实现单例模式的多种方法
1.立即加载 -- “饿汉模式”
立即加载就是使用类的时候已经将对象创建完毕。 测试代码如下:
1 public class Singleton { 2 private static Singleton instance=new Singleton(); 3 private Singleton(){} 4 public static Singleton getInstance(){ 5 /* 6 * 此代码为立即加载,缺点是不能有其他实例变量 7 * 因为getInstance()方法没有同步 8 * 所以有可能出现非线程安全问题 9 */ 10 return instance; 11 } 12 } 13
1 public class Run { 2 public static void main(String[] args) { 3 MyThread t1=new MyThread(); 4 MyThread t2=new MyThread(); 5 MyThread t3=new MyThread(); 6 7 t1.start(); 8 t2.start(); 9 t3.start(); 10 } 11 12 }
1 public class MyThread extends Thread { 2 @Override 3 public void run() { 4 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 5 System.out.println(Singleton.getInstance().hashCode()); 6 } 7 } 8
以上的Run类和MyThread类在本文测试前四种方法一样,接下来就不在重复编码。 运行结果如下:
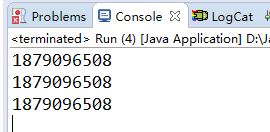
2.延迟加载 -- “懒汉模式”
延迟加载就是在调用getXXX方法时,实例才会被创建。
2.1 普通“懒汉模式”
测试代码如下:
1 public class Singleton { 2 private static Singleton instance; 3 private Singleton(){} 4 public static Singleton getInstance(){ 5 try { 6 if (instance == null) { 7 // 模拟在创建对象过程中有准备工作 8 Thread.sleep(2000); 9 instance = new Singleton(); 10 } 11 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 12 // TODO Auto-generated catch block 13 e.printStackTrace(); 14 } 15 return instance; 16 } 17 18 }
此种方式,在多线程的环境下将无法实现单例。 运行结果如下:
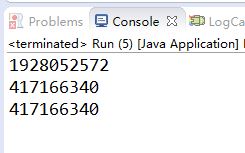
2.2 线程安全下的“懒汉模式”
(1)使用synchronize关键字
测试代码如下:
1 public class Singleton { 2 private static Singleton instance; 3 4 private Singleton() { 5 } 6 7 synchronized public static Singleton getInstance() { 8 try { 9 if (instance == null) { 10 // 模拟在创建对象过程中有准备工作 11 Thread.sleep(2000); 12 instance = new Singleton(); 13 } 14 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 15 // TODO Auto-generated catch block 16 e.printStackTrace(); 17 } 18 return instance; 19 } 20 21 } 22
运行结果:
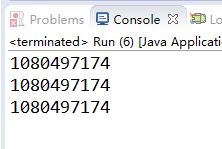
此方法虽然可以解决线程安全问题,但是对整个方法进行加锁无疑会使整个方法的运行效率大大降低。
(2)尝试同步代码块
测试代码如下:
1 public class Singleton { 2 private static Singleton instance; 3 4 private Singleton() { 5 } 6 7 public static Singleton getInstance() { 8 try { 9 synchronized (Singleton.class) { 10 11 if (instance == null) { 12 // 模拟在创建对象过程中有准备工作 13 Thread.sleep(2000); 14 instance = new Singleton(); 15 } 16 } 17 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 18 // TODO Auto-generated catch block 19 e.printStackTrace(); 20 } 21 return instance; 22 } 23 24 } 25
运行结果:
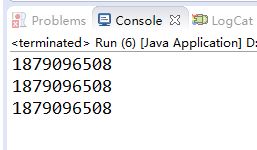
此方法虽然也是可以解决线程安全问题,但是它的运行效率和上一个方法的运行效率差不多,也是会大大拉低程序的效率
(3)针对某些重要的代码进行单独的同步
测试代码如下:
1 public class Singleton { 2 private static Singleton instance; 3 4 private Singleton() { 5 } 6 7 public static Singleton getInstance() { 8 try { 9 if (instance == null) { 10 // 模拟在创建对象过程中有准备工作 11 Thread.sleep(2000); 12 synchronized (Singleton.class) { 13 instance = new Singleton(); 14 } 15 } 16 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 17 // TODO Auto-generated catch block 18 e.printStackTrace(); 19 } 20 return instance; 21 } 22 23 } 24
运行结果:
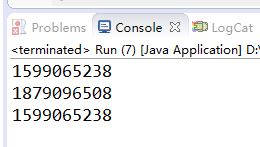
此方法虽然大幅度的解决了程序效率问题,但是却无法解决线程安全问题
(4)使用DCL双检查锁机制
测试代码如下:
1 public class Singleton { 2 private volatile static Singleton instance; 3 4 private Singleton() { 5 } 6 7 public static Singleton getInstance() { 8 try { 9 if (instance == null) { 10 // 模拟在创建对象过程中有准备工作 11 Thread.sleep(2000); 12 synchronized (Singleton.class) { 13 if(instance==null) 14 instance = new Singleton(); 15 } 16 } 17 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 18 // TODO Auto-generated catch block 19 e.printStackTrace(); 20 } 21 return instance; 22 } 23 24 } 25
1 public class Singleton { 2 private volatile static Singleton instance; 3 4 private Singleton() { 5 } 6 7 public static Singleton getInstance() { 8 try { 9 if (instance == null) { 10 // 模拟在创建对象过程中有准备工作 11 Thread.sleep(2000); 12 synchronized (Singleton.class) { 13 if(instance==null) 14 instance = new Singleton(); 15 } 16 } 17 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 18 // TODO Auto-generated catch block 19 e.printStackTrace(); 20 } 21 return instance; 22 } 23 24 } 25
运行结果如下:
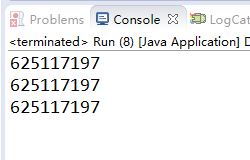
此方法即完美解决了效率问题,也解决了线程安全问题,在懒汉模式下的最佳方法
3.使用静态内置类实现
测试代码如下:
1 public class Singleton{ 2 3 private static class SigntonHandle{ 4 private static final Singleton instance=new Singleton(); 5 } 6 7 private Singleton(){} 8 9 public static Singleton getInstance(){ 10 return SigntonHandle.instance; 11 } 12 13 }
运行结果:
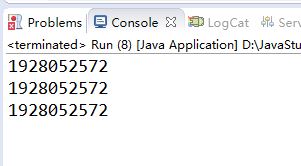
由运行结果可知此方法可以实现单例模式,并且无线程安全问题,但是如果遇到序列化对象的时候,默认的运行方式就不是单例的
4.使用static块实现
1 public class Singleton{ 2 private static Singleton instance=null; 3 static{ 4 instance=new Singleton(); 5 } 6 private Singleton(){} 7 8 public static Singleton getInstance(){ 9 return instance; 10 } 11 }
运行结果:
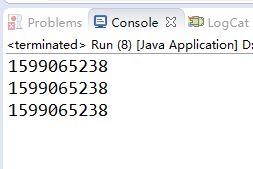
由运行结果可知此方法可以实现单例模式,并且无线程安全问题。
5.使用序列化和反序列化实现
测试代码如下:
1 public class Singleton implements Serializable{ 2 3 private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L; 4 5 private static class SigntonHandle{ 6 private static final Singleton instance=new Singleton(); 7 } 8 9 private Singleton(){} 10 11 public static Singleton getInstance(){ 12 return SigntonHandle.instance; 13 } 14 15 protected Object readResolve(){ 16 System.out.println("已調用readResolve方法"); 17 return SigntonHandle.instance; 18 } 19 20 }
1 public class SaveAndRead { 2 public static void main(String[] args) { 3 try{ 4 Singleton instance=Singleton.getInstance(); 5 6 FileOutputStream fos=new FileOutputStream(new File("MyObject.txt")); 7 ObjectOutputStream oos=new ObjectOutputStream(fos); 8 oos.writeObject(instance); 9 oos.close(); 10 fos.close(); 11 System.out.println(instance.hashCode()); 12 }catch(Exception e){ 13 e.printStackTrace(); 14 } 15 try{ 16 FileInputStream fis=new FileInputStream(new File("MyObject.txt")); 17 ObjectInputStream ois=new ObjectInputStream(fis); 18 Singleton instance1=(Singleton) ois.readObject(); 19 ois.close(); 20 fis.close(); 21 System.out.println(instance1.hashCode()); 22 }catch(Exception e){ 23 e.printStackTrace(); 24 } 25 } 26 27 }
运行结果:

若注释调Singleton类中的readResolve方法,则运行结果如下:
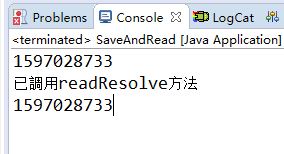
由运行结果可知此方法可以实现单例模式,并且无线程安全问题,并且解决了在序列化对象中出现不是单例的情况。
6.使用enum枚举数据类型实现
此方法还含有MyThread类和Run类和之前的一致。
测试代码如下:
1 public class Singleton{ 2 public enum EnumSingleton{ 3 singleton; 4 private Singleton instance; 5 private EnumSingleton(){ 6 instance=new Singleton(); 7 } 8 public Singleton getInstance(){ 9 return instance; 10 } 11 } 12 13 public static Singleton getInstance(){ 14 return EnumSingleton.singleton.getInstance(); 15 } 16 17 }
运行结果:
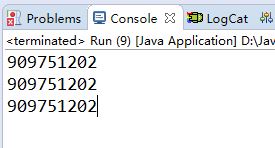
由运行结果可知此方法可以实现单例模式,并且无线程安全问题。


