vue项目、路由
Vue项目创建
1) 进入存放项目的目录
>: cd vue_project
2) 创建项目
>: vue create v-proj
3) 项目初始化
- 输入
npm run serve初始化项目
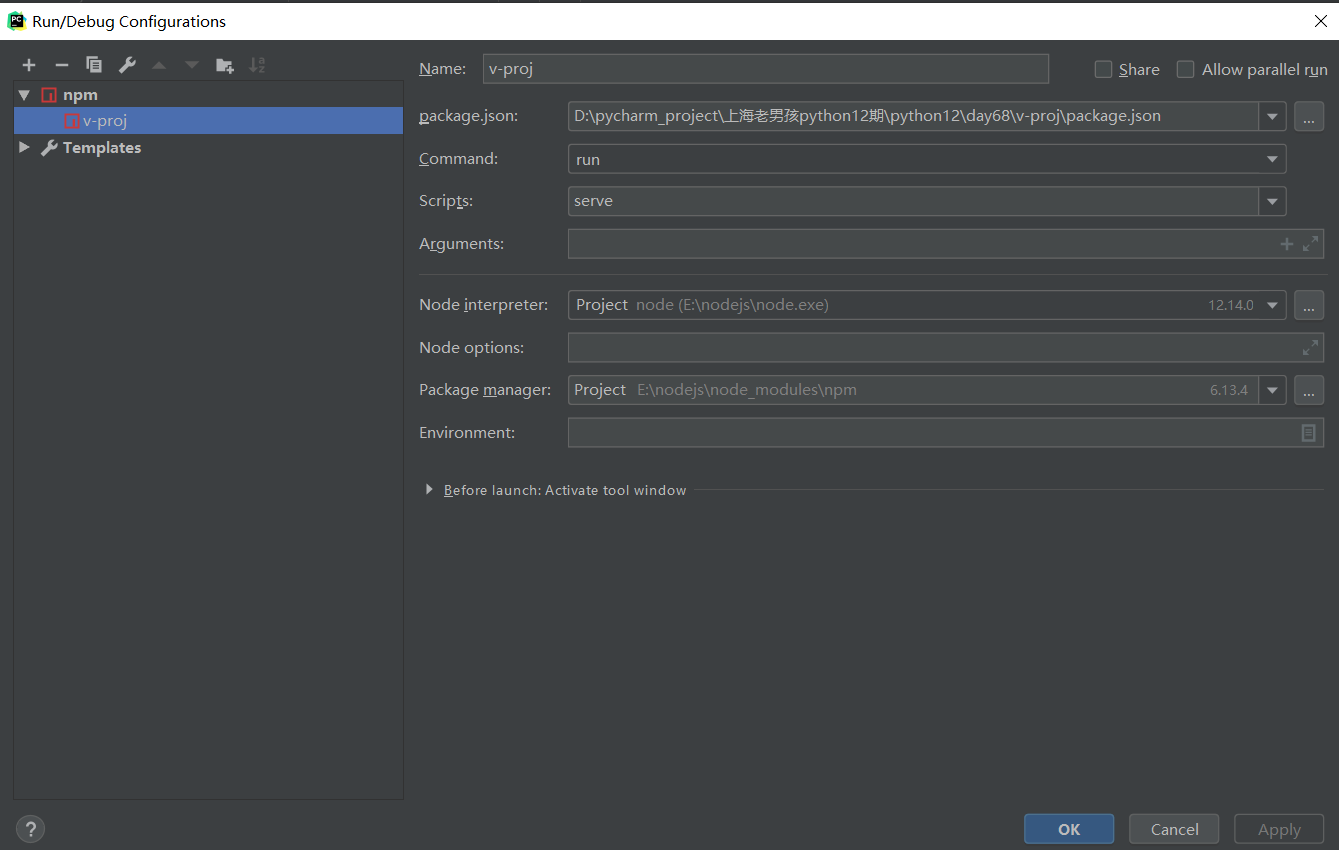
pycharm配置并启动vue项目
1) 用pycharm打开vue项目
2) 添加配置npm启动
vue项目目录结构分析
├── v-proj
| ├── node_modules // 当前项目所有依赖,一般不可以移植给其他电脑环境
| ├── public
| | ├── favicon.ico // 标签图标
| | └── index.html // 当前项目唯一的页面
| ├── src
| | ├── assets // 静态资源img、css、js
| | ├── components // 小组件
| | ├── views // 页面组件
| | ├── App.vue // 根组件
| | ├── main.js // 全局脚本文件(项目的入口)
| | ├── router
| | | └── index.js// 路由脚本文件(配置路由 url链接 与 页面组件的映射关系)
| | └── store
| | | └── index.js// 仓库脚本文件(vuex插件的配置文件,数据仓库)
| ├── README.md
└ └── package.json等配置文件
js原型补充
function A() {}
let a1 = new A();
let a2 = new A();
// 为A类添加原型 类似于类属性
A.prototype.num = 100;
console.log(a1.num);
console.log(a2.num);
// ES6语法下的类
class B {
constructor(name) {
this.name = name
}
}
let b1 = new B('cwz');
let b2 = new B('neo');
B.prototype.count = 666;
console.log(b1.count);
console.log(b2.count);
console.log(b1.name);
console.log(b2.name);
vue项目生命周期
全局脚本文件main.js 文件入口
import Vue from 'vue'
import App from './App.vue'
import router from './router'
import store from './store'
Vue.config.productionTip = false
new Vue({
router,
store,
render: h => h(App)
}).$mount('#app');
改为:
// 项目一启动,加载一堆环境
import Vue from 'vue'
import App from './App.vue'
import router from './router'
import store from './store'
Vue.config.productionTip = false
// 创建根组件
new Vue({ // 挂载、 渲染挂载点
el: '#app',
router: router, // 把路由、仓库配置到vue对象中
store: store,
render: function (read_vue_fn) {
return read_vue_fn(App)
}
});
-
启动项目,加载主脚本文件 mian.js,加载vue环境, 创建根组件完成渲染;加载系统已有的第三方环境:router、store;加载自定义的第三方环境与自己配置的环境,后期项目不断添加
-
router被加载,就会解析router文件夹下的index.js脚本文件,完成路由-组件 的映射关系
-
新建视图组件.vue(在views文件夹中), 在路由中配置(在router的index.js中),设置路由跳转(在导航栏组件中)
<router-link to="/user">去用户页面</router-link> 完成标签跳转 this.$router.push('/user') 完成逻辑跳转
页面组件
views文件夹下新建Home.vue
<!--
template标签负责组件的html结构,有且只有一个根标签
-->
<template>
