UI基础 - frame | bounds | center
■ 简言
1. UI 是用户能看到的各种各样的页面元素!通俗来讲,iOS App = 各种 UI 控件 + 业务逻辑算法
■ frame | bounds | center
1. frame 是一个 CGRect 结构体,包含 origin、size
其中 origin 也是一个结构体,包含 x、y
同样 size 也是一个结构体,包含 width、height
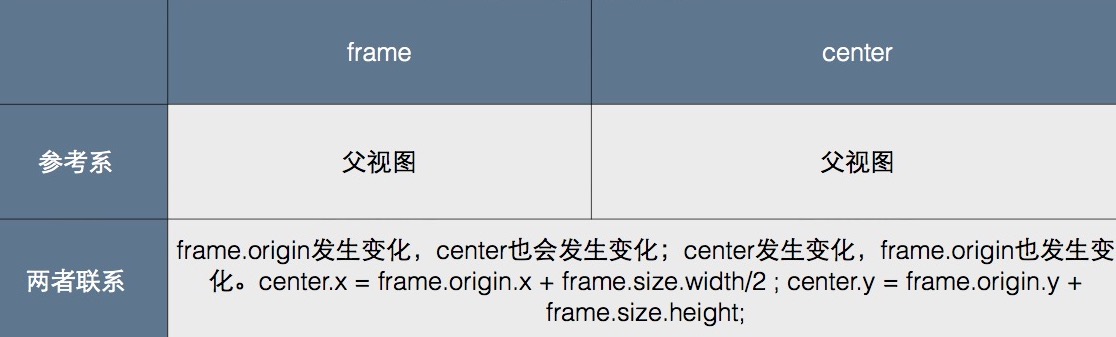
2. center 是一个结构体,包含 x、y,同 frame 的关系如下
center.x = frame.origin.x + frame.size.width/2
center.y = frame.origin.y + frame.size.height/2
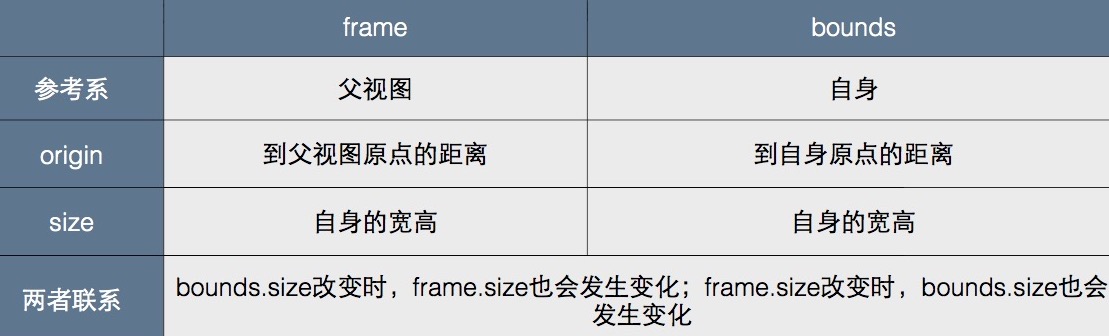
3. bounds 同 frame 一样,也是一个 CGRect 结构体
当一个 view 设置 bounds 时,会把自己当成一个容器,定义自己的边界大小以及左上角的初始坐标
当子视图添加到父视图时,会根据 bounds 指定的原点(0, 0)计算 frame
4. 三者之间的关系

5. 代码示例
1 #import "ViewController.h" 2 @interface ViewController () 3 4 @end 5 6 @implementation ViewController 7 8 - (void)viewDidLoad { 9 [super viewDidLoad]; 10 11 //----------------------------- frame 12 // aView 13 UIView *aView = [[UIView alloc] initWithFrame:CGRectMake(50, 50, 150, 150)]; 14 aView.backgroundColor = [UIColor colorWithRed:arc4random() % 256 / 255.0 green:arc4random() % 256 / 255.0 blue:arc4random() % 256 / 255.0 alpha: 1.0];// 背景颜色:随机 15 //aView.alpha = 0.5; // 透明度一旦改变,所有子视图也随之改变 16 //aView.clipsToBounds = YES;// 默认 NO 17 [self.view addSubview:aView]; 18 19 // bView 20 UIView *bView = [[UIView alloc] initWithFrame:CGRectMake(20, 30, 50, 300)]; 21 // 如果 aView.clipsToBounds = YES,超出父视图的部分将被裁掉 22 bView.backgroundColor = [UIColor redColor]; 23 [aView addSubview:bView]; 24 NSLog(@"bView 的 center:%@", NSStringFromCGPoint(bView.center));// {45, 180} 25 // {20+50/2.0 == 45, 50+300/2.0 = 180} 26 27 // 修改 aView 的 frame 28 aView.frame = CGRectMake(100, 100, 