java web使用WebSocket
一.WebSocket是什么
1.概念
WebSocket协议是基于TCP的一种新的网络协议,它实现了浏览器与服务器双全工(full-duplex)通信——允许服务器主动发送信息给客户端。
2.实现原理
在实现WebSocket连线过程中,需要通过浏览器发出WebSocket连线请求,然后服务器发出回应,这个过程通常称为“握手”。在WebSocket API,浏览器和服务器只需要做一个握手的动作,然后浏览器和服务器之间就形成了一条快速通道,两者间就可以直接互相传送数据。

二.在java web使用WebSocket
1.创建一个jsp项目
往简单来说,就是用idea创建一个maven项目 ,add support为web application的项目。
2.maven添加WebSocket库
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.websocket</groupId>
<artifactId>javax.websocket-api</artifactId>
<version>1.1</version>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
3.声明WebSocket类
import javax.websocket.*; import javax.websocket.server.PathParam; import javax.websocket.server.ServerEndpoint; import java.io.IOException; @ServerEndpoint(value = "/websocketTest/{userId}") public class TestWebSocket { private static String userId; //连接时执行 @OnOpen public void onOpen(@PathParam("userId") String userId, Session session) throws IOException { this.userId = userId; System.out.println("新连接:" + userId); } //关闭时执行 @OnClose public void onClose() { System.out.println("连接:" + this.userId + " 关闭"); } //收到消息时执行 @OnMessage public void onMessage(String message, Session session) throws IOException { System.out.println("收到用户" + this.userId + "的消息" + message); session.getBasicRemote().sendText("收到 " + this.userId + " 的消息 "); //回复用户 } //连接错误时执行 @OnError public void onError(Session session, Throwable error) { System.out.println("用户id为:" + this.userId + "的连接发送错误"); error.printStackTrace(); } }
使用@ServerEndpoint来声明接口:@serverEndpoint(value=“/websocket/{paraName}”);其中“{}”用来表示带参数的连接,如果需要获取{}参数,可以在方法中添加@PathParam("paraName") 。连接地址格式为:ws://localhost:8080/projectName/websocket/abc。
Session代表的是两个WebSocket端点的会话。当WebSocket握手成功后,WebSocket就会提供一个打开的session,可以通过这个session来对另一个端点发送数据。如果这个session关闭了,那发送数据将会报错。
4.前端代码
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title></title> </head> <body> websocket Demo---- user000 <br /> <input id="text" type="text" /> <button onclick="send()"> Send </button> <button onclick="closeWebSocket()"> Close </button> <div id="message"> </div> <script type="text/javascript"> //判断当前浏览器是否支持WebSocket if('WebSocket' in window){ websocket = new WebSocket("ws://localhost:8080/test/websocketTest/user000"); console.log("link success") }else{ alert('Not support websocket') } //连接发生错误的回调方法 websocket.onerror = function(){ setMessageInnerHTML("error"); }; //连接成功建立的回调方法 websocket.onopen = function(event){ setMessageInnerHTML("open"); } console.log("-----") //接收到消息的回调方法 websocket.onmessage = function(event){ setMessageInnerHTML(event.data); } //连接关闭的回调方法 websocket.onclose = function(){ setMessageInnerHTML("close"); } //监听窗口关闭事件,当窗口关闭时,主动去关闭websocket连接,防止连接还没断开就关闭窗口,server端会抛异常。 window.onbeforeunload = function(){ websocket.close(); } //将消息显示在网页上 function setMessageInnerHTML(innerHTML){ document.getElementById('message').innerHTML += innerHTML + '<br/>'; } //关闭连接 function closeWebSocket(){ websocket.close(); } //发送消息 function send(){ var message = document.getElementById('text').value; websocket.send(message); } </script> </body> </html>
在前端打开WebSocket,根据地址和后端交互。
websocket = new WebSocket("ws://localhost:8080/test/websocketTest/user000");
注意上面这一段中的test是这个项目在tomcat设置的启动地址名称。
5.测试运行
在浏览器打开页面后,就立即进行了连接。建立了连接,在前端发送数据,然后就接收到后端返回的信息。
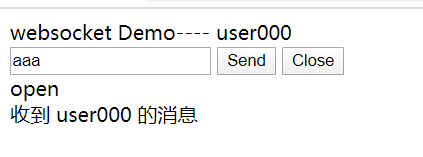
在后端可以看到连接的建立和接收到的信息。

三.总结
1.WebSocket建立连接后,通信就是全双工模式,客户端和服务端就可以在任何时间里自由发送数据。适合于服务端要主动推送实时数据的场景。






【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语,封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· .NET Core 中如何实现缓存的预热?
· 从 HTTP 原因短语缺失研究 HTTP/2 和 HTTP/3 的设计差异
· AI与.NET技术实操系列:向量存储与相似性搜索在 .NET 中的实现
· 基于Microsoft.Extensions.AI核心库实现RAG应用
· TypeScript + Deepseek 打造卜卦网站:技术与玄学的结合
· 阿里巴巴 QwQ-32B真的超越了 DeepSeek R-1吗?
· 【译】Visual Studio 中新的强大生产力特性
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语 ── 封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· 【设计模式】告别冗长if-else语句:使用策略模式优化代码结构