iOS开发 - description | SEL
▶ description
一般情况下使用 NSLog 和 %@ 输出某个对象时,就会调用这个对象的 description方法,其返回值就是 NSString 字符串型,默认实现返回的格式是 <类名: 对象的内存地址>
代码示例
DemoA:没有重写 description方法
#import <Foundation/Foundation.h> @interface Person : NSObject @property(nonatomic,assign)int age; @property(nonatomic,strong)NSString *name; @end @implementation Person @end
int main(int argc, const char * argv[]) { @autoreleasepool { Person *p1 = [[Person alloc] init]; p1.age = 20; p1.name = @"Bruce"; NSLog(@"%@",p1); } return 0; }
日志信息
![]()
DemoB:重写了 description方法
#import <Foundation/Foundation.h> @interface Person : NSObject @property(nonatomic,assign)int age; @property(nonatomic,strong)NSString *name; @end @implementation Person -(NSString*)description{ return [NSString stringWithFormat:@"age = %d name = %@",self.age,_name]; // 注意:使用 %@ 和 self 代表要调用 self 的 description方法 // return [NSString stringWithFormat:@"%@",self];// 最终结果就是陷入死循环,程序crash } @end int main(int argc, const char * argv[]) { @autoreleasepool { Person *p1 = [[Person alloc] init]; p1.age = 20; p1.name = @"Bruce"; NSLog(@"%@",p1); } return 0; }
日志信息
![]()
▶ SEL
SEL 就是 Selector,它表示方法的存储位置。工作原理如下
A. 首先把方法名 test 包装成 SEL型数据
B. 其次根据 SEL 找到对应方法的地址后进行调用
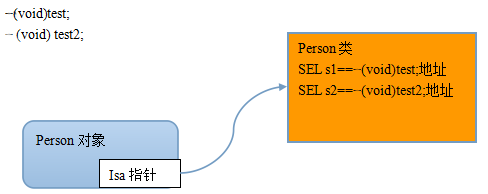
代码示例:在 ARC模式下 使用 SEL 时会存在警告
1 #import <Foundation/Foundation.h> 2 @interface Person : NSObject 3 4 @property(nonatomic,assign)int age; 5 @property(nonatomic,strong)NSString *name; 6 7 @end 8 @implementation Person 9 10 -(NSString*)description{ 11 return [NSString stringWithFormat:@"age = %d name = %@",self.age,_name]; 12 } 13 14 -(id)init{ 15 16 if (self = [super init]) { 17 18 [self performSelector:@selector(makeSomeValues)]; 19 [self performSelector:@selector(makeSomeValuse:) withObject:@"man"]; 20 21 NSString *methodName = @"test01"; 22 SEL sm = NSSelectorFromString(methodName); 23 // 警告:PerformSelector may cause a leak because its selector is unknown 24 [self performSelector:sm]; 25 26 } 27 28 return self; 29 } 30 31 -(void)makeSomeValues{ 32 33 _age = 200; 34 _name = @"Rose"; 35 } 36 37 -(void)makeSomeValuse:(NSString*)sex{ 38 39 NSLog(@"%@",sex); 40 } 41 42 -(void)test01{ 43 44 NSLog(@"Hello,SEL"); 45 } 46 47 @end 48 49 //------------------------------------------------------------------ 50 51 int main(int argc, const char * argv[]) { 52 @autoreleasepool { 53 Person *p1 = [[Person alloc] init]; 54 p1.age = 20; 55 p1.name = @"Bruce"; 56 NSLog(@"%@",p1); 57 } 58 return 0; 59 }
日志信息

为什么产生警告 ?因为当在 ARC 中调用一个方法,Runtime 必须需要知道对于返回值该怎么办!返回值可能有各种类型,如下
A. 直接忽略的。比如 void、int
B. 把返回值先 retain,等到用不到的时候再 release。最常见的情况
C. 不会 retain,等到用不到的时候直接 release。用于 copy 这一类的方法或者标注 ns_returns_retained 的方法
D. 什么也不做,默认返回值在返回前后是始终有效的,一直到最近的 release pool 结束为止。用于标注 ns_returns_autoreleased 的方法
在使用 performSelector 时理论上系统返回值并不是基本类型,也就意味着系统不会做 retain、release 相关处理。可是一旦开着 ARC,编译器就会认为从 performSelector 返回的对象没理由不能 retain、release,因为在编译器眼里它毕竟是个对象。所以即使它的返回值是基本类型或是 void,编译器还是有 retain、release 的可能,这很可能直接导致 crash
代码示例:如何去警告