200, 200); 29 NSLog(@"修改 aView 的 frame:%@", NSStringFromCGRect(aView.frame));// {{100, 100}, {200, 200}} 30 NSLog(@"bView 的 center:%@", NSStringFromCGPoint(bView.center));// {45, 180} 31 // {20+50/2.0 == 45, 50+300/2.0 = 180} 32 33 //----------------------------- bounds 34 aView.bounds = CGRectMake(-20, 20, 200, 200); 35 NSLog(@"aView 的 bounds:%@", NSStringFromCGRect(aView.bounds));// {{-20, 20}, {200, 200}} 36 // aView 的 bounds.origin 修改后,子视图 cView.origin 的起始位置改变(往右、上方各移 20 个点) 37 UIView *cView = [[UIView alloc] initWithFrame:CGRectMake(1, 1, 30, 40)]; 38 NSLog(@"cView 的 bounds:%@", NSStringFromCGRect(cView.bounds));// {{0, 0}, {30, 40}} 39 NSLog(@"cView 的 frame:%@", NSStringFromCGRect(cView.frame)); // {{1, 1}, {30, 40}} 40 cView.backgroundColor = [UIColor cyanColor]; 41 [aView addSubview:cView]; 42 NSLog(@"bView 的 bounds:%@", NSStringFromCGRect(bView.bounds));// {{0, 0}, {50, 300}} 43 44 //----------------------------- center 45 NSLog(@"aView 的 center:%@", NSStringFromCGPoint(aView.center));// {200, 200} 46 NSLog(@"cView 的 center:%@", NSStringFromCGPoint(cView.center));// {16, 21} 47 // {1+30/2.0 == 16, 1+40/2.0 = 21} 48 } 49 50 @end
运行效果
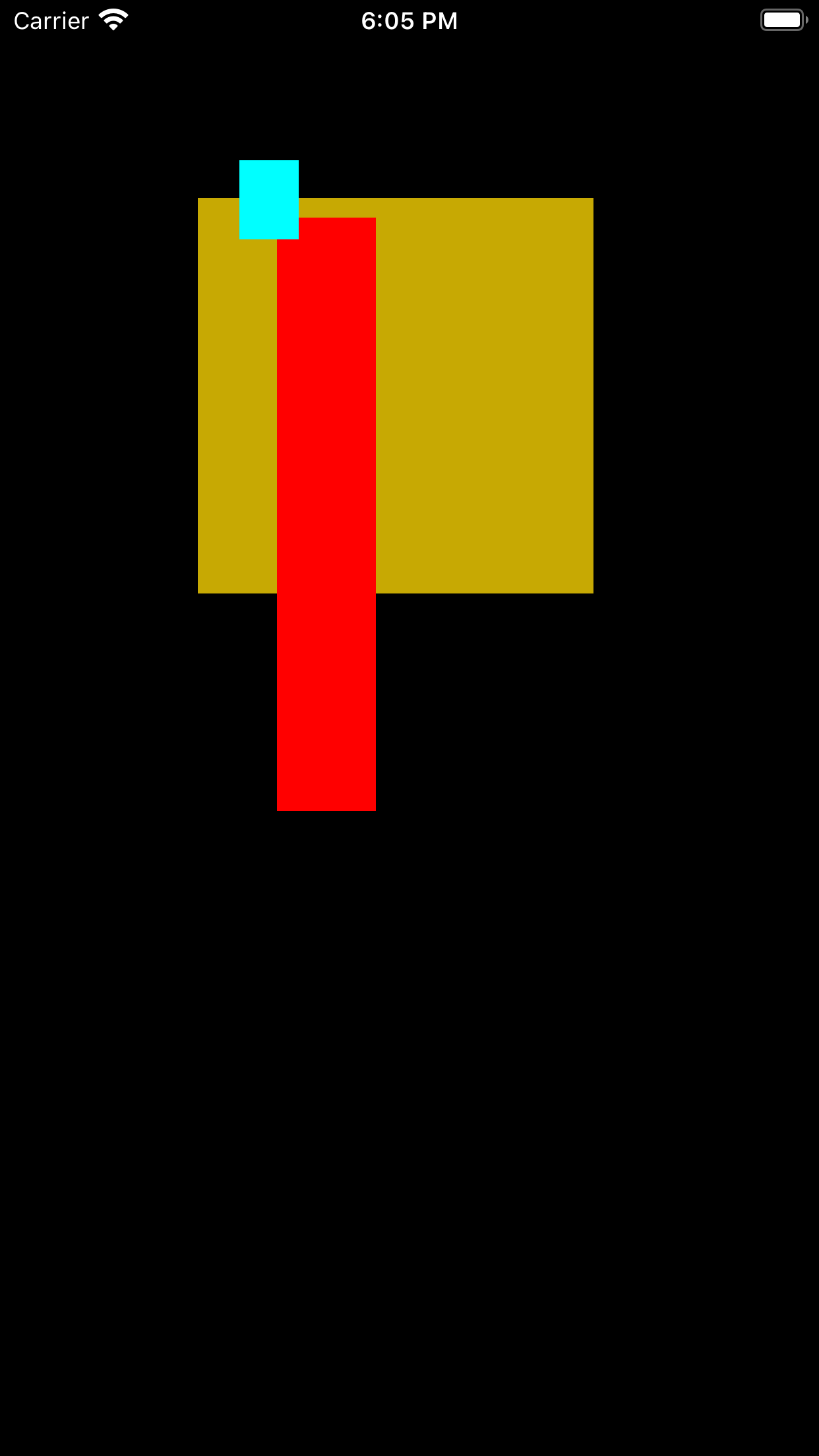
分类:
UI章节




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· AI与.NET技术实操系列:向量存储与相似性搜索在 .NET 中的实现
· 基于Microsoft.Extensions.AI核心库实现RAG应用
· Linux系列:如何用heaptrack跟踪.NET程序的非托管内存泄露
· 开发者必知的日志记录最佳实践
· SQL Server 2025 AI相关能力初探
· 震惊!C++程序真的从main开始吗?99%的程序员都答错了
· 【硬核科普】Trae如何「偷看」你的代码?零基础破解AI编程运行原理
· 单元测试从入门到精通
· 上周热点回顾(3.3-3.9)
· winform 绘制太阳,地球,月球 运作规律