160. Intersection of Two Linked Lists(找出两个链表的交点) &&两个链表的第一个公共结点(剑指offer)
Write a program to find the node at which the intersection of two singly linked lists begins.
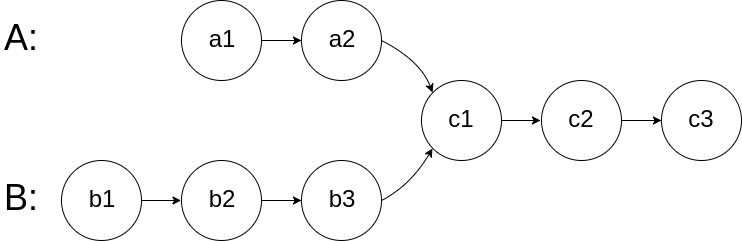
For example, the following two linked lists:
begin to intersect at node c1.
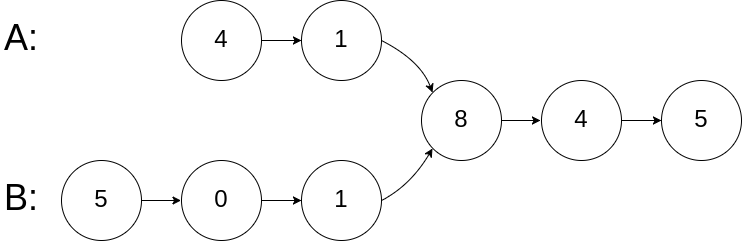
Example 1:
Input: intersectVal = 8, listA = [4,1,8,4,5], listB = [5,0,1,8,4,5], skipA = 2, skipB = 3 Output: Reference of the node with value = 8 Input Explanation: The intersected node's value is 8 (note that this must not be 0 if the two lists intersect). From the head of A, it reads as [4,1,8,4,5]. From the head of B, it reads as [5,0,1,8,4,5]. There are 2 nodes before the intersected node in A; There are 3 nodes before the intersected node in B.
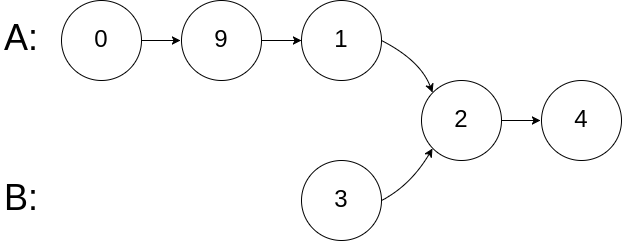
Example 2:
Input: intersectVal = 2, listA = [0,9,1,2,4], listB = [3,2,4], skipA = 3, skipB = 1 Output: Reference of the node with value = 2 Input Explanation: The intersected node's value is 2 (note that this must not be 0 if the two lists intersect). From the head of A, it reads as [0,9,1,2,4]. From the head of B, it reads as [3,2,4]. There are 3 nodes before the intersected node in A; There are 1 node before the intersected node in B.
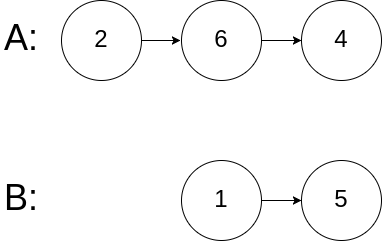
Example 3:
Input: intersectVal = 0, listA = [2,6,4], listB = [1,5], skipA = 3, skipB = 2 Output: null Input Explanation: From the head of A, it reads as [2,6,4]. From the head of B, it reads as [1,5]. Since the two lists do not intersect, intersectVal must be 0, while skipA and skipB can be arbitrary values. Explanation: The two lists do not intersect, so return null.
Notes:
- If the two linked lists have no intersection at all, return
null. - The linked lists must retain their original structure after the function returns.
- You may assume there are no cycles anywhere in the entire linked structure.
- Your code should preferably run in O(n) time and use only O(1) memory.
方法一:双指针
分析:链表a的长度a+c,链表b的长度:b+c 。链表重合部分的长度是:c
那么如果指向a的指针走过长度是:a+c+b
指向b的指针走过的长度是:b+c+a
的时候两个指针指向 的下一个结点就是第一个公共链的结点。(不然就是空节点,没有公共链)
时间复杂度:o(n+m) 空间复杂度:o(1)
/* public class ListNode { int val; ListNode next = null; ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; } }*/ public class Solution { public ListNode FindFirstCommonNode(ListNode pHead1, ListNode pHead2) { ListNode headA=pHead1; ListNode headB=pHead2; while (pHead1!=pHead2){ pHead1=(pHead1==null)?headB:pHead1.next; pHead2=(pHead2==null)?headA:pHead2.next; } return pHead1; } }
方法二:利用hashset特性
hashset用于存储对象,用它存储pHead1链表所有结点。虽然它是无序的,不保证存入和取出的顺序相同,但是遍历pHead2的时候是有序的。遍历到第一个结点时就会立刻返回。
import java.util.HashSet; /* public class ListNode { int val; ListNode next = null; ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; } }*/ public class Solution { public ListNode FindFirstCommonNode(ListNode pHead1, ListNode pHead2) { HashSet<ListNode> set=new HashSet<ListNode>(); while (pHead1!=null){ set.add(pHead1); pHead1=pHead1.next; } while (pHead2!=null){ if(set.contains(pHead2)) return pHead2; pHead2=pHead2.next; } return pHead2; } }
苟有恒,何必三更眠五更起;最无益,莫过一日暴十日寒。