1 #import <Foundation/Foundation.h> 2 3 // 为解决警告使用的宏 4 #define SuppressPerformSelectorLeakWarning(Stuff) \ 5 do { \ 6 _Pragma("clang diagnostic push") \ 7 _Pragma("clang diagnostic ignored \"-Warc-performSelector-leaks\"") \ 8 Stuff; \ 9 _Pragma("clang diagnostic pop") \ 10 } while (0) 11 12 // Person 13 @interface Person : NSObject 14 15 @property(nonatomic,assign)int age; 16 @property(nonatomic,strong)NSString *name; 17 18 @end 19 20 21 @implementation Person 22 23 -(NSString*)description{ 24 25 return [NSString stringWithFormat:@"age = %d name = %@",_age,_name]; 26 } 27 28 -(id)init{ 29 30 if (self = [super init]) { 31 // 赋值 32 [self performSelector:@selector(makeSomeValue1)]; 33 [self performSelector:@selector(makeSomeValue2:) withObject:@"man"]; 34 35 // 忽略警告的处理方式 36 [self correctedBy01]; // 方式一:仅仅忽略警告 37 [self correctedBy02]; // 方式二:建议处理方式 38 } 39 40 return self; 41 } 42 43 -(void)makeSomeValue1{ 44 _age = 200; 45 _name = @"Rose"; 46 } 47 48 -(void)makeSomeValue2:(NSString*)sex{ 49 NSLog(@"I am %@",sex); 50 } 51 52 //------------------------------- 53 54 // 无参 55 -(void)test01{ 56 NSLog(@"Hello,SEL"); 57 } 58 59 // 带参 60 -(NSString*)test02:(NSString *)color hobby:(NSString*)interest{ 61 62 NSString *resultStr = [NSString stringWithFormat:@"I love %@ and %@",color,interest]; 63 return resultStr; 64 } 65 66 // 方式一 67 - (void)correctedBy01{ 68 69 // ------------- 无参无返回值 -------------- 70 NSString *methodA = @"test01"; 71 SEL mA = NSSelectorFromString(methodA); 72 73 // 优化前:若多处需要使用,可定义成宏 74 #pragma clang diagnostic push 75 #pragma clang diagnostic ignored "-Warc-performSelector-leaks" 76 [self performSelector:mA]; 77 #pragma clang diagnostic pop 78 79 // 优化后:直接使用前面定义好的宏 80 SuppressPerformSelectorLeakWarning( 81 [self performSelector:mA]; 82 ); 83 84 85 // ------------- 有参有返回值 ------------- 86 NSString *methodB = @"test02:hobby:"; 87 SEL mB = NSSelectorFromString(methodB); 88 id resultName; 89 SuppressPerformSelectorLeakWarning( 90 resultName = [self performSelector:mB withObject:@"yellow" withObject:@"biting"]; 91 NSLog(@"resultName = %@",resultName); 92 ); 93 } 94 95 // 方式二 96 -(void)correctedBy02{ 97 98 // ------------- 无参无返回值 ------------- 99 NSString *methodA = @"test01"; 100 SEL mA = NSSelectorFromString(methodA); 101 ((void (*)(id, SEL))[self methodForSelector:mA])(self, mA); 102 103 // ------------- 有参有返回值 ------------- 104 SEL selector = NSSelectorFromString(@"test02:hobby:"); 105 IMP imp = [self methodForSelector:selector]; 106 107 // (void *) 只是告诉编译器,不用报类型强转的 warning 108 NSString *(*func)(id, SEL, NSString *, NSString *) = (void*)imp; 109 NSString *finalString = func(self, selector, @"yellow", @"biting"); 110 NSLog(@"finalString = %@",finalString); 111 } 112 113 @end 114 115 // main函数 116 int main(int argc, const char * argv[]) { 117 @autoreleasepool { 118 Person *p1 = [[Person alloc] init]; 119 p1.age = 20; 120 p1.name = @"Bruce"; 121 NSLog(@"%@",p1); 122 } 123 return 0; 124 }


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号