hashMap理解以及jdk1.7、jdk1.8其中区别
package test; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.Map; public class testHashMap { public static void main(String[] args) { Map<Integer, String> map = new HashMap<Integer, String>(); map.put(1, "小明"); } }
网上有很多优秀的讲解hashmap源码的文章,写这个随笔只是想加强下自己的理解,有错误的地方欢迎指正
首先,hashmap的存储结构,图来自网络
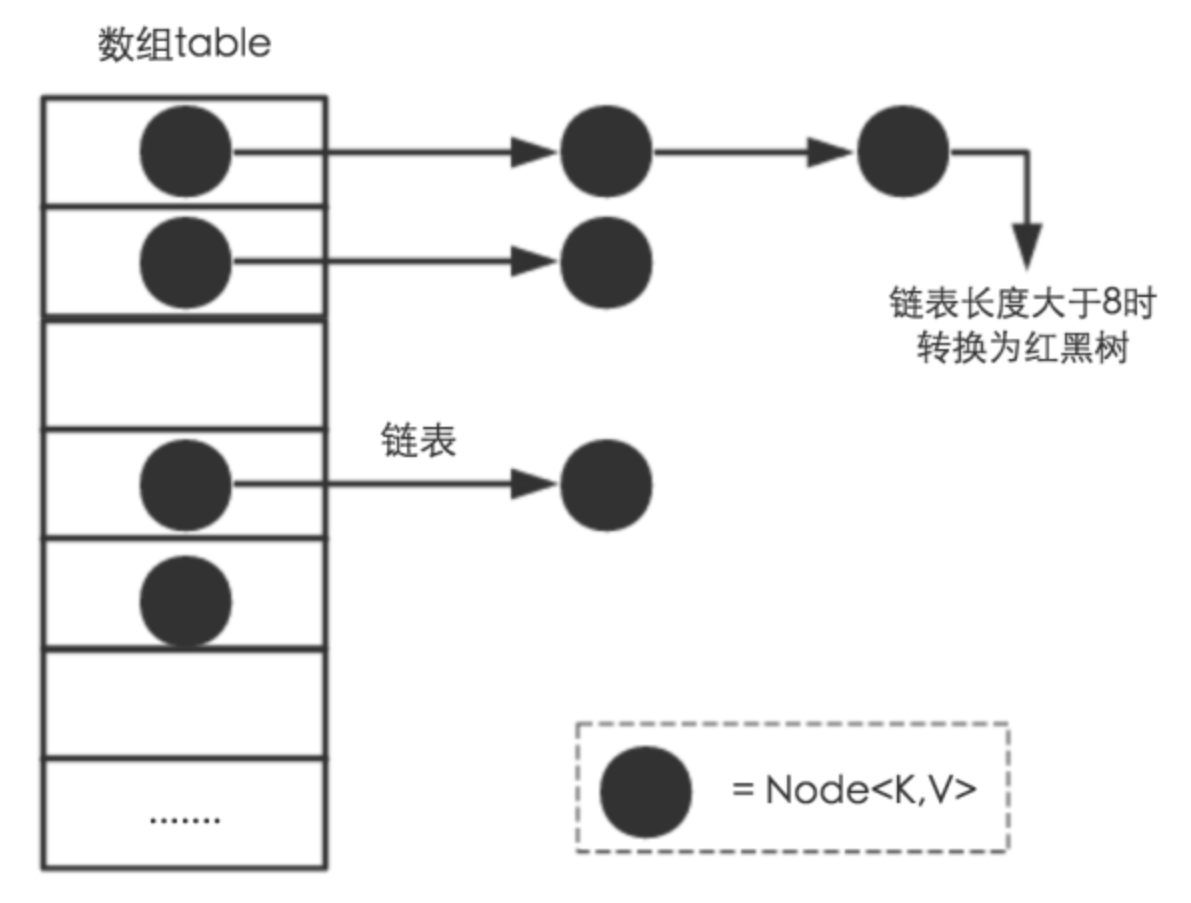
注:链表长度大于8切
此处引入的是jdk1.8
从put处(Ctrl+alt+B)进入到源码HashMap.java中的put方法
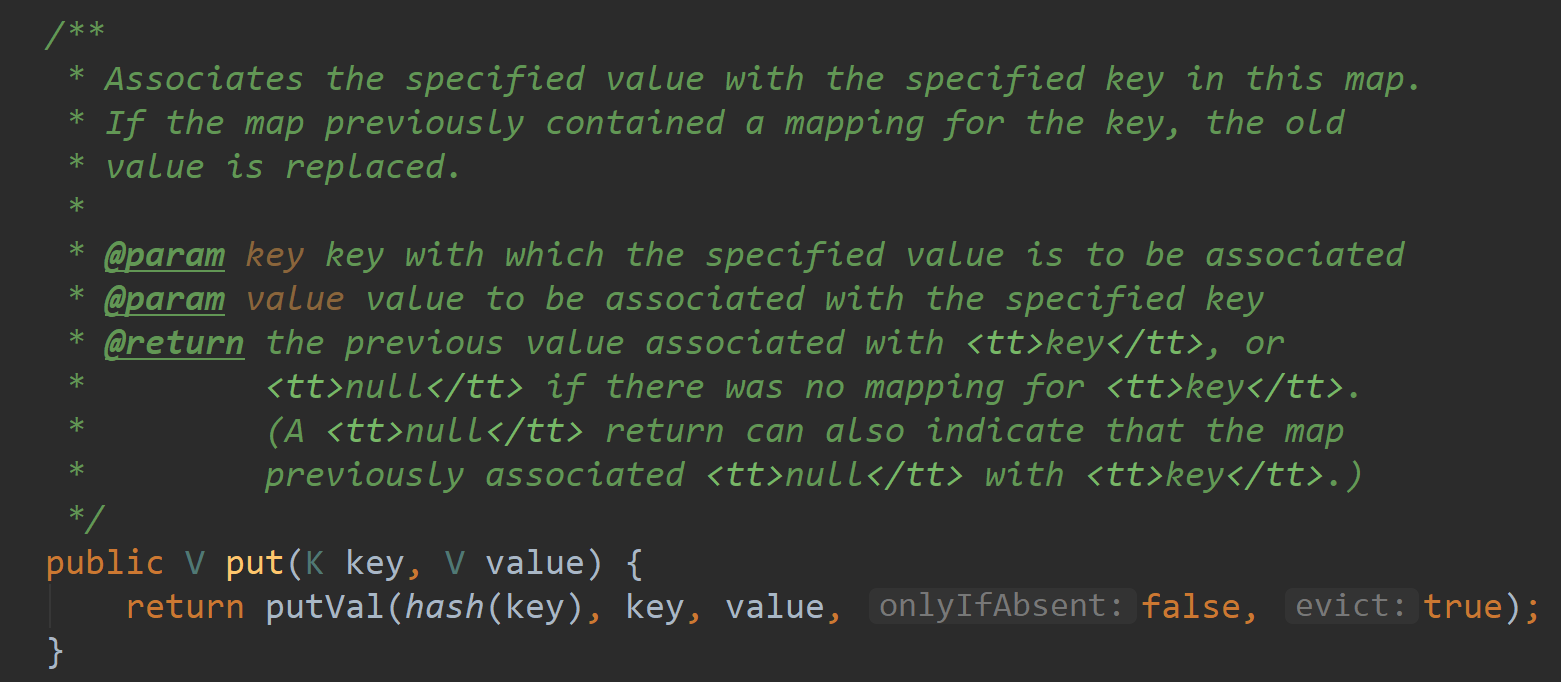
注意hash(key)

贴一个解释的很好的贴子https://www.cnblogs.com/zxporz/p/11204233.html
putVal源码如下:
final V putVal(int hash, K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent,
boolean evict) {
//jdk1.8 Node<K,V>[] tab是hashMap类中有一个非常重要的字段,即哈希桶数组
Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> p; int n, i;
//判断table是否为空
if ((tab = table) == null || (n = tab.length) == 0)
n = (tab = resize()).length;
//table不为空,根据(n-1)&hash算出key的落点,并且判断落点处为空,则将数据put进来
if ((p = tab[i = (n - 1) & hash]) == null)
tab[i] = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
//落点处不为空
else {
Node<K,V> e; K k;
//key值相同则替换
if (p.hash == hash &&
((k = p.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
e = p;
//为红黑树结构,则走红黑树的方法
else if (p instanceof TreeNode)
e = ((TreeNode<K,V>)p).putTreeVal(this, tab, hash, key, value);
//链表结构,循着链表继续向下寻找
else {
for (int binCount = 0; ; ++binCount) {
if ((e = p.next) == null) {
p.next = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD - 1) // -1 for 1st
treeifyBin(tab, hash);
break;
}
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
break;
p = e;
}
}
if (e != null) { // existing mapping for key
V oldValue = e.value;
if (!onlyIfAbsent || oldValue == null)
e.value = value;
afterNodeAccess(e);
return oldValue;
}
}
++modCount;
if (++size > threshold)
//扩容
resize();
afterNodeInsertion(evict);
return null;
}
说到扩容,就得看一下hashmap中几个重要的参数了,hashmap源码中的构造函数如下:
/** * Constructs an empty <tt>HashMap</tt> with the specified initial * capacity and load factor. * * @param initialCapacity the initial capacity * @param loadFactor the load factor * @throws IllegalArgumentException if the initial capacity is negative * or the load factor is nonpositive */ public HashMap(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor) { if (initialCapacity < 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal initial capacity: " + initialCapacity); if (initialCapacity > MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) initialCapacity = MAXIMUM_CAPACITY; if (loadFactor <= 0 || Float.isNaN(loadFactor)) throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal load factor: " + loadFactor); this.loadFactor = loadFactor; this.threshold = tableSizeFor(initialCapacity); } /** * Constructs an empty <tt>HashMap</tt> with the specified initial * capacity and the default load factor (0.75). * * @param initialCapacity the initial capacity. * @throws IllegalArgumentException if the initial capacity is negative. */ public HashMap(int initialCapacity) { this(initialCapacity, DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR); } /** * Constructs an empty <tt>HashMap</tt> with the default initial capacity * (16) and the default load factor (0.75). */ public HashMap() { this.loadFactor = DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR; // all other fields defaulted } /** * Constructs a new <tt>HashMap</tt> with the same mappings as the * specified <tt>Map</tt>. The <tt>HashMap</tt> is created with * default load factor (0.75) and an initial capacity sufficient to * hold the mappings in the specified <tt>Map</tt>. * * @param m the map whose mappings are to be placed in this map * @throws NullPointerException if the specified map is null */ public HashMap(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> m) { this.loadFactor = DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR; putMapEntries(m, false); }
initialCapacity:初始容量。
capacity:指HashMap中桶的数量。默认值为16。一般第一次扩容时会扩容到64,之后都是以2的幂数增加。
loadFactor:装载因子,默认值为0.75f。
threshold:阀值,满足公式threshold=loadFactor*capacity。当HashMap的size大于threshold时会执行扩容(resize)操作。
关于jdk1.7和jdk1.8的区别:
- jdk1.7 table类型为entry jdk1.8table类型为node
- jdk1.7 存储结构为数组+链表 jdk1.8存储结构为数组+链表+红黑树
注:并不是链表长度大于8就转红黑树。当数组长度小于64的时候,会先选择扩容,当数组长度扩容到大于64且链表长度大于8的时候才会转红黑树
![]()







