C++数据结构学习之顺序表
顺序表是数据结构中最基本也是应用相当广泛的一种数据结构类型。它通常包含三个私有成分,即指向数据数组的头指针、当前表长以及表的实际容量。表的头指针通常指向数据数组的基地址,通过数组的形式进行访问数据数组中的每个元素。其基本结构类型如下图所示:
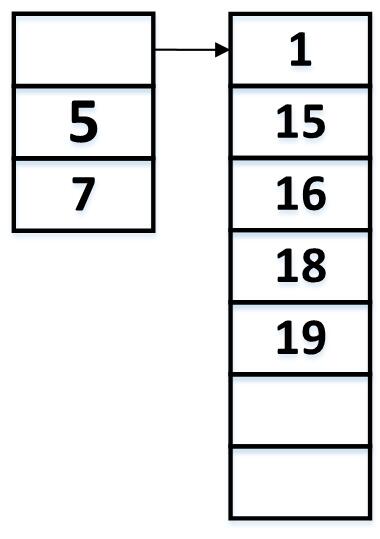
从上图可以看到,其基本结构包含一个指向数据数组的头指针,当前表长为5,但是该顺序表实际表的容量有7。
下面附上实现该数据结构的各项操作代码
在C.h文件中存放可能要用到的C++库:
1 #ifndef _C_H_ 2 #define _C_H_ 3 #include<iostream> 4 #include<fstream> 5 #include<iomanip> 6 #include<cmath> 7 #include<vector> 8 #include<list> 9 #include<stack> 10 #include<queue> 11 #include<deque> 12 #include<string> 13 #include<bitset> 14 #include<algorithm> 15 #include<ctime> 16 #include<cstdarg> 17 #include<assert.h> 18 using namespace std; 19 #endif // _C_H_
在SequenceTable.h存放对应的数据结构类型:
1 #ifndef _SEQUENCETABLE_H_ 2 #define _SEQUENCETABLE_H_ 3 template<typename T>class STL{ 4 private: 5 T *elem; //save the base address of STL 6 int length; //save the current length of STL; 7 int listsize; //save the opacity of STL 8 public: 9 //a function to create k length STL, if k doesn't exist, it can use default function to create 1 length STL 10 STL(int k=1){ 11 elem = new T[k]; 12 length = 0; 13 listsize = k; 14 } 15 //destruct STL 16 ~STL(){ 17 delete[]elem; 18 } 19 int getLength(); 20 int getListsize(); 21 void Insert(int k, int data); //a function to insert elem in the specific location 22 void Delete(int k, int data); //a function to delete elem in the specific location 23 int getElem(int k); //get elem in the specific location 24 int getLocation(int data); 25 void ListEmpty(); 26 void showSTL(); 27 }; 28 29 template<typename T> 30 int STL<T>::getListsize(){ 31 return listsize; 32 } 33 34 template<typename T> 35 int STL<T>::getLength(){ 36 return length; 37 } 38 39 template<typename T> 40 void STL<T>::Insert(int k, int data){ 41 //confirm whether the k is reasonable 42 if(k <= 0 || k > (length+1)){ 43 cout<<"k is unreasonable!"<<endl; 44 } 45 int t; //an empty bottle 46 //insert data while satisfy this situation 47 while(length<listsize && k<=length){ 48 if(k<length){ 49 t = elem[k]; 50 elem[k] = data; 51 data = elem[k+1]; 52 k++; 53 } 54 else{ 55 length++; 56 t = elem[k]; 57 elem[k] = data; 58 data = elem[k+1]; 59 k++; 60 } 61 } 62 if(k==(length+1)){ 63 if(length<listsize){ 64 length++; 65 elem[k] = data; 66 } 67 else{ 68 listsize++; 69 length++; 70 elem[k] = data; 71 } 72 } 73 } 74 75 template<typename T> 76 void STL<T>::Delete(int k, int data){ 77 //confirm whether the k is reasonable 78 if(k <= 0 || k > (length+1)){ 79 cout<<"k is unreasonable!"<<endl; 80 } 81 //insert data while satisfy this situation 82 if(elem[k]==data){ 83 while(k<=length){ 84 if(k<length){ 85 elem[k] = elem[k+1]; 86 k++; 87 } 88 else{ 89 k++; 90 } 91 } 92 length--; 93 } 94 else{ 95 cout<<"delete error!"<<endl; 96 } 97 } 98 99 template<typename T> 100 int STL<T>::getLocation(int data){ 101 int i = 0; //consider when the length is 0 but the listsize is 1 102 while(i<=length){ 103 if(elem[i] == data){ 104 return i; 105 } 106 i++; 107 } 108 } 109 110 template<typename T> 111 int STL<T>::getElem(int k){ 112 if(k<=0 || k>=(length+1)){ 113 cout<<"k is unreasonable!"<<endl; 114 } 115 else{ 116 return elem[k]; 117 } 118 119 } 120 121 template<typename T> 122 void STL<T>::ListEmpty(){ 123 length = 0; 124 } 125 126 template<typename T> 127 void STL<T>::showSTL(){ 128 for(int i=1;i<=length; i++){ 129 cout<<elem[i]<<endl; 130 } 131 } 132 #endif
然后再main.cpp文件中实现对该数据结构的调用:
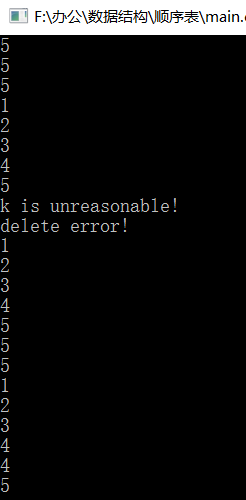
1 #include "C.h" 2 #include "SequenceTable.h" 3 typedef int T; 4 int main(){ 5 STL<T> L; 6 for(int i=0; i<5;i++){ 7 L.Insert(i+1, i+1); 8 } 9 cout<<L.getLocation(5)<<endl; 10 cout<<L.getLength()<<endl; 11 cout<<L.getListsize()<<endl; 12 L.showSTL(); 13 int a = L.getElem(0); 14 L.Delete(1,5); 15 L.showSTL(); 16 cout<<L.getLength()<<endl; 17 cout<<L.getListsize()<<endl; 18 L.Delete(5,5); 19 L.showSTL(); 20 cout<<L.getLength()<<endl; 21 cout<<L.getListsize()<<endl; 22 }
运行实现: