.password: "test123" # Kibana can also authenticate to Elasticsearch via "service account tokens". # If may use this token instead of a username/password. # elasticsearch.serviceAccountToken: "my_token" # Enables SSL and paths to the PEM-format SSL certificate and SSL key files, respectively. # These settings enable SSL for outgoing requests from the Kibana server to the browser. #server.ssl.enabled: false #server.ssl.certificate: /path/to/your/server.crt #server.ssl.key: /path/to/your/server.key # Optional settings that provide the paths to the PEM-format SSL certificate and key files. # These files are used to verify the identity of Kibana to Elasticsearch and are required when # xpack.security.http.ssl.client_authentication in Elasticsearch is set to required. #elasticsearch.ssl.certificate: /path/to/your/client.crt #elasticsearch.ssl.key: /path/to/your/client.key # Optional setting that enables you to specify a path to the PEM file for the certificate # authority for your Elasticsearch instance. #elasticsearch.ssl.certificateAuthorities: [ "/path/to/your/CA.pem" ] # To disregard the validity of SSL certificates, change this setting's value to 'none'. #elasticsearch.ssl.verificationMode: full # Time in milliseconds to wait for Elasticsearch to respond to pings. Defaults to the value of # the elasticsearch.requestTimeout setting. #elasticsearch.pingTimeout: 1500 # Time in milliseconds to wait for responses from the back end or Elasticsearch. This value # must be a positive integer. #elasticsearch.requestTimeout: 30000 # List of Kibana client-side headers to send to Elasticsearch. To send *no* client-side # headers, set this value to [] (an empty list). #elasticsearch.requestHeadersWhitelist: [ authorization ] # Header names and values that are sent to Elasticsearch. Any custom headers cannot be overwritten # by client-side headers, regardless of the elasticsearch.requestHeadersWhitelist configuration. #elasticsearch.customHeaders: {} # Time in milliseconds for Elasticsearch to wait for responses from shards. Set to 0 to disable. #elasticsearch.shardTimeout: 30000 # Logs queries sent to Elasticsearch. Requires logging.verbose set to true. #elasticsearch.logQueries: false # Specifies the path where Kibana creates the process ID file. #pid.file: /run/kibana/kibana.pid # Enables you to specify a file where Kibana stores log output. #logging.dest: stdout # Set the value of this setting to true to suppress all logging output. #logging.silent: false # Set the value of this setting to true to suppress all logging output other than error messages. #logging.quiet: false # Set the value of this setting to true to log all events, including system usage information # and all requests. #logging.verbose: false # Set the interval in milliseconds to sample system and process performance # metrics. Minimum is 100ms. Defaults to 5000. #ops.interval: 5000 # Specifies locale to be used for all localizable strings, dates and number formats. # Supported languages are the following: English - en , by default , Chinese - zh-CN . i18n.locale: "zh-CN"
6 所有安装包

有需要的可以留言联系我索取安装包,我都放到我的阿里网盘里了。
7 安全组开放的端口

8 Java restful方式操作es
import com.alibaba.fastjson2.JSONArray; import com.alibaba.fastjson2.JSONObject; import com.google.gson.Gson; import com.google.gson.GsonBuilder; import com.google.gson.JsonObject; import com.google.gson.JsonParser; import org.apache.http.HttpEntity; import org.apache.http.HttpResponse; import org.apache.http.auth.AuthScope; import org.apache.http.auth.UsernamePasswordCredentials; import org.apache.http.client.CredentialsProvider; import org.apache.http.client.methods.*; import org.apache.http.entity.ContentType; import org.apache.http.entity.StringEntity; import org.apache.http.impl.client.BasicCredentialsProvider; import org.apache.http.impl.client.CloseableHttpClient; import org.apache.http.impl.client.HttpClients; import org.apache.http.util.EntityUtils; import java.io.IOException; public class ElasticsearchClient { private static final String ES_BASE_URL = "http://127.0.0.1:9200"; // 替换为你的Elasticsearch URL private static final String USERNAME = "elastic"; // 替换为你的Elasticsearch用户名 private static final String PASSWORD = "test123"; // 替换为你的Elasticsearch密码 private final CloseableHttpClient httpClient; public ElasticsearchClient() { CredentialsProvider credsProvider = new BasicCredentialsProvider(); credsProvider.setCredentials(AuthScope.ANY, new UsernamePasswordCredentials(USERNAME, PASSWORD)); this.httpClient = HttpClients.custom() .setDefaultCredentialsProvider(credsProvider) .build(); } // 