Java-异常处理结构
1.异常(Exception)
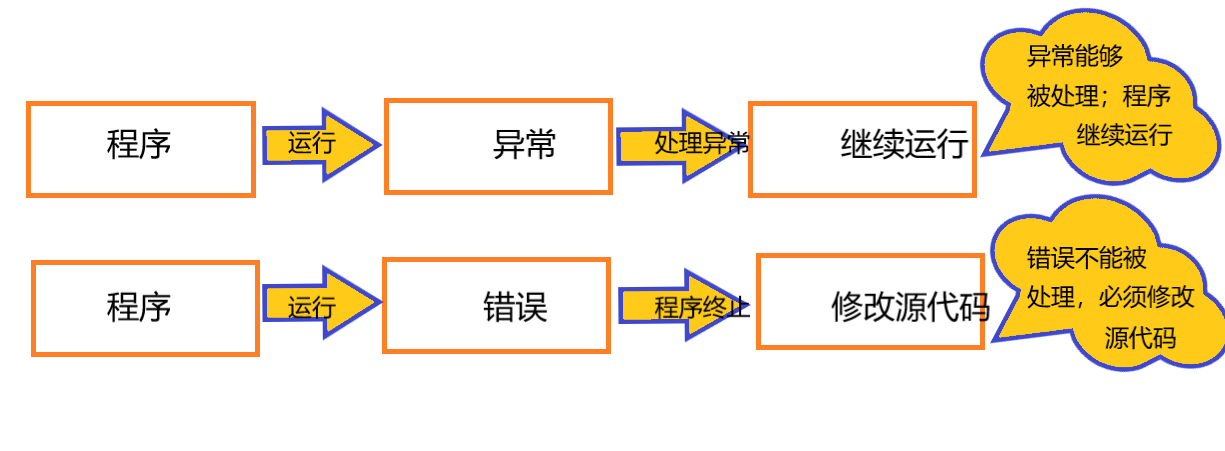
异常指的是程序运行时发生的不正常事件;异常能够被程序处 理,保证程序继续运行下去;例如除数为0、文件没有找到、输入的数字格式不对……
下面程序因为除数为0,所以发生了异常
-
public class Test1 { public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println("程序出现异常案例:"); //出现异常java.lang.ArithmeticException算数错误情形 System.out.println(100 / 0); System.out.println("程序继续运行"); } }
2.错误(Error)
错误(Error):错误程序没法处理,例如内存泄漏。发生错误后,一般虚拟机会选择 终止程序运行,程序员需要修改代码才能解决相关错误;
下面程序因为数组长度过长,内存溢出
-
public class Test1 { public static void main(String[] args) { //出现错误java.lang.OutOfMemoryError堆内存溢出 int [] a =new int[1024*1204*1024]; } }
知识点2-熟悉异常结构及常见运行时异常
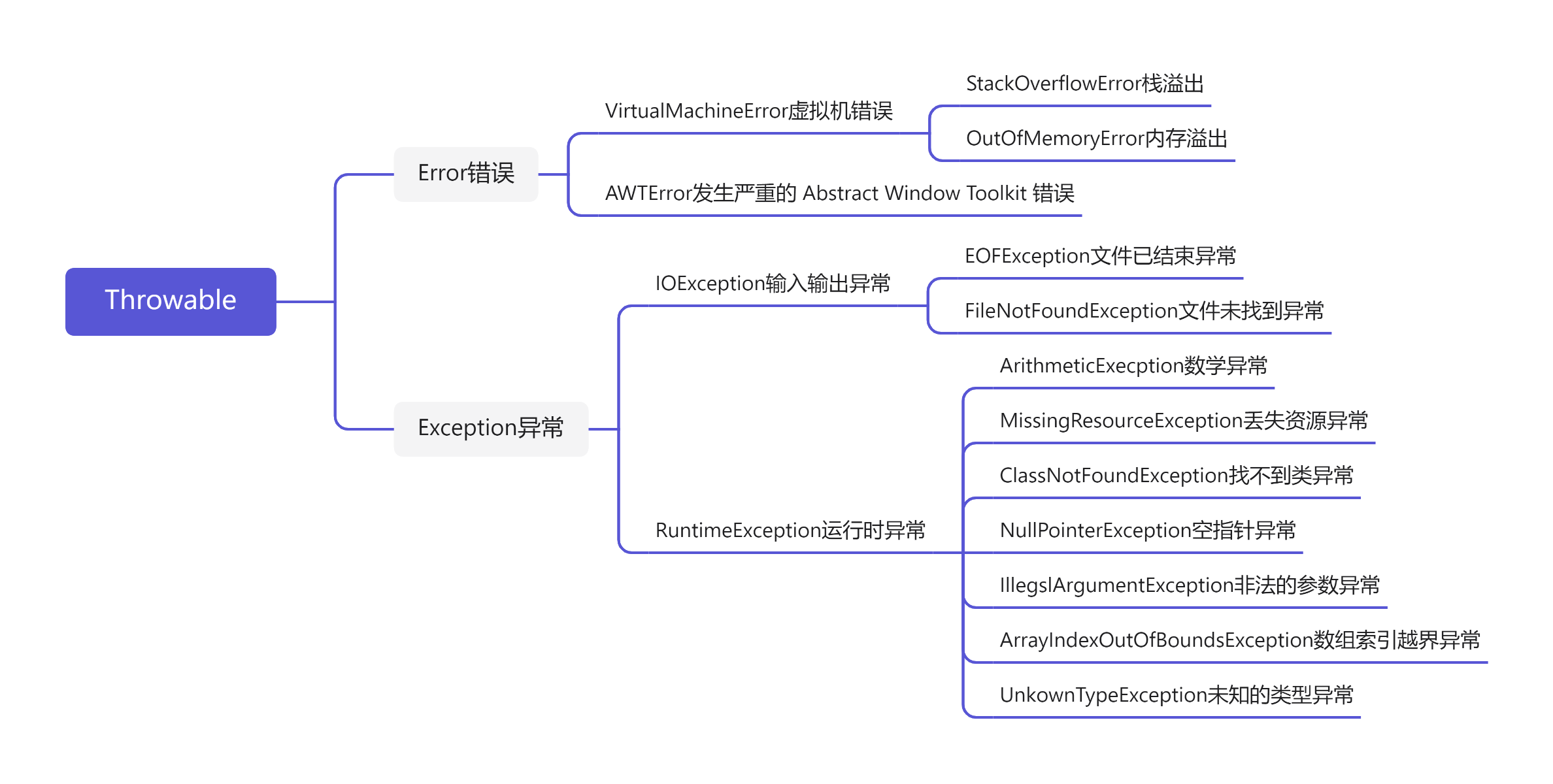
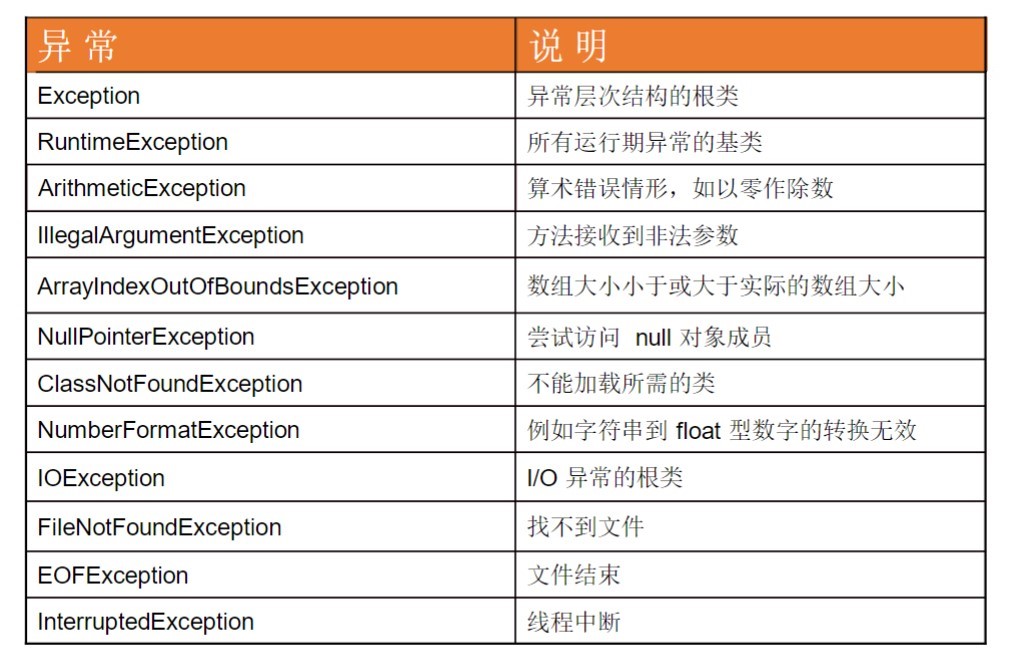
1.异常层次关系:
2.Throwable类
API中标准异常的顶级父类是Throwable类;
Throwable类有两个子类:Exception和Error;所有异常都是Exception类的直接或 间接子类;所有错误都是Error的直接或间接子类;
3.Exception
Exception有很多子类;这些子类又可以分为两大类;
3.1.运行时异常
RuntimeException的子类都是运行时异常
-
运行时异常:也称为非检测异常(unchecked Exception), 这些异常在编译 期不检测,程序中可以选择处理,也可以不处理,编译通过,如果不处理运行时 会中断,但是编译没问题;
-
NullPointerException-空指针异常
-
发生前提:当对一个空对象,即没有初始化,依然为null的对象调用属性或方法时;
public class RuntimeExceptionTest { public static void main(String[] args) { // test01(); test02(); } private static void test01() { String str = null; //出现异常java.lang.NullPointerException空指针异常 System.out.println(str.length()); } private static void test02() { String str = ""; //输出0,不会发生空指针异常 System.out.println(str.length()); } } -
-
ArithmeticException-数学异常
