netty源码分析(一)
一、先看服务端的入门示例代码
public class MyServer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
//第一步 创建bossGroup 接受数据然后转发给workerGroup,是一个死循环
EventLoopGroup bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(1);
//第二步 创建workerGroup 完成实际数据的处理,也是一个死循环
EventLoopGroup workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
try {
//第三步 启动bossGroup和workerGroup
ServerBootstrap serverBootstrap = new ServerBootstrap();
serverBootstrap.group(bossGroup, workerGroup)
.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)
.handler(new LoggingHandler(LogLevel.WARN))
//自定义的序列化器
.childHandler(new MyServerInitializer());
//第四步 绑定服务端的端口
ChannelFuture channelFuture = serverBootstrap.bind(8899).sync();
channelFuture.channel().closeFuture().sync();
} finally {
bossGroup.shutdownGracefully();
workerGroup.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
}
二、EventLoopGroup
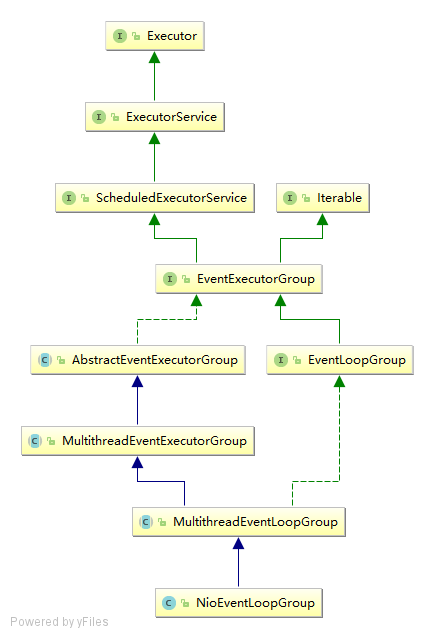
//EventLoopGroup 首先是一个接口,继承了EventExecutorGroup ,主要的功能是在时间循环对Channel的注册
public interface EventLoopGroup extends EventExecutorGroup {
//返回得到下一个EventLoop
@Override
EventLoop next();
//将参数channel注册到EventLoop当中,返回ChannelFuture
ChannelFuture register(Channel channel);
//将参数ChannelPromise注册到EventLoop当中,返回ChannelFuture
ChannelFuture register(ChannelPromise promise);
//废弃的方法
@Deprecated
ChannelFuture register(Channel channel, ChannelPromise promise);
}
EventLoopGroup是一个接口,继承了EventExecutorGroup,ScheduledExecutorService,ExecutorService。实例化的是他的实现类的子类NioEventLoopGroup,调用他的构造方法最终会使用父类MultithreadEventExecutorGroup的构造方法。
public NioEventLoopGroup() {
this(0);
}
public NioEventLoopGroup(int nThreads) {
this(nThreads, (Executor) null);
}
public NioEventLoopGroup(int nThreads, Executor executor) {
this(nThreads, executor, SelectorProvider.provider());
}
public NioEventLoopGroup(
int nThreads, Executor executor, final SelectorProvider selectorProvider) {
this(nThreads, executor, selectorProvider, DefaultSelectStrategyFactory.INSTANCE);
}
public NioEventLoopGroup(int nThreads, Executor executor, final SelectorProvider selectorProvider,
final SelectStrategyFactory selectStrategyFactory) {
//添加了线程拒绝执行策略
super(nThreads, executor, selectorProvider, selectStrategyFactory, RejectedExecutionHandlers.reject());
}
protected MultithreadEventLoopGroup(int nThreads, Executor executor, Object... args) {
super(nThreads == 0 ? DEFAULT_EVENT_LOOP_THREADS : nThreads, executor, args);
}
DEFAULT_EVENT_LOOP_THREADS:EventLoop默认的线程数。
private static final int DEFAULT_EVENT_LOOP_THREADS;
static {
//如果配置了io.netty.eventLoopThreads会取io.netty.eventLoopThreads的值,否则就去系统cpu的核数*2,注意,现在的cpu都有超频技术
DEFAULT_EVENT_LOOP_THREADS = Math.max(1, SystemPropertyUtil.getInt(
"io.netty.eventLoopThreads", NettyRuntime.availableProcessors() * 2));
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("-Dio.netty.eventLoopThreads: {}", DEFAULT_EVENT_LOOP_THREADS);
}
}
1、具体的实例化过程
//DefaultEventExecutorChooserFactory.INSTANCE,通过这个EventLoop选择器工厂可以实例化GenericEventExecutorChooser这个类,
//这个类是EventLoopGroup线程池里面的EventLoop的选择器,调用GenericEventExecutorChooser.next()方法可以从线程池中选择出一个合适的EventLoop线程。
protected MultithreadEventExecutorGroup(int nThreads, Executor executor, Object... args) {
this(nThreads, executor, DefaultEventExecutorChooserFactory.INSTANCE, args);
}
protected MultithreadEventExecutorGroup(int nThreads, Executor executor,
EventExecutorChooserFactory chooserFactory, Object... args) {
//1.线程池初始化
if (nThreads <= 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(String.format("nThreads: %d (expected: > 0)", nThreads));
}
//初始化线程工厂,这里的executor起到创建线程的作用,它的方法内部就是new Thread().start()
if (executor == null) {
executor = new ThreadPerTaskExecutor(newDefaultThreadFactory());
}
//这里的children数组, 其实就是线程池的核心实现,线程池中就是通过指定的线程数组来实现线程池;
//数组中每个元素其实就是一个EventLoop,EventLoop是EventExecutor的子接口。
children = new EventExecutor[nThreads];
//for循环实例化children数组,NioEventLoop对象
for (int i = 0; i < nThreads; i ++) {
boolean success = false;
try {
//newChild(executor, args) 函数在NioEventLoopGroup类中实现了,
//实质就是就是存入了一个 NIOEventLoop类实例
children[i] = newChild(executor, args);
success = true;
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO: Think about if this is a good exception type
throw new IllegalStateException("failed to create a child event loop", e);
} finally {//失败清理资源
if (!success) {
for (int j = 0; j < i; j ++) {
children[j].shutdownGracefully();
}
for (int j = 0; j < i; j ++) {
EventExecutor e = children[j];
try {
while (!e.isTerminated()) {
e.awaitTermination(Integer.MAX_VALUE, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
}
} catch (InterruptedException interrupted) {
// Let the caller handle the interruption.
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
break;
}
}
}
}
}
//2.实例化线程工厂执行器选择器: 根据children获取选择器
chooser = chooserFactory.newChooser(children);
//3.创建线程终止监听器
final FutureListener<Object> terminationListener = new FutureListener<Object>() {
@Override
public void operationComplete(Future<Object> future) throws Exception {
if (terminatedChildren.incrementAndGet() == children.length) {
terminationFuture.setSuccess(null);
}
}
};
//为每个EventExecutor添加监听器表示终止后要做的操作
for (EventExecutor e: children) {
e.terminationFuture().addListener(terminationListener);
}
//4.将children 添加到对应的set集合中去重, 表示只可读
Set<EventExecutor> childrenSet = new LinkedHashSet<EventExecutor>(children.length);
Collections.addAll(childrenSet, children);
readonlyChildren = Collections.unmodifiableSet(childrenSet);
}
2、线程工厂初始化executor = new ThreadPerTaskExecutor(newDefaultThreadFactory());
protected ThreadFactory newDefaultThreadFactory() {
return new DefaultThreadFactory(getClass());
}
//参数poolType为newDefaultThreadFactory的class,false表示线程不是守护线程,
//Thread.NORM_PRIORITY,是正常的线程的优先级(三个优先级:MIN_PRIORITY = 1;NORM_PRIORITY = 5;MAX_PRIORITY = 10;)。
public DefaultThreadFactory(Class<?> poolType) {
this(poolType, false, Thread.NORM_PRIORITY);
}
//toPoolName(poolType)的功能:比如我们给定当前newDefaultThreadFactory的poolType为io.netty.util.concurrent.newDefaultThreadFactory,
//那么经过toPoolName()方法返回为newDefaultThreadFactory的字符串
public DefaultThreadFactory(Class<?> poolType, boolean daemon, int priority) {
this(toPoolName(poolType), daemon, priority);
}
public DefaultThreadFactory(String poolName, boolean daemon, int priority) {
this(poolName, daemon, priority, System.getSecurityManager() == null ?
Thread.currentThread().getThreadGroup() : System.getSecurityManager().getThreadGroup());
}
//初始化了线程工厂
public DefaultThreadFactory(String poolName, boolean daemon, int priority, ThreadGroup threadGroup) {
ObjectUtil.checkNotNull(poolName, "poolName");
if (priority < Thread.MIN_PRIORITY || priority > Thread.MAX_PRIORITY) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"priority: " + priority + " (expected: Thread.MIN_PRIORITY <= priority <= Thread.MAX_PRIORITY)");
}
prefix = poolName + '-' + poolId.incrementAndGet() + '-';
this.daemon = daemon;
this.priority = priority;
this.threadGroup = threadGroup;
}
public final class ThreadPerTaskExecutor implements Executor {
private final ThreadFactory threadFactory;
//把传进来的ThreadFactory也就是DefaultThreadFactory赋值给ThreadFactory
public ThreadPerTaskExecutor(ThreadFactory threadFactory) {
this.threadFactory = ObjectUtil.checkNotNull(threadFactory, "threadFactory");
}
@Override
public void execute(Runnable command) {
//ThreadFactory执行命令 创建线程 并执行
threadFactory.newThread(command).start();
}
}
@Override
public Thread newThread(Runnable r) {
Thread t = newThread(FastThreadLocalRunnable.wrap(r), prefix + nextId.incrementAndGet());
try {
if (t.isDaemon() != daemon) {
t.setDaemon(daemon);
}
if (t.getPriority() != priority) {
t.setPriority(priority);
}
} catch (Exception ignored) {
// Doesn't matter even if failed to set.
}
return t;
}
protected Thread newThread(Runnable r, String name) {
return new FastThreadLocalThread(threadGroup, r, name);
}
总结:1、NIOEventLoopGroup的线程池实现其实就是一个NIOEventLoop数组,一个NIOEventLoop可以理解成就是一个线程
2、所有的NIOEventLoop线程是使用相同的 executor、SelectorProvider、SelectStrategyFactory、RejectedExecutionHandler以及是属于某一个NIOEventLoopGroup的。因为在实例化NIOEventLoop的时候,调用newChild(executor, args)方法是在NIOEventLoopGroup类中实现的,入参是同一个
3、当有IO事件来时,需要从线程池中选择一个线程出来执行,这时候的NioEventLoop选择策略是由GenericEventExecutorChooser实现的, 并调用该类的next() 方法获取到下一个 NioEventLoop。
三、EventLoop
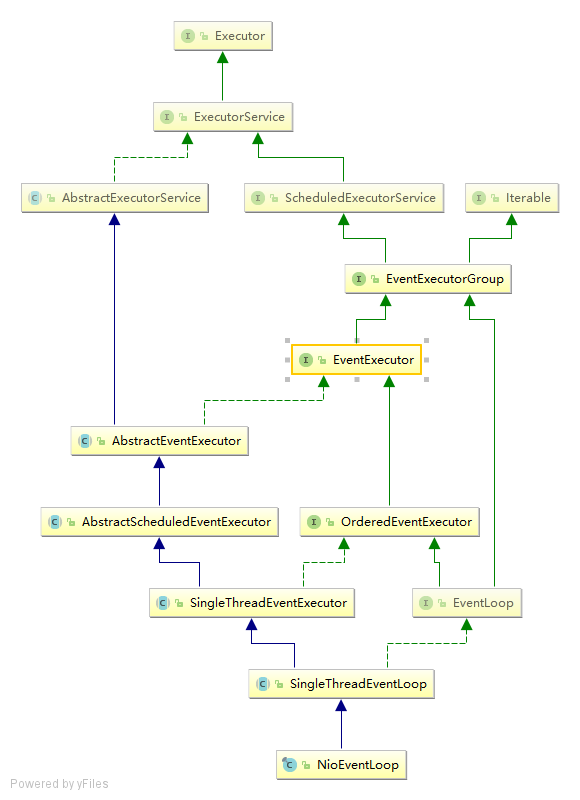
NIOEventLoop的初始化就是在children[i] = newChild(executor, args);这一步实现的,具体看代码。
@Override
protected EventLoop newChild(Executor executor, Object... args) throws Exception {
EventLoopTaskQueueFactory queueFactory = args.length == 4 ? (EventLoopTaskQueueFactory) args[3] : null;
return new NioEventLoop(this, executor, (SelectorProvider) args[0],
((SelectStrategyFactory) args[1]).newSelectStrategy(), (RejectedExecutionHandler) args[2], queueFactory);
}
NioEventLoop(NioEventLoopGroup parent, Executor executor, SelectorProvider selectorProvider,
SelectStrategy strategy, RejectedExecutionHandler rejectedExecutionHandler,
EventLoopTaskQueueFactory queueFactory) {
//调用父类构造器
super(parent, executor, false, newTaskQueue(queueFactory), newTaskQueue(queueFactory),
rejectedExecutionHandler);
this.provider = ObjectUtil.checkNotNull(selectorProvider, "selectorProvider");
this.selectStrategy = ObjectUtil.checkNotNull(strategy, "selectStrategy");
//selector的包装类 openSelector()方法调用了provider.openSelector();
final SelectorTuple selectorTuple = openSelector();
this.selector = selectorTuple.selector;
this.unwrappedSelector = selectorTuple.unwrappedSelector;
}
//Integer的最大值,可认为是一个无界队列
protected static final int DEFAULT_MAX_PENDING_TASKS = Math.max(16,
SystemPropertyUtil.getInt("io.netty.eventLoop.maxPendingTasks", Integer.MAX_VALUE));
//创建任务队列,
private static Queue<Runnable> newTaskQueue(
EventLoopTaskQueueFactory queueFactory) {
if (queueFactory == null) {
return newTaskQueue0(DEFAULT_MAX_PENDING_TASKS);
}
return queueFactory.newTaskQueue(DEFAULT_MAX_PENDING_TASKS);
}
protected SingleThreadEventLoop(EventLoopGroup parent, Executor executor,
boolean addTaskWakesUp, Queue<Runnable> taskQueue, Queue<Runnable> tailTaskQueue,
RejectedExecutionHandler rejectedExecutionHandler) {
super(parent, executor, addTaskWakesUp, taskQueue, rejectedExecutionHandler);
//tailTaskQueue尾部任务队列
tailTasks = ObjectUtil.checkNotNull(tailTaskQueue, "tailTaskQueue");
}
protected SingleThreadEventExecutor(EventExecutorGroup parent, Executor executor,
boolean addTaskWakesUp, Queue<Runnable> taskQueue,
RejectedExecutionHandler rejectedHandler) {
super(parent);
this.addTaskWakesUp = addTaskWakesUp;
this.maxPendingTasks = DEFAULT_MAX_PENDING_EXECUTOR_TASKS;
this.executor = ThreadExecutorMap.apply(executor, this);
//任务队列
this.taskQueue = ObjectUtil.checkNotNull(taskQueue, "taskQueue");
this.rejectedExecutionHandler = ObjectUtil.checkNotNull(rejectedHandler, "rejectedHandler");
}
总结:1、初始化的过程中打开了selecor,等待注册。
2、netty中的channel需要注册到selector上,其实就是要注册到EventLoopGroup中的一个EventLoop的selector上。
参考链接:https://nyimac.gitee.io/2021/04/25/Netty%E5%9F%BA%E7%A1%80/




