16.<tag-链表和加法运算>-面试题 02.05. 链表求和 + lt.86. 分隔链表
@[TOC ]
面试题 02.05. 链表求和
[案例需求]
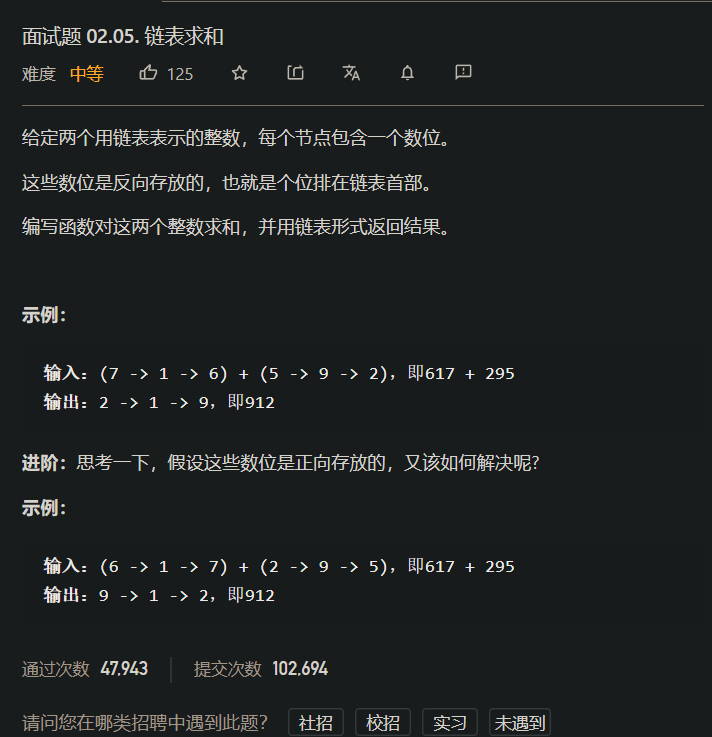
[思路分析]
- 对于上述题目的这种加法问题, 其实在链表结点和字符串中经常能看到, 解决这一类问题的共性在于如何对数字进行加操作, 如何对加数和结果进行处理, 比如加法的进位用一个carry变量存储下来, 在解题时, 要把carry进行传递,
- carry的计算就是对加数结果 sum进行取模, 得到sum的十位上的数;
- 而sum的个位数通常是直接除以10得到的, 他是我们此次计算真正要存入结果数组或链表, 字符串中发数;
[代码实现]
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode addTwoNumbers(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
//遍历两条链表, 每个结点相加,
//进位保留下来, 加数的个位作为新的链表结点
int carry = 0;
ListNode dummyNode = new ListNode(-1);
ListNode temp = dummyNode;
while(l1 != null || l2 != null || carry != 0){
int sum = carry;
if(l1 != null){
sum += l1.val;
l1 = l1.next;
}
if(l2 != null){
sum += l2.val;
l2 = l2.next;
}
//sum += carry;
temp.next = new ListNode(sum % 10);
temp = temp.next;
carry = sum / 10;
}
return dummyNode.next;
}
}

扩展问题: 数字是正向存储的如何进行加法运算呢?
-
进阶问题中,输入的两个链表都是正向存放数字的位数的,因此链表中数位的顺序与我们做加法的顺序是相反的。
-
为了反向处理所有数位,我们可以使用栈:把所有数字压入栈中,再依次取出相加。计算过程中需要注意进位的情况。
class Solution {
public ListNode addTwoNumbers(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
Deque<Integer> stack1 = new ArrayDeque<Integer>();
Deque<Integer> stack2 = new ArrayDeque<Integer>();
while (l1 != null) {
stack1.push(l1.val);
l1 = l1.next;
}
while (l2 != null) {
stack2.push(l2.val);
l2 = l2.next;
}
int carry = 0;
ListNode ans = null;
while (!stack1.isEmpty() || !stack2.isEmpty() || carry != 0) {
int a = stack1.isEmpty() ? 0 : stack1.pop();
int b = stack2.isEmpty() ? 0 : stack2.pop();
int cur = a + b + carry;
carry = cur / 10;
cur %= 10;
ListNode curnode = new ListNode(cur);
curnode.next = ans;
ans = curnode;
}
return ans;
}
}

lt.86. 分隔链表
[案例需求]
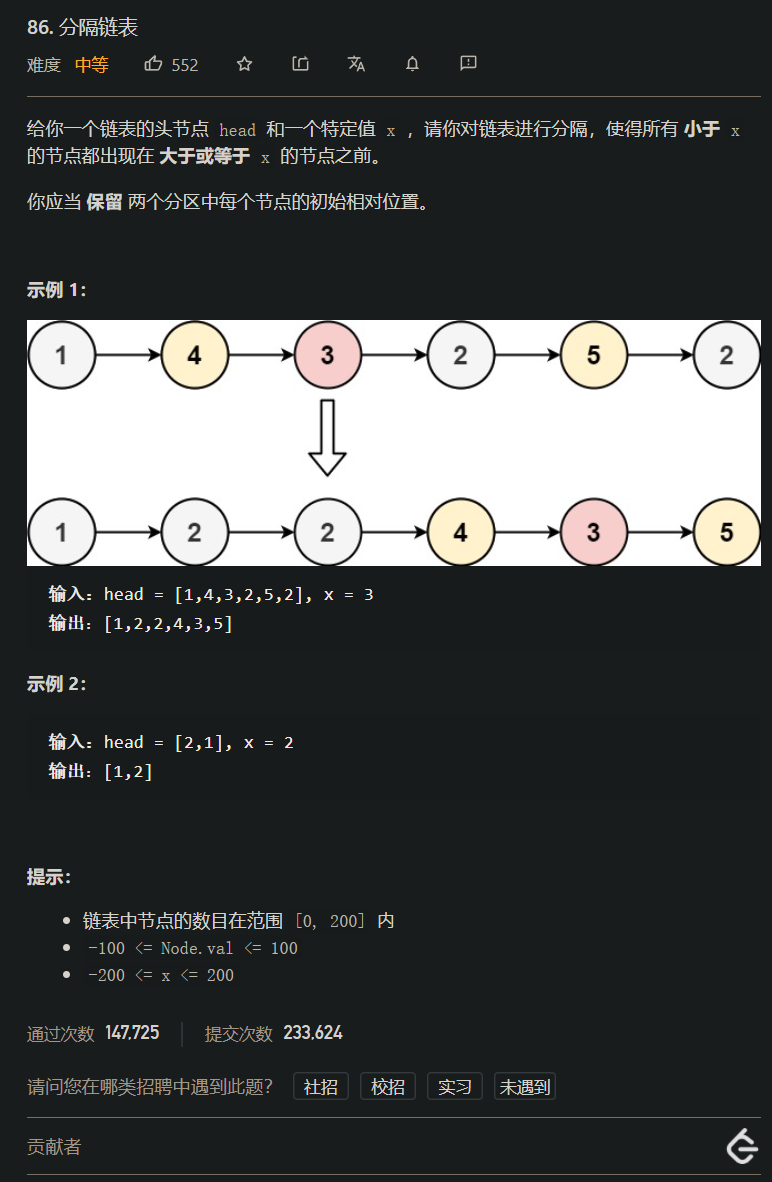
[思路分析]

[代码实现]
class Solution {
public ListNode partition(ListNode head, int x) {
ListNode small = new ListNode(0);
ListNode smallHead = small;
ListNode large = new ListNode(0);
ListNode largeHead = large;
while (head != null) {
if (head.val < x) {
small.next = head;
small = small.next;
} else {
large.next = head;
large = large.next;
}
head = head.next;
}
large.next = null;
small.next = largeHead.next;
return smallHead.next;
}
}



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号