判断索引是否存在 public boolean existsIndex(String indexName) throws IOException { boolean flag = false; HttpGet request = new HttpGet(ES_BASE_URL + "/" + indexName); request.addHeader("Accept", "application/json"); HttpResponse response = httpClient.execute(request); int statusCode = response.getStatusLine().getStatusCode(); if (statusCode == 200) { // 索引存在,但这里我们其实不需要解析响应体来确认索引名,因为URL已经指定了 // 如果需要确认索引的详细信息,可以解析响应体 System.out.println("索引 '"+indexName+"' 存在。"); flag = true; } else if (statusCode == 404) { // 索引不存在 System.out.println("索引 '"+indexName+"' 不存在。"); } else if (statusCode == 401) { // 身份验证失败 System.out.println("身份验证失败,请检查用户名和密码。"); } else { // 其他错误 System.out.println("请求失败,状态码: " + statusCode); } return flag; } // 添加索引 public void createIndex(String indexName, JsonObject mappings) throws IOException { HttpPut request = new HttpPut(ES_BASE_URL + "/" + indexName); request.addHeader("Content-Type", "application/json"); request.setEntity(new StringEntity(mappings.toString())); HttpResponse response = httpClient.execute(request); int statusCode = response.getStatusLine().getStatusCode(); if (statusCode != 200) { throw new RuntimeException("创建索引失败,状态码: " + statusCode); } } // 删除索引 public void deleteIndex(String indexName) throws IOException { HttpDelete request = new HttpDelete(ES_BASE_URL + "/" + indexName); HttpResponse response = httpClient.execute(request); int statusCode = response.getStatusLine().getStatusCode(); if (statusCode != 200 && statusCode != 204) { // 204 No Content 也是可能的成功响应 throw new RuntimeException("删除索引失败,状态码: " + statusCode); } } // 更新索引映射(通过重新索引实现) // 注意:这不是一个真正的“更新映射”操作,因为Elasticsearch不允许在现有索引上更改映射类型。 // 这里的方法是为了说明目的而提供的,你可能需要实现自己的重新索引逻辑。 public void updateIndexMapping(String indexName, JsonObject newMapping) throws IOException { // 通常,这意味着你需要创建一个新索引,将数据从旧索引重新索引到新索引,然后删除旧索引。 // 这里只是一个占位符方法。 throw new UnsupportedOperationException("Elasticsearch不支持直接更新索引映射。"); } // 插入文档数据 // public void indexDocument(String indexName, String documentId, JsonObject document) throws IOException { // HttpPost request = new HttpPost(ES_BASE_URL + "/" + indexName + "/" + "_doc/" + documentId); public void indexDocument(String indexName, JsonObject document) throws IOException { HttpPost request = new HttpPost(ES_BASE_URL + "/" + indexName + "/" + "_doc"); request.addHeader("Content-Type", "application/json;charset=UTF-8"); request.setEntity(new StringEntity(document.toString(), ContentType.APPLICATION_JSON.withCharset("UTF-8"))); HttpResponse response = httpClient.execute(request); int statusCode = response.getStatusLine().getStatusCode(); if (statusCode != 200 && statusCode != 201) { // 201 Created 也是可能的成功响应 throw new RuntimeException("插入文档失败,状态码: " + statusCode); } } // 修改文档数据(通过重新索引实现) /*public void updateDocument(String indexName, String documentId, JsonObject newDocument) throws IOException { // 在Elasticsearch中,更新文档实际上是通过删除旧文档并索引新文档来实现的。 indexDocument(indexName, documentId, newDocument); // 使用相同的documentId来“覆盖”旧文档 }*/ // 查询文档数据 public JsonObject getDocument(String indexName, String documentId) throws IOException { HttpGet request = new HttpGet(ES_BASE_URL + "/" + indexName + "/" + "_doc/" + documentId); HttpResponse response = httpClient.execute(request); int statusCode = response.getStatusLine().getStatusCode(); if (statusCode == 200) { HttpEntity entity = response.getEntity(); String jsonResponse = EntityUtils.toString(entity); return JsonParser.parseString(jsonResponse).getAsJsonObject(); } else { throw new RuntimeException("查询文档失败,状态码: " + statusCode); } } // 删除文档数据 public void deleteDocument(String indexName, String documentId) throws IOException { HttpDelete request = new HttpDelete(ES_BASE_URL + "/" + indexName + "/" + "_doc/" + documentId); HttpResponse response = httpClient.execute(request); int statusCode = response.getStatusLine().getStatusCode(); if (statusCode != 200 && statusCode != 204) { // 204 No Content 也是可能的成功响应 throw new RuntimeException("删除文档失败,状态码: " + statusCode); } } // 多条件查询文档 public String searchDocuments(String indexName, JsonObject document) throws IOException { HttpPost request = new HttpPost(ES_BASE_URL + "/" + indexName + "/_search"); request.addHeader("Content-Type", "application/json"); // 将查询体设置为请求实体 request.setEntity(new StringEntity(document.toString(), ContentType.APPLICATION_JSON.withCharset("UTF-8"))); // 执行请求并获取响应 HttpResponse response = httpClient.execute(request); int statusCode = response.getStatusLine().getStatusCode(); if (statusCode != 200 && statusCode != 204) { // 204 No Content 也是可能的成功响应 throw new RuntimeException("搜索文档失败,状态码: " + statusCode); } HttpEntity responseEntity = response.getEntity(); String responseBody = EntityUtils.toString(responseEntity, "UTF-8"); return responseBody; // 返回响应体(通常是JSON格式的查询结果) } // 关闭HttpClient public void close() throws IOException { httpClient.close(); } public static void main(String[] args) { ElasticsearchClient client = new ElasticsearchClient(); try { // 判断索引是否存在 // boolean rs = client.existsIndex("jinhang"); // 删除索引 // client.deleteIndex("linhang"); // 示例:创建一个索引 // ... 设置mappings内容 ... String mapping = "" + "{ \n" + " \"mappings\": { \n" + " \"properties\": { \n" + " \"code\": { \n" + " \"type\": \"keyword\" \n" + " }, \n" + " \"title\": { \n" + " \"type\": \"text\", \n" + " \"analyzer\": \"standard\" \n" + " }, \n" + " \"orgName\": { \n" + " \"type\": \"text\", \n" + " \"analyzer\": \"standard\" \n" + " }, \n" + " \"publishDate\": { \n" + " \"type\": \"date\", \n" + " \"format\": \"yyyy-MM-dd'T'HH:mm:ss.SSSZ||yyyy-MM-dd'T'HH:mm:ss||epoch_millis\" \n" + " }, \n" + " \"publisUserName\": { \n" + " \"type\": \"text\", \n" + " \"analyzer\": \"standard\" \n" + " }, \n" + " \"publisUserId\": { \n" + " \"type\": \"keyword\" \n" + " }, \n" + " \"documentContent\": { \n" + " \"type\": \"text\", \n" + " \"analyzer\": \"standard\" \n" + " }, \n" + " \"type\": { \n" + " \"type\": \"keyword\" \n" + " }, \n" + " \"remark\": { \n" + " \"type\": \"text\", \n" + " \"analyzer\": \"standard\" \n" + " } \n" + " } \n" + " } \n" + "}"; JsonObject mappings = JsonParser.parseString(mapping).getAsJsonObject(); // client.createIndex("linhang", mappings); // 示例:插入一个文档 String doc = "{\n" + " \"code\": \"ABC456\",\n" + " \"title\": \"示例文档标题3\",\n" + " \"orgName\": \"示例组织3\",\n" + " \"publishDate\": \"2023-10-05T14:48:10.000Z\",\n" + " \"publisUserName\": \"发布者姓名2\",\n" + " \"publisUserId\": \"user456\",\n" + " \"documentContent\": \"这是文档的详细内容,可以包含任何文本信息3。\",\n" + " \"type\": \"涉密文档\",\n" + " \"remark\": \"这是一些备注信息3\"\n" + "}"; JsonObject document = JsonParser.parseString(doc).getAsJsonObject(); // ... 设置document内容 ... // client.indexDocument("linhang", document); // 删除一个文档 // client.deleteDocument("linhang", "x5025pIBGS6xF5FxLf5t"); // 示例:查询一个文档 // JsonObject retrievedDocument = client.getDocument("linhang", "x5025pIBGS6xF5FxLf5t"); // System.out.println(retrievedDocument); // 搜索文档 String param = "{\n" + " \"query\": {\n" + " \"bool\": {\n" + " \"must\": [\n" + " {\n" + " \"range\": {\n" + " \"publishDate\": {\n" + " \"gte\": \"2020-10-05T14:48:00.000Z\",\n" + " \"lte\": \"2029-10-05T14:48:00.000Z\"\n" + " }\n" + " }\n" + " }\n" + " ]\n" + " }\n" + " }\n" + "}"; JsonObject paramObj = JsonParser.parseString(param).getAsJsonObject(); String rs = client.searchDocuments("linhang", paramObj); System.out.println("搜索的结果:"+rs); // 其他操作... } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { try { client.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } }
9 安装和使用 Ingest-Attachment
Ingest-Attachment是一个开箱即用的插件,可以实现对(PDF,DOC等)主流格式文件的文本抽取及自动导入。
安装(可以手动下载插件包放入到es plugin目录下):
cmd 进入到elasticsearch bin目录下,执行以下命令,等待安装插件
elasticsearch-plugin install ingest-attachment
卸载:
cmd 进入到elasticsearch bin目录下,执行以下命令
elasticsearch-plugin remove ingest-attachment
kibana tool工具操作 使用ingest-attachment
建立ElasticSearch文件存储,用于检索文件名称、文件内容
9.1、建立文本抽取管道pipeline(全局执行一次即可使用)
PUT _ingest/pipeline/attachment { "description": "Extract attachment information", "processors": [ { "attachment": { "field": "data", "indexed_chars": -1,# -1 表示提取所有字符 "ignore_missing": true } }, { "remove": { "field": "data"# 提取完成后移除原始 base64 数据,节省存储空间 } } ] }
9.2、建立索引filedata
属性列:文件名称,文件扩展名,文件路径,读取的文件内容
PUT /filedata { "mappings": { "properties": { "filename": { "type": "text", "analyzer": "ik_max_word" }, "fileext": { "type": "keyword" }, "filepath": { "type": "keyword" }, "attachment.data": { "type": "text", "analyzer": "ik_max_word" } } } }
9.3、kibana tool批量创建数据
PUT /filedata/_bulk?pipeline=attachment&pretty=true {"index":{}} {"filename":"小黑","fileext":"txt","filepath":"d:/tempfile", "data":"5LiJ5aSp5LiN5omT5LiK5oi/5o+t55OmIOS9oOivtOeahOWvueS4jeWvuQ=="} {"index":{}} {"filename":"小白","fileext":"txt","filepath":"d:/tempfile","data":"5Lit5Y2O5Lq65ZCN5YWx5ZKM5Zu9IOaIkeeahOelluWbvQ=="}
存储的数据如下:
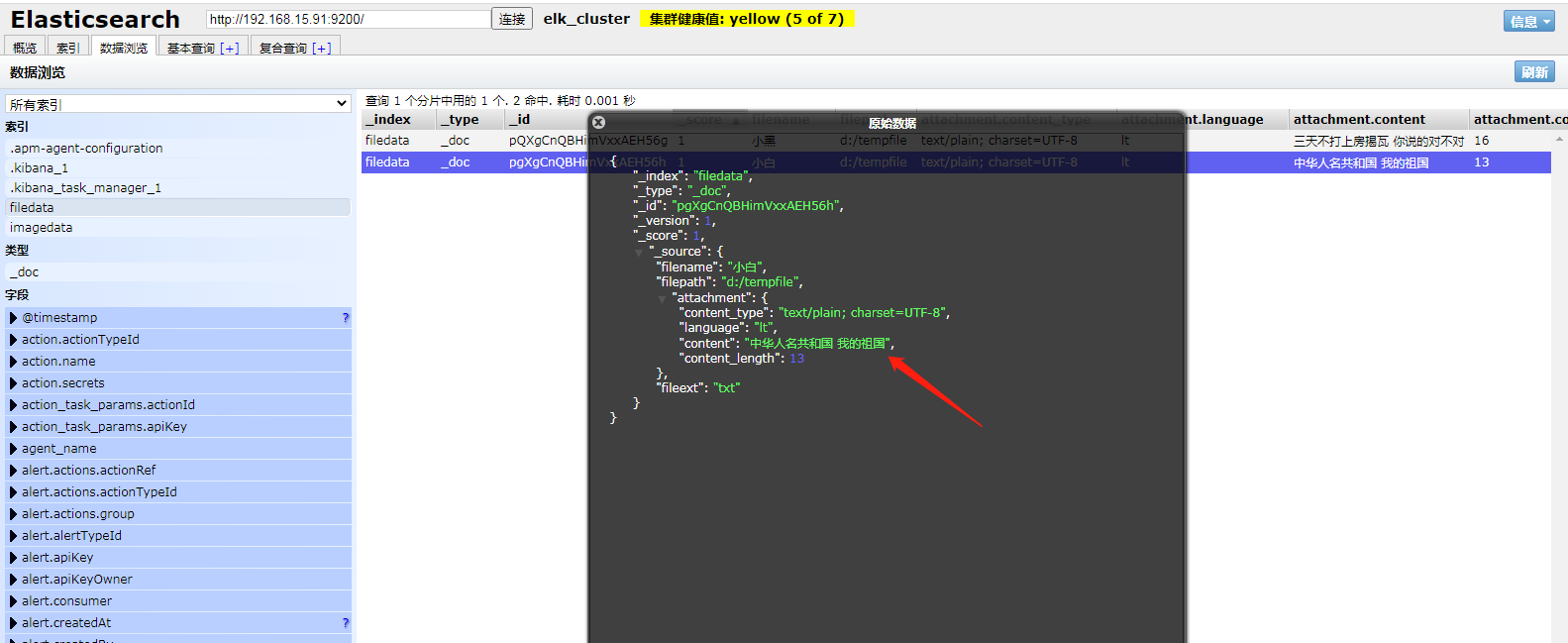
9.4、通过IK分词插件查询
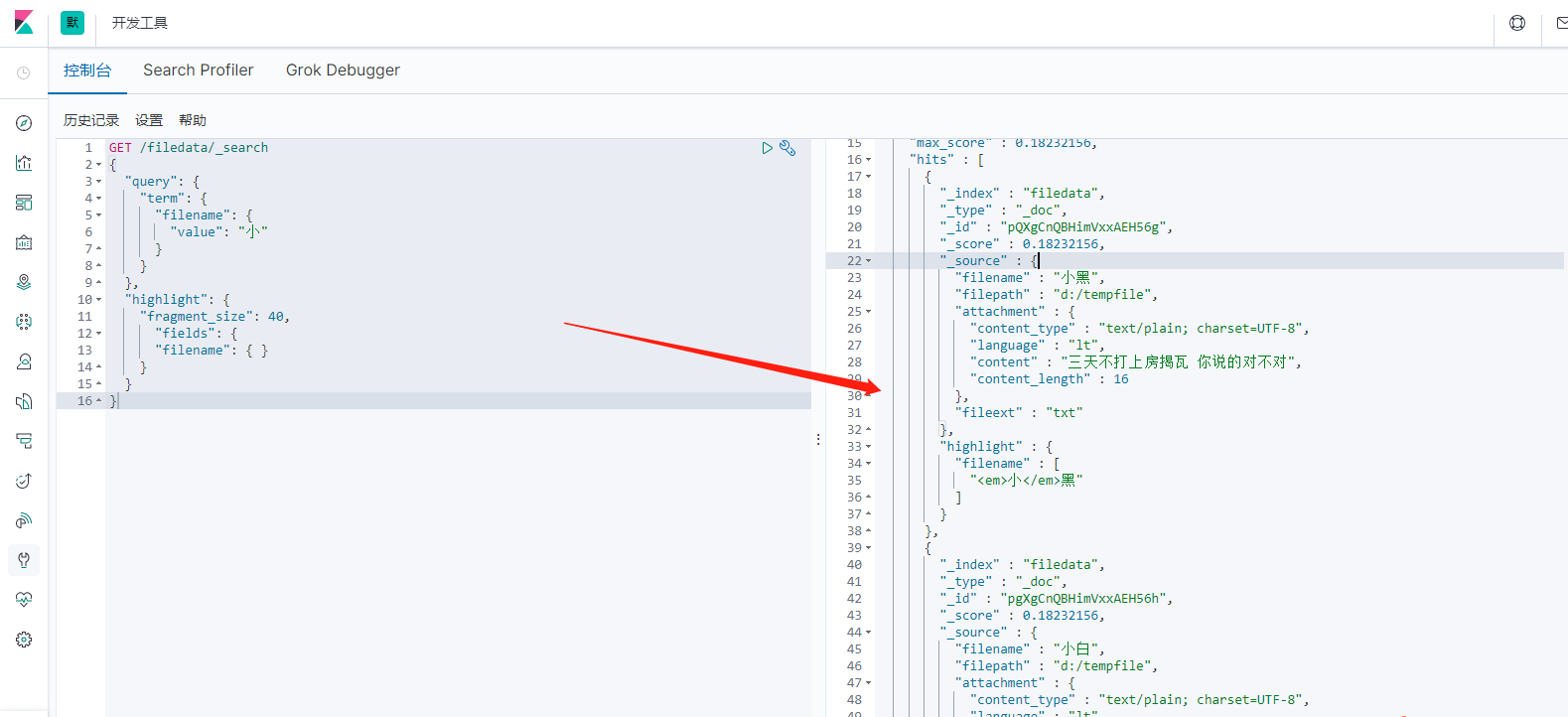
term根据IK分词查询,highlight高亮显示,此查询为根据文件名称查询
GET /filedata/_search { "query": { "term": { "filename": { "value": "小" } } }, "highlight": { "fragment_size": 40, "fields": { "filename": { } } } }
查询结果如下图:
9.5、ingest-attachment 通过管道pipeline提取文本数据,根据文本内容查询
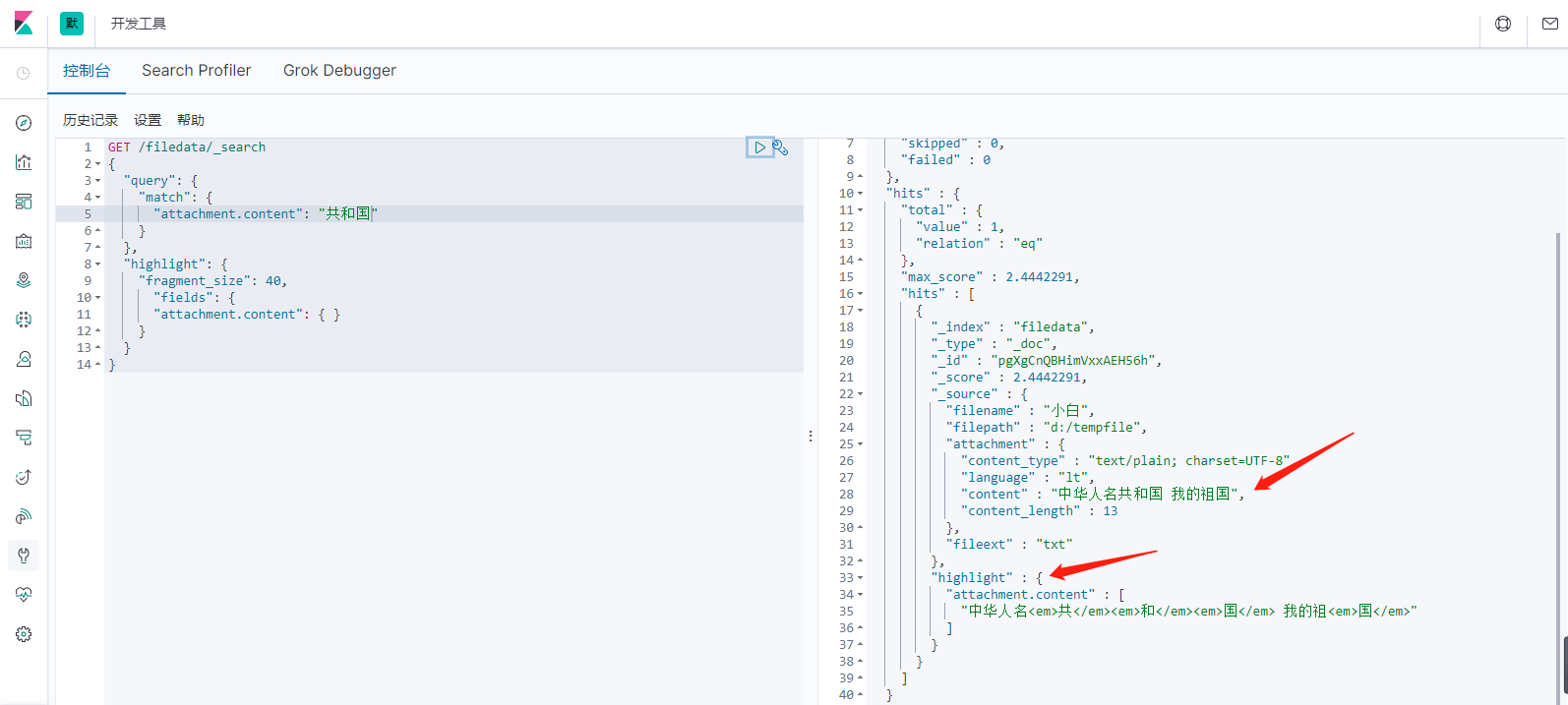
match根据属性查询,highlight高亮显示
GET /filedata/_search { "query": { "match": { "attachment.content": "共和国" } }, "highlight": { "fragment_size": 40, "fields": { "attachment.content": { } } } }
查询结果如下
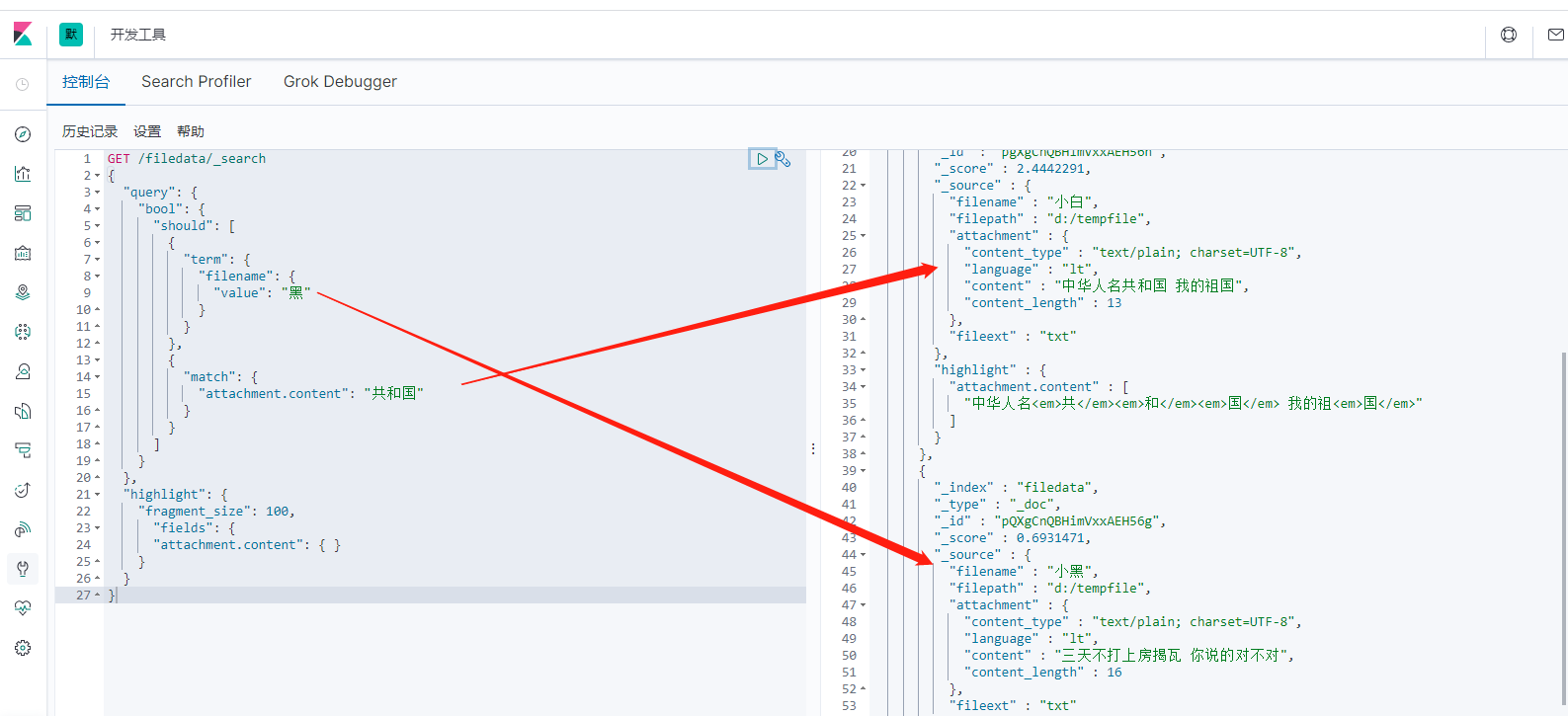
9.6、Elasticsearch bool过滤查询,match和term联合查询
GET /filedata/_search { "query": { "bool": { "should": [ { "term": { "filename": { "value": "黑" } } }, { "match": { "attachment.content": "共和国" } } ] } }, "highlight": { "fragment_size": 100, "fields": { "attachment.content": { } } } }
查询结果如下
到此ingest-attachment插件,安装,应用已完成(ingest-attachment应用体现在管道pipeline提取文本数据)。
注:在使用时,需要将其文本数据转成base64的编码,使用管道将其base64编码放入es 即可,ingest-attachment 会自动从你添加的base64的编码中提取文本放入 attament.content 中。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 | 准备文件并上传索引Ingest Attachment Plugin 需要文件以 Base64 编码形式存储在字段中。你需要在 Java 中读取文件并进行 Base64 编码。Java 示例代码依赖在 pom.xml 中添加 Base64 编码支持:<dependency> <groupId>commons-codec</groupId> <artifactId>commons-codec</artifactId> <version>1.15</version></dependency>Base64 编码文件import org.apache.commons.codec.binary.Base64;import java.io.File;import java.io.FileInputStream;import java.io.IOException;import java.util.Base64;public class FileEncoder { public static String encodeFileToBase64(File file) { try (FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(file)) { byte[] fileContent = new byte[(int) file.length()]; fis.read(fileContent); return Base64.getEncoder().encodeToString(fileContent); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } return null; }}<br><br> |
索引文档到 Elasticsearch import co.elastic.clients.elasticsearch.ElasticsearchClient; import co.elastic.clients.elasticsearch.core.IndexRequest; import co.elastic.clients.elasticsearch.core.IndexResponse; import java.io.File; import java.io.IOException; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.Map; public class ElasticsearchAttachmentIndexer { private final ElasticsearchClient client; public ElasticsearchAttachmentIndexer(ElasticsearchClient client) { this.client = client; } public void indexDocument(File file) throws IOException { String base64Content = FileEncoder.encodeFileToBase64(file); Map<String, Object> document = new HashMap<>(); document.put("file_name", file.getName()); document.put("data", base64Content); IndexRequest<Map<String, Object>> request = IndexRequest.of(i -> i .index("documents") .pipeline("attachment_pipeline") // 使用指定的 Ingest Pipeline .document(document) ); IndexResponse response = client.index(request); System.out.println("Document indexed with ID: " + response.id()); } } 搜索索引数据 解析后的文件内容存储在字段 attachment.content 中。你可以使用此字段进行全文搜索。 搜索示例 import co.elastic.clients.elasticsearch.core.SearchRequest; import co.elastic.clients.elasticsearch.core.SearchResponse; import co.elastic.clients.elasticsearch.core.search.Hit; import java.io.IOException; import java.util.List; public class DocumentSearcher { private final ElasticsearchClient client; public DocumentSearcher(ElasticsearchClient client) { this.client = client; } public void searchDocuments(String keyword) throws IOException { SearchRequest request = new SearchRequest.Builder() .index("documents") .query(q -> q .match(t -> t .field("attachment.content") // 搜索解析后的文本内容 .query(keyword) ) ) .build(); SearchResponse<Map> response = client.search(request, Map.class); List<Hit<Map>> hits = response.hits().hits(); System.out.println("Search results:"); for (Hit<Map> hit : hits) { System.out.println("Document ID: " + hit.id()); System.out.println("File Name: " + hit.source().get("file_name")); System.out.println("Content Preview: " + ((Map<String, Object>) hit.source().get("attachment")) .get("content").toString().substring(0, 100) + "..."); } } } 验证和测试 上传文件并索引: 使用 ElasticsearchAttachmentIndexer 进行文件上传和索引。 搜索测试: 使用 DocumentSearcher 搜索文件内容。
注意事项
Base64 编码文件大小限制:
默认情况下,Elasticsearch 对上传文件大小有限制,通常为 100MB。如果需要处理更大的文件,可以在 elasticsearch.yml 中配置 ingest.attachment.max_size。
性能优化:
大文件的 Base64 编码会占用较多的存储空间,建议配置 indexed_chars 参数来限制提取的字符数。
建议对文件内容使用适当的 analyzer,如 standard 或 english 分析器,以提高搜索效果。
权限配置:
确保 Elasticsearch 用户具有足够的权限来使用 Ingest Pipeline。
使用 Ingest Attachment Plugin 可以大大简化对二进制文件的文本提取和索引操作,适合需要处理各种复杂格式文档的搜索需求。





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 开源Multi-agent AI智能体框架aevatar.ai,欢迎大家贡献代码
· Manus重磅发布:全球首款通用AI代理技术深度解析与实战指南
· 被坑几百块钱后,我竟然真的恢复了删除的微信聊天记录!
· 没有Manus邀请码?试试免邀请码的MGX或者开源的OpenManus吧
· 园子的第一款AI主题卫衣上架——"HELLO! HOW CAN I ASSIST YOU TODAY
2023-10-26 Linux服务器远程文件拷贝两种方法介绍