<div class="home">
<h1>主页</h1>
<hr>
<Nav></Nav>
</div>
</template>
<!--
script标签负责组件的js逻辑:逻辑固定导出(外界才可以导入)
-->
<script>
import Nav from '../components/Nav'
export default {
data() {
return {}
},
methods: {},
components: {
Nav,
}
}
</script>
<!--
style标签负责组件的css样式: scoped保证样式的组件化 样式只在该组件内部起作用
-->
<style scoped>
</style>
根组件 App.vue:
<template>
<div id="app">
<!--页面组件占位符-->
<router-view/>
</div>
</template>
配置自定义全局样式
在mian.js中配置:
// 配置全局样式 @就代表src文件夹的绝对路径
// import '@/assets/css/global.css'
// import './assets/css/global.css'
require('./assets/css/global.css'); // 官方提倡required加载静态文件
路由逻辑跳转
this.$router 控制路由跳转
this.$route 控制路由数据
this.$router.push('/') 往下再跳转一页
this.$router.go(-2) go是历史记录前进后退, 正为前进,负为后退,数字为步数
// router文件夹 index.js中
const routes = [
{
path: '/',
name: 'home',
component: Home
},
{
path: '/course',
name: 'course',
component: Course
},
]
// 其中name的用法:
<router-link :to="{name: 'course'}">课程页</router-link>
路由重定向
const routes = [
{
path: '/',
name: 'home',
component: Home
},
{
path: '/home/',
redirect: '/',
},
]
组件的生命周期钩子
- 一个组件从创建到销毁的众多时间节点回调的方法
- 这些方法都是vue组件 实例的成员
- 生命周期钩子的作用就是满足不同时间节点需要完成的事
new Vue({
el: "#app",
data: {
msg: "message"
},
beforeCreate () {
console.log("组件要创建了");
console.log(this.msg);
},
created () { // 在该钩子中完成后台数据的请求
console.log("实例创建成功, data, methods已拥有");
console.log(this.msg);
},
beforeMount() {
console.log("组件准备加载")
},
mounted () { // 特别耗时的数据请求,可以延后到组件初步加载成功,再慢慢请求
console.log("组件加载完成");
},
destroyed() {
console.log("组件销毁成功了")
}
// 拿到需求 => 确定钩子函数 => 解决需求的逻辑代码块
})
路由传参
第一种:
{
path: '/course/detail',
name: 'course-detail',
component: CourseDetail
}
{
path: '/detail',
redirect: '/course/detail'
}
this.$router.push('/course/detail');
this.$router.push('/course/detail?pk=1'); => this.$route.query.pk
第二种:
{
path: '/course/detail/:pk',
name: 'course-detail',
component: CourseDetail
}
this.$router.push('/course/detail/10'); => this.$route.params.pk


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号