-
发生前提:整数除以0时发生数学异常
-
浮点数除以0不会发生数学异常
1 public class Test { 2 public static void main(String[] args) { 3 //不抛出异常,输出Infinity 4 System.out.println(10.0 / 0); 5 //数学异常 6 //抛出异常java.lang.ArithmeticException: / by zero 7 System.out.println(10 / 0); 8 } -
-
IndexOutOfBoundsException:索引越界异常
-
字符串索引StringIndexOutOfBoundsException
-
数组索引ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException
-
发生前提:当访问字符串中的字符或者数组中的元素,超过了其长度时
public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { int a[] = new int[3]; //数组索引java.lang.ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException: 3 //异常类型 : 提示信息 System.out.println(a[3]); } }public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { //字符串索引java.lang.StringIndexOutOfBoundsException: String index out of range: 17 //异常类型 : 提示信息 String str = "SEVENTEEN"; System.out.println(str.charAt(17)); } } -
-
NumberFormatException-数字格式异常
-
发生前提:当把一个字符串转换成数字时,字符串内容不是数字时发生
public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { String str = "carat"; //数字格式异常 //java.lang.NumberFormatException: For input string: "carat" System.out.println(Integer.valueOf(str)); } } -
-
ClassCastException-类型转换异常
-
发生前提:把父类对象转换成不相关的子类类型时
public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { Object o = new Object(); //类型转换异常 //java.lang.ClassCastException: java.lang.Object cannot be cast to java.lang.String String s = (String)o; System.out.println(s); } } -
-
3.2.非运行时异常:其他的都是非运行时异常
-
也称为检测异常(checked Exception), 在编译期就会被检测,是必须进行处理 的异常,如果不处理,将发生编译期错误;
public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { //Java: 未报告的异常错误java.io.FileNotFoundException; 必须对其进行捕获或声明以便抛出 FileReader f = new FileReader("a.txt"); } }
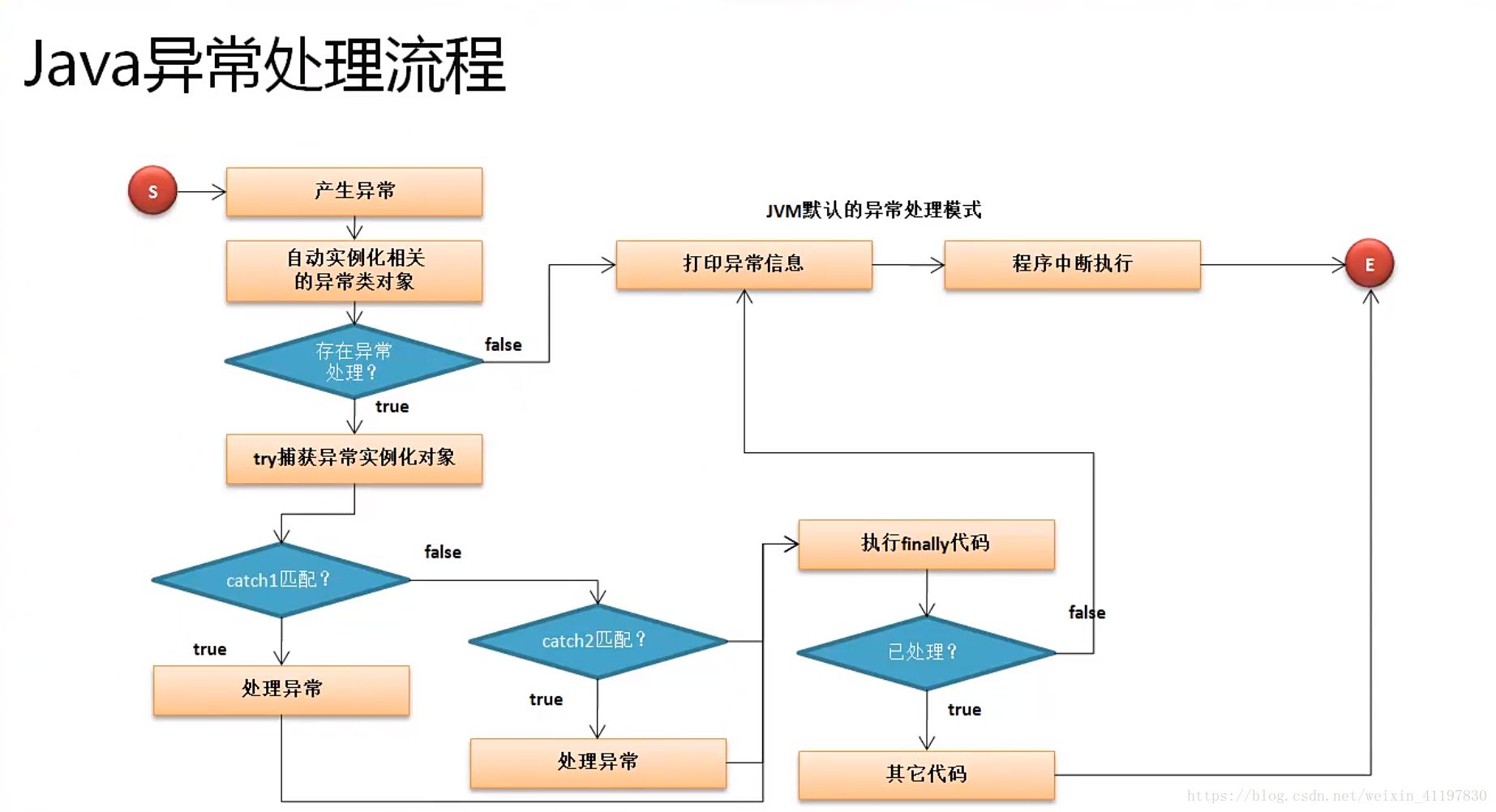
4.标准异常处理流程
转载图
5.try-catch-finally
Java语言中异常处理主要使用到try/catch/finally三种语句
5.1.语法
try{
可能抛出异常的代码块;
}catch(异常类型 变量名){
处理异常的代码;
}finally{
不管什么情况,一定被执行的代码块;
}
5.2. 异常会发生三种情况:
- 发生异常被捕获处理;
- 发生异常没有被捕获处理;
- 没发生异常
当try块中中代码抛出了异常对象后,异常处理机制就将这个对象的类型与try后的 catch语句中的异常类型进行匹配,如果类型相同,或者抛出的是捕获的子类,就称 为匹配成功,那么异常就被捕获,就运行catch块中的语句;否则,称为异常没有被 捕获,程序将中断;
5.2.1. 抛出异常并处理成功
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
int x = 100;
int y = 0;
///抛出 ArithmeticException异常,try中之后代码不运行
System.out.println("x/y=" + (x / y));
System.out.println("计算完成");
//异常处理机制将 ArithmeticException与catch语句的异常类型匹配
//匹配成功,运行catch代码块,异常被处理;
} catch (ArithmeticException e) {
//程序继续运行。
System.out.println("处理数学异常");
}
}
}
5.2.2. 抛出异常,但是没有被处理
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
int x = 100;
int y = 0;
///抛出 ArithmeticException异常,try中之后代码不运行
System.out.println("x/y=" + (x / y));
System.out.println("计算完成");
//异常处理机制将 ArithmeticException与catch语句的异常类型匹配
//匹配失败,不运行catch代码块,异常不被处理;
} catch (NullPointerException e) {
//程序中断。
System.out.println("处理数学异常");
}
}
}
5.2.3. 没有抛出异常
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
int x = 100;
int y = 100;
//没有抛出 ArithmeticException异常
System.out.println("x/y=" + (x / y));
System.out.println("计算完成");
//跳过catch代码块
} catch (ArithmeticException e) {
//不执行
System.out.println("处理数学异常");//运行结束
}
}
}
5.3. catch语句里都写什么代码
-
可以写任意需要对异常进行处理的代码;
-
可以调用异常对象的方法,例如printStackTrace,查看异常发生的栈轨迹
public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { //没有发生异常 try { int x = 100; int y = 0; System.out.println("x/y=" + x / y); System.out.println("x/y计算结束"); } catch (ArithmeticException e) { e.printStackTrace(); System.out.println("发生了数学异常,注意除数不能为0."); } System.out.println("main方法运行结束"); } }
5.4. 多个catch语句
-
如果try块中有多行代码,可能抛出多种类型异常,可以使用多个catch语句,当捕获一个catch时,就不匹配其他的catch;
- 如果catch的类型Exception放在第一位,后面的catch就没有意义了(编译错误);
-
注意:catch语句的异常类型必须从子类到父类的顺序,否则编译错误;
public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { try { int x = 100; int y = 0; String s = null; //当y=0时,发生数学异常,运行 catch(ArithmeticException e)代码块; System.out.println("x/y=" + x / y); System.out.println("x/y计算结束"); System.out.println("字符串长度" + s.length()); //当y不等于0时, 发生空指针异常,运行catch(NullPointerException e)代码块; } catch (ArithmeticException e) { System.out.println("发生了数学异常,注意除数不能为0."); } catch (NullPointerException e) { System.out.println("发生了空指针异常"); } catch (Exception e) { //从来不会运行这个catch块,因为没有其他类型异 常;可见异常只要被成功捕获一次,就被处理了,不会再继续抛出了。 System.out.println("发生了其他异常"); } System.out.println("main方法运行结束"); } }
5.5.finally块
如果希望不管什么情况,有一些代码都必须被执行,那么就可以把这些代码写到 finally块中。
5.6. try-finally
必须有try,catch可以有1个或多个,finally最多1个,可以没有,不能有多个; 还有另外一种组合:只有try和finally,没有catch
如果try块中抛出了异常,则肯定不能被捕获,程序中断,但是finally代码块依然会被执行
5.6.1. 发生异常时的运行结果
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
int x = 100;
int y = 0;
System.out.println("x/y=" + x / y);
System.out.println("x/y计算结束");
} finally {
System.out.println("finally代码块");
}
System.out.println("main方法运行结束");
}
}
/*
finally代码块
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.ArithmeticException: / by zero
at com.tjetc.Test.main(Test.java:10)
*/
5.6.2. 没发生异常时的运行结果
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
int x = 100;
int y = 10;
System.out.println("x/y=" + x / y);
System.out.println("x/y计算结束");
} finally {
System.out.println("finally代码块");
}
System.out.println("main方法运行结束");
}
}
/*
x/y=10
x/y计算结束
finally代码块
main方法运行结束
*/
6.throw关键字在方法体中使用
抛出异常其实就是创建了一个异常对象,然后用throw关键字交给异常处理机制去处 理;throw关键字在方法体中使用,用法如下:
1.throw 异常对象 throw new Exception();
2.catch(Exception e){ throw e;}
6.1. 运行时异常是JVM自动抛出
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
int x = 100;
int y = 0;
//JVM自行执行了一条抛出异常语句:throw new ArithmeticException();
System.out.println("x/y=" + x / y);//抛出ArithmeticException异 常,try中之后代码不运行
System.out.println("x/y计算结束");
} catch (ArithmeticException e) {//异常处理机制将 ArithmeticException与catch语句的异常类型匹配
System.out.println("发生了数学异常,注意除数不能为0.");//匹配成 功, 运行catch代码块,异常被处理;
}
System.out.println("main方法运行结束");//程序继续运行。
}
}
/*
发生了数学异常,注意除数不能为0.
main方法运行结束
*/
6.2. 非运行时异常需要程序员用throw关键字抛出
6.2.1. throw
以下代码发生编译错误:由于抛出了Exception,是非运行时异常,所以编译期检 测,要求必须处理,处理的方式有两种:
-
使用try/catch/finally进行处理;
-
不处理,用throws声明异常;
如果用第一种方法,几乎没有意义,因为调用div方法时,不能再捕获这个异常,不能灵活处理。
所以,当用throw抛出异常后,基本都使用throws进行声明!
public class Calculator {
public void div(int x,int y){
//当除数为0时,抛出异常
if(y == 0){
throw new Exception();//不处理,编译错误
}
System.out.println(x / y);
}
}
6.2.2. throws
-
throws用在方法声明处,声明该方法可能发生的异常类型;
-
throws后可以声明多种类型,用逗号隔开即可;
-
抽象方法也可以使用throws声明该方法可能抛出的异常类型;
public class Calculator { public void div(int x, int y) throws Exception { //当除数为0时,抛出异常 if (y == 0) { throw new Exception();//使用throws后,不再有编译错误 } System.out.println(x / y); } }
6.2.3. 调用带有throws方法必须处理这些异常
一个方法如果使用了throws,那么调用该方法时,编译期会提醒必须处理这些异常,否则编译错误;
public class Calculator {
public void div(int x, int y) throws Exception {
//当除数为0时,抛出异常
if (y == 0) {
throw new Exception();//使用throws后,不再有编译错误
}
System.out.println(x / y);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Calculator c = new Calculator();
//未报告的异常错误java.lang.Exception; 必须对其进行捕获或声明以便抛出
c.div(10, 1);
}
}
依然可以用两种方法处理,可以try/catch,可以继续throws(二选一即可)
public class Calculator {
public void div(int x, int y) throws Exception {
//当除数为0时,抛出异常
if (y == 0) {
throw new Exception();//使用throws后,不再有编译错误
}
System.out.println(x / y);
}
public static void main(String[] args)/*方式一:*/throws Exception {
Calculator c = new Calculator();
//1、接续抛出,异常处理推迟
//2、try-catch
//方式二
try {
c.div(10, 1);
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("除数不能为0");
}
}
}
6.2.4. 异常先统一处理,可以处理后再抛出
如果希望对异常先统一处理,可以处理后再抛出 调用的时候可以继续处理
public class Calculator {
public void div(int x, int y) throws Exception { //当除数为0时,抛出异常
try {
if (y == 0) {
throw new Exception(); //使用throws后,不再有编译错误
}
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("Calculator发生了异常");
throw e;//将异常继续抛出,调用div的方法可以再次捕获处理;
}
System.out.println("x/y=" + x / y);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Calculator calculator = new Calculator();
try {
calculator.div(10, 0);//再次捕获处理了div中的异常对象
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("再处理一次,除数不能为0");
}
}
}
6.2.5. 如果希望不管有没有异常都做统一处理,有异常声明 抛出,可以使用try/finally
public class Calculator {
public void div(int x, int y) throws Exception {
//当除数为0时,抛出异常
try {
if (y == 0) {
throw new Exception(); //使用throws后,不再有编译错误
}
} finally {//不管有没有异常,都运行finally,如果有异常,不会捕获,抛出 给调用者。
System.out.println("不管有没有异常,都运行finally");
}
System.out.println("x/y=" + x / y);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Calculator calculator = new Calculator();
try {
calculator.div(10, 0);//捕获处理了div中的异常对象
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("除数不能为0");
}
}
}
6.2.6. 总结throw和throws的区别
throws和throw
throws在方法后边声明异常,其实就是自己不想对异常做出任何的处理,告诉别人 自己可能出现的异常,交给别人处理,然别人处理
throw:就是自己处理一个异常,有两种方式要么是自己捕获异常try...catch代码块,
要么是抛出一个异常(throws 异常)
-
throws:用来声明一个方法可能产生的所有异常,不做任何处理而是将异常往 上传,谁调用我我就抛给谁。
用在方法声明后面,跟的是异常类名
可以跟多个异常类名,用逗号隔开
表示抛出异常,由该方法的调用者来处理 throws表示出现异常的一种可能性,并不一定会发生这些异常
-
throw:则是用来抛出一个具体的异常类型。
用在方法体内,跟的是异常对象名
只能抛出一个异常对象名
表示抛出异常,由方法体内的语句处理 throw则是抛出了异常,执行throw则一定抛出了某种异常
7. 自定义异常类
7.1.多层次异常处理的方式
-
为了能够标记项目中的异常事件,需要使用throw抛出异常;
-
如果抛出的是API中的标准异常,那么很可能与API中方法抛出的异常混淆,因 此需要自定义异常;
-
项目组根据业务需求定义业务异常,对团队协作开发非常有意义
7.2.自定义业务异常的实现方法和一般规则
7.2.1.自定义异常类实现
-
自定义异常类非常简单,只要继承API中任意一个标准异常类即可;
-
多数情况下,继承Exception类;也可以选择继承其他类型异常;
-
一般自定义异常类中不写其他方法,只重载必要的构造方法;
public class DataValueException extends Exception {
public DataValueException() {
}
public DataValueException(String message) {
super(message);
}
public DataValueException(Throwable cause) {
super(cause);
}
public DataValueException(String message, Throwable cause) {
}
}
7.2.2.使用自定义异常与使用API中标准异常一样
-
可以用throw抛出自定义异常对象,使用throws声明自定义异常类型;
-
可以使用try/catch/finally处理异常;
public class Employee{ private String name; private double salary; @Override public String toString() { return "Employee{" + "name='" + name + '\'' + ", salary=" + salary + '}'; } public Employee(String name, double salary) { this.name = name; this.salary = salary; } public String getName() { return name; } public double getSalary() { return salary; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public void setSalary(double salary) throws DataValueException { if (salary <= 2500) { //setSalary方法对参数值有要求,不能低于2500,如果低于2500则抛出自定义的 DataValueException异常; throw new DataValueException("薪资不能低于2500元"); } else { this.salary = salary; } } public static void main(String[] args) { Employee e = new Employee("张晓明", 3000); try { e.setSalary(2400); } catch (DataValueException e1) { e1.printStackTrace(); } } }

 1、掌握异常的概念
2、熟悉异常结构及常见运行时异常
3、掌握异常的处理-捕获异常try、catch和finally
4、掌握异常的处理-层层抛出
5、了解finally与return和System类的exit方法
6、掌握自定义异常
1、掌握异常的概念
2、熟悉异常结构及常见运行时异常
3、掌握异常的处理-捕获异常try、catch和finally
4、掌握异常的处理-层层抛出
5、了解finally与return和System类的exit方法
6、掌握自定义异常



【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 分享一个免费、快速、无限量使用的满血 DeepSeek R1 模型,支持深度思考和联网搜索!
· 基于 Docker 搭建 FRP 内网穿透开源项目(很简单哒)
· ollama系列01:轻松3步本地部署deepseek,普通电脑可用
· 按钮权限的设计及实现
· 25岁的心里话