ABP中的拦截器之AuditingInterceptor
在上面两篇介绍了ABP中的ValidationInterceptor之后,我们今天来看看ABP中定义的另外一种Interceptor即为AuditingInterceptor,顾名思义就是一种审计相关的作用,在了解这篇文章之前,你也可以先看一下ABP官方文档,从而对这个过程有一个更清晰的理解,整个过程也是从AbpBootstrapper中的AddInterceptorRegistrars方法开始的,在这个方法中首先对AuditingInterceptor进行初始化操作,具体的来看看下面的代码。
internal static class AuditingInterceptorRegistrar
{
public static void Initialize(IIocManager iocManager)
{
iocManager.IocContainer.Kernel.ComponentRegistered += (key, handler) =>
{
if (!iocManager.IsRegistered<IAuditingConfiguration>())
{
return;
}
var auditingConfiguration = iocManager.Resolve<IAuditingConfiguration>();
if (ShouldIntercept(auditingConfiguration, handler.ComponentModel.Implementation))
{
handler.ComponentModel.Interceptors.Add(new InterceptorReference(typeof(AuditingInterceptor)));
}
};
}
private static bool ShouldIntercept(IAuditingConfiguration auditingConfiguration, Type type)
{
if (auditingConfiguration.Selectors.Any(selector => selector.Predicate(type)))
{
return true;
}
if (type.GetTypeInfo().IsDefined(typeof(AuditedAttribute), true))
{
return true;
}
if (type.GetMethods().Any(m => m.IsDefined(typeof(AuditedAttribute), true)))
{
return true;
}
return false;
}
}
在这个方法内部,首先将整个ABP中唯一的IoCManager作为参数传递到里面,然后订阅依赖注入容器的ComponentRegister事件,这里订阅的函数有两个参数,一个是key,另外一个是IHandle的接口,这段代码意思是说当Ioc中有组件被注册的时候(也就是往Ioc添加某个类型的时候), 就会触发ComponentRegister事件,然后执行事件的订阅操作,在这个订阅事件处理中首先判断当前的ABP中是否注册过IAuditingConfiguration这个接口,如果没有注册过那么就直接返回了,如果对前面的文章有过印象的话,你就知道这个注册的过程是沿着下面的过程来进行的:UseAbp--》InitializeAbp(app)--》abpBootstrapper.Initialize()--》IocManager.IocContainer.Install(new AbpCoreInstaller());在最后执行AbpCoreInstaller的时候,在这个类中有一个Install方法,在这个里面就对ABP中常用的接口都注册并注入到容器中了。
internal class AbpCoreInstaller : IWindsorInstaller
{
public void Install(IWindsorContainer container, IConfigurationStore store)
{
container.Register(
Component.For<IUnitOfWorkDefaultOptions, UnitOfWorkDefaultOptions>().ImplementedBy<UnitOfWorkDefaultOptions>().LifestyleSingleton(),
Component.For<INavigationConfiguration, NavigationConfiguration>().ImplementedBy<NavigationConfiguration>().LifestyleSingleton(),
Component.For<ILocalizationConfiguration, LocalizationConfiguration>().ImplementedBy<LocalizationConfiguration>().LifestyleSingleton(),
Component.For<IAuthorizationConfiguration, AuthorizationConfiguration>().ImplementedBy<AuthorizationConfiguration>().LifestyleSingleton(),
Component.For<IValidationConfiguration, ValidationConfiguration>().ImplementedBy<ValidationConfiguration>().LifestyleSingleton(),
Component.For<IFeatureConfiguration, FeatureConfiguration>().ImplementedBy<FeatureConfiguration>().LifestyleSingleton(),
Component.For<ISettingsConfiguration, SettingsConfiguration>().ImplementedBy<SettingsConfiguration>().LifestyleSingleton(),
Component.For<IModuleConfigurations, ModuleConfigurations>().ImplementedBy<ModuleConfigurations>().LifestyleSingleton(),
Component.For<IEventBusConfiguration, EventBusConfiguration>().ImplementedBy<EventBusConfiguration>().LifestyleSingleton(),
Component.For<IMultiTenancyConfig, MultiTenancyConfig>().ImplementedBy<MultiTenancyConfig>().LifestyleSingleton(),
Component.For<ICachingConfiguration, CachingConfiguration>().ImplementedBy<CachingConfiguration>().LifestyleSingleton(),
Component.For<IAuditingConfiguration, AuditingConfiguration>().ImplementedBy<AuditingConfiguration>().LifestyleSingleton(),
Component.For<IBackgroundJobConfiguration, BackgroundJobConfiguration>().ImplementedBy<BackgroundJobConfiguration>().LifestyleSingleton(),
Component.For<INotificationConfiguration, NotificationConfiguration>().ImplementedBy<NotificationConfiguration>().LifestyleSingleton(),
Component.For<IEmbeddedResourcesConfiguration, EmbeddedResourcesConfiguration>().ImplementedBy<EmbeddedResourcesConfiguration>().LifestyleSingleton(),
Component.For<IAbpStartupConfiguration, AbpStartupConfiguration>().ImplementedBy<AbpStartupConfiguration>().LifestyleSingleton(),
Component.For<IEntityHistoryConfiguration, EntityHistoryConfiguration>().ImplementedBy<EntityHistoryConfiguration>().LifestyleSingleton(),
Component.For<ITypeFinder, TypeFinder>().ImplementedBy<TypeFinder>().LifestyleSingleton(),
Component.For<IAbpPlugInManager, AbpPlugInManager>().ImplementedBy<AbpPlugInManager>().LifestyleSingleton(),
Component.For<IAbpModuleManager, AbpModuleManager>().ImplementedBy<AbpModuleManager>().LifestyleSingleton(),
Component.For<IAssemblyFinder, AbpAssemblyFinder>().ImplementedBy<AbpAssemblyFinder>().LifestyleSingleton(),
Component.For<ILocalizationManager, LocalizationManager>().ImplementedBy<LocalizationManager>().LifestyleSingleton()
);
}
}
有了上面的分析,你大概知道了这个继承自IAuditingConfiguration接口的AuditingConfiguration会作为唯一的实例注入到ABP中的容器内部。在这之后会执行一个非常重要的函数ShouldIntercept,这个方法用来判断哪些形式的能够最终执行当前的Interceptor,在这个方法中,后面两种都比较好理解,如果一个类比如说继承自IApplicationService的一个应用服务类在其顶部或者内部的方法中添加了AuditAttribute自定义CustomerAttribute,那么就会执行审计过程,如果是定义在类的级别中那么该类中的所有请求的方法都会执行后面的审计AuditingInterceptor,如果不是定义在类级别上,而是定义在类里面的方法中,那么只有请求了该方法的时候才会执行当前审计操作。这里面不太好理解的就是第一种判断方式。在ABP中默认添加了一个Selector,这个实在AbpKenelModule的PreInitialize()中添加的。
private void AddAuditingSelectors()
{
Configuration.Auditing.Selectors.Add(
new NamedTypeSelector(
"Abp.ApplicationServices",
type => typeof(IApplicationService).IsAssignableFrom(type)
)
);
}
这个也是比较好理解的,就是所有从IApplicationService继承的类都会默认添加AuditingInterceptor,另外我们在我们自己的项目中的PreInitialize()方法中自定义规则,这个是ABP中对外扩展的一种方式。在了解完这些后你应该完全了解ABP中默认对哪些类型进行AuditingInterceptor拦截了。
接下来的重点就是去分析 AuditingInterceptor这个Interceptor这个具体的拦截器到底是怎样工作的。
internal class AuditingInterceptor : IInterceptor
{
private readonly IAuditingHelper _auditingHelper;
public AuditingInterceptor(IAuditingHelper auditingHelper)
{
_auditingHelper = auditingHelper;
}
public void Intercept(IInvocation invocation)
{
if (AbpCrossCuttingConcerns.IsApplied(invocation.InvocationTarget, AbpCrossCuttingConcerns.Auditing))
{
invocation.Proceed();
return;
}
if (!_auditingHelper.ShouldSaveAudit(invocation.MethodInvocationTarget))
{
invocation.Proceed();
return;
}
var auditInfo = _auditingHelper.CreateAuditInfo(invocation.TargetType, invocation.MethodInvocationTarget, invocation.Arguments);
if (invocation.Method.IsAsync())
{
PerformAsyncAuditing(invocation, auditInfo);
}
else
{
PerformSyncAuditing(invocation, auditInfo);
}
}
private void PerformSyncAuditing(IInvocation invocation, AuditInfo auditInfo)
{
var stopwatch = Stopwatch.StartNew();
try
{
invocation.Proceed();
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
auditInfo.Exception = ex;
throw;
}
finally
{
stopwatch.Stop();
auditInfo.ExecutionDuration = Convert.ToInt32(stopwatch.Elapsed.TotalMilliseconds);
_auditingHelper.Save(auditInfo);
}
}
private void PerformAsyncAuditing(IInvocation invocation, AuditInfo auditInfo)
{
var stopwatch = Stopwatch.StartNew();
invocation.Proceed();
if (invocation.Method.ReturnType == typeof(Task))
{
invocation.ReturnValue = InternalAsyncHelper.AwaitTaskWithFinally(
(Task) invocation.ReturnValue,
exception => SaveAuditInfo(auditInfo, stopwatch, exception)
);
}
else //Task<TResult>
{
invocation.ReturnValue = InternalAsyncHelper.CallAwaitTaskWithFinallyAndGetResult(
invocation.Method.ReturnType.GenericTypeArguments[0],
invocation.ReturnValue,
exception => SaveAuditInfo(auditInfo, stopwatch, exception)
);
}
}
private void SaveAuditInfo(AuditInfo auditInfo, Stopwatch stopwatch, Exception exception)
{
stopwatch.Stop();
auditInfo.Exception = exception;
auditInfo.ExecutionDuration = Convert.ToInt32(stopwatch.Elapsed.TotalMilliseconds);
_auditingHelper.Save(auditInfo);
}
}
在这个里面,当我们将要被执行Auditing方法之前,首先会执行AuditingInterceptor 类中的Intercept方法,在这个方法体内部,首先也是执行AbpCrossCuttingConcerns.IsApplied方法,在这个方法中首先会判断这个执行当前方法所属的类是否是从IAvoidDuplicateCrossCuttingConcerns接口继承,如果从这个接口继承的话,那么将执行方法的所属的类转换为IAvoidDuplicateCrossCuttingConcerns类型,然后再看当前接口中定义的List<string>类型的AppliedCrossCuttingConