状态机相关知识点(1)--序列检测器1100101
1,mealy状态机与moore状态机的特征区别?
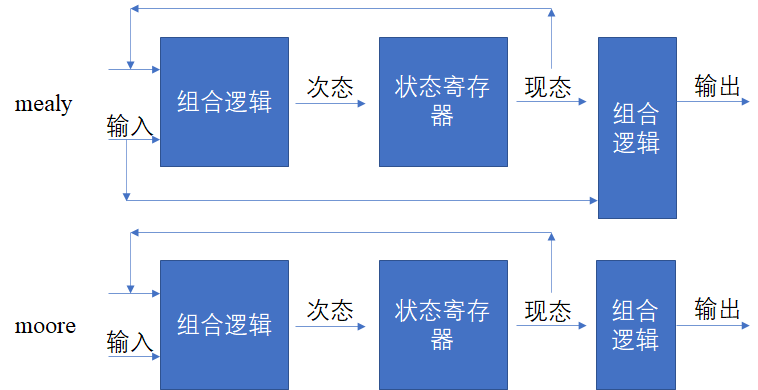
可以从图中较为明显的发现:mealy状态机的输出是不仅跟当前状态有关,还跟输入信号有关。
moore状态机的输出只跟当前状态有关。
因此mealy状态机的输出容易受到输入中的毛刺影响,且moore状态机相比mealy状态机在输出时,多等待一个时钟周期。
状态机又可分为二段式和三段式,因此状态机类型可分为mealy二段,mealy三段,moore二段,moore三段。
2,个人理解中,状态机最重要的部分是:状态的转换-即always组合逻辑部分。通过判断不同状态个数,设置合理的寄存器bit位,可避免出现资源的浪费。又当需要对状态进行精简时,可使用mealy状态机。
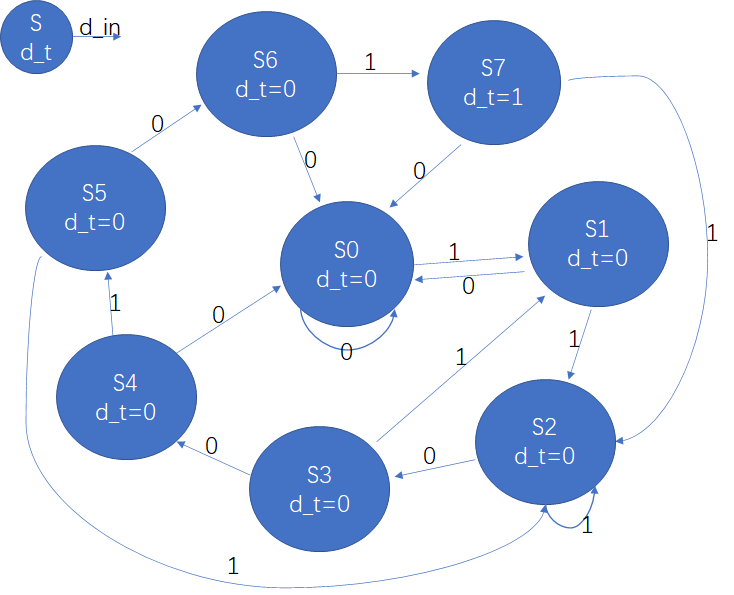
3,序列检测器--1100101
moore二段式写法,状态转移图如下(线还是丑了一些,勉强看吧)
主程序:
module sequence_fsm (
clk,rst,d_in,d_out
);
input clk;
input rst;
input d_in;
output d_out;
reg d_out;
parameter s0 = 3'b000;
parameter s1 = 3'b001;
parameter s2 = 3'b010;
parameter s3 = 3'b011;
parameter s4 = 3'b100;
parameter s5 = 3'b101;
parameter s6 = 3'b110;
parameter s7 = 3'b111;
reg [3:0]state,nextstate;
always @(posedge clk or negedge rst) begin
if(!rst) begin
state <= s0;
end
else begin
state <= nextstate;
end
end
always @(state or d_in) begin
d_out = 1'b0;
nextstate = 3'bxxx;
case(state)
s0: begin
d_out = 1'b0;
if(d_in == 1'b0) begin
nextstate = s0;
end
else begin
nextstate = s1;
end
end
s1: begin
d_out = 1'b0;
if(d_in == 1'b0) begin
nextstate = s0;
end
else begin
nextstate = s2;
end
end
s2: begin
d_out = 1'b0;
if(d_in == 1'b0) begin
nextstate = s3;
end
else begin
nextstate = s2;
end
end
s3: begin
d_out = 1'b0;
if (d_in == 1'b0) begin
nextstate = s4;
end
else begin
nextstate = s1;
end
end
s4: begin
d_out = 1'b0;
if (d_in == 1'b0) begin
nextstate = s0;
end
else begin
nextstate = s5;
end
end
s5: begin
d_out = 1'b0;
if (d_in == 1'b0) begin
nextstate = s6;
end
else begin
nextstate = s2;
end
end
s6: begin
d_out = 1'b0;
if (d_in == 1'b0) begin
nextstate = s0;
end
else begin
nextstate = s7;
end
end
s7: begin
d_out = 1'b1;
if (d_in == 1'b0) begin
nextstate = s0;
end
else begin
nextstate = s2;
end
end
default: begin
d_out = 1'b0;
nextstate = s0;
end
endcase
end
endmodule
tb程序:
`timescale 1ns/1ps
module sequence_fsm_tb;
reg clk;
reg rst;
reg d_in;
wire d_out;
sequence_fsm u1(
.clk(clk),
.rst(rst),
.d_in(d_in),
.d_out(d_out)
);
initial begin
clk = 1'b1;
rst = 1'b0;
#10;
rst = 1'b1;
end
always #5 clk = ~clk;
initial begin
#10 d_in = 0;
$display("display:simulation time is : %t",$time,"the value is :%b",d_in);
#10 d_in = 0;
$display("display:simulation time is : %t",$time,"the value is :%b",d_in);
#10 d_in = 1;
$display("display:simulation time is : %t",$time,"the value is :%b",d_in);
#10 d_in = 1;
$display("display:simulation time is : %t",$time,"the value is :%b",d_in);
#10 d_in = 0;
$display("display:simulation time is : %t",$time,"the value is :%b",d_in);
#10 d_in = 0;
$display("display:simulation time is : %t",$time,"the value is :%b",d_in);
#10 d_in = 1;
$display("display:simulation time is : %t",$time,"the value is :%b",d_in);
#10 d_in = 0;
$display("display:simulation time is : %t",$time,"the value is :%b",d_in);
#10 d_in = 1;
$display("display:simulation time is : %t",$time,"the value is :%b",d_in);
#10 d_in = 1;
$display("display:simulation time is : %t",$time,"the value is :%b",d_in);
#10 d_in = 0;
$display("display:simulation time is : %t",$time,"the value is :%b",d_in);
#10 d_in = 0;
$display("display:simulation time is : %t",$time,"the value is :%b",d_in);
#10 d_in = 1;
$display("display:simulation time is : %t",$time,"the value is :%b",d_in);
#10 d_in = 0;
$display("display:simulation time is : %t",$time,"the value is :%b",d_in);
#10 d_in = 1;
$display("display:simulation time is : %t",$time,"the value is :%b",d_in);
#10 d_in = 0;
$display("display:simulation time is : %t",$time,"the value is :%b",d_in);
#10 d_in = 0;
$display("display:simulation time is : %t",$time,"the value is :%b",d_in);//前面的赋值验证正确性,后面采用随机赋值
forever #10 begin
d_in = {$random}%2;
$display("display:simulation time is : %t",$time,"the value is :%b",d_in);
end
end
endmodule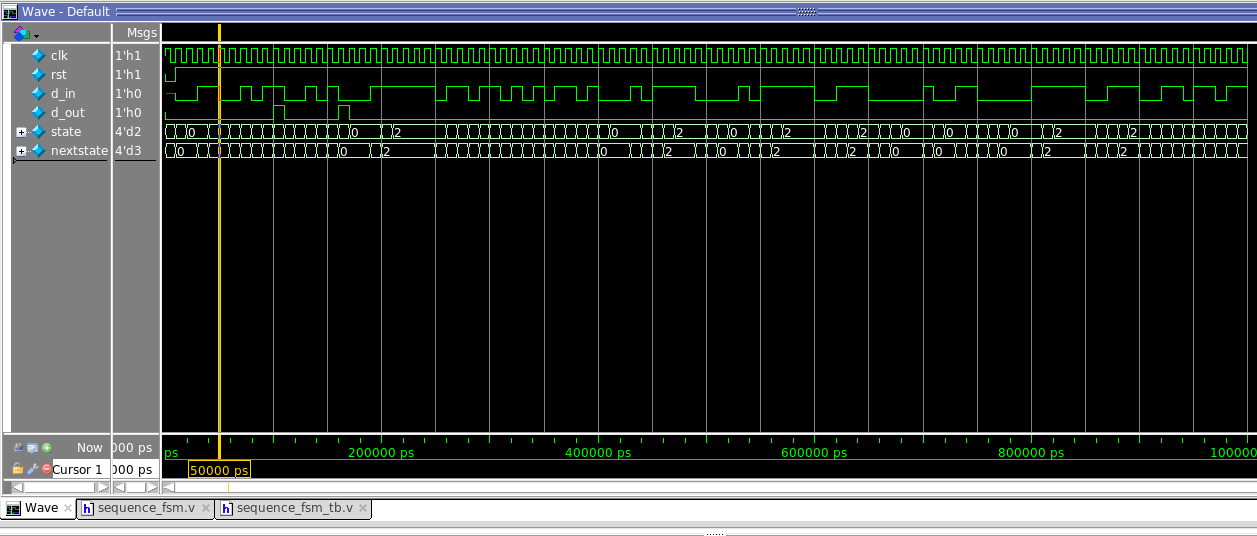
局部放大:
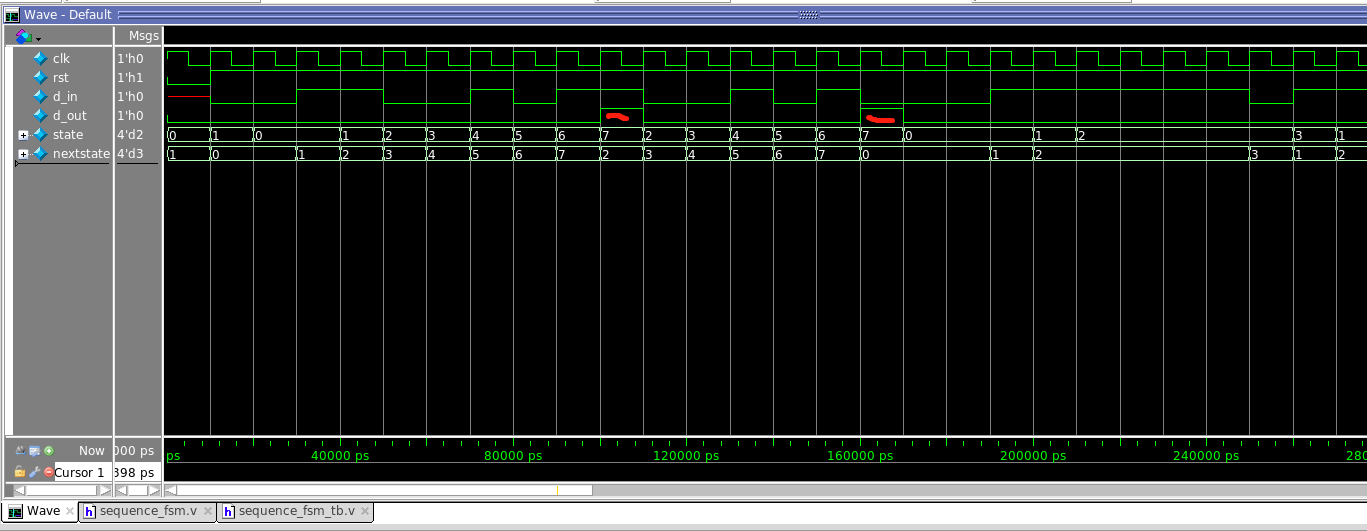
由仿真结果可以看出;moore的输出要晚一个时钟。
总结:forever只能用于仿真和测试程序,不能进行可综合设计,且一般用在initial过程块中,如果在forever语句中没有加延时语句,则forever将在0延时后无限循环。
$random%b:如果忽略b的值,则会返回一个随机的32位有符号数,如果考虑b的值,则会返回[1-b,b-1]这个区间内的等概率有符号随机数。
{$random}%b:因为{ }返回的是无符号数,所以可以通过位拼接符将返回的有符号数转变为无符号数。当b>0时,返回的无符号随机数的范围[0,b-1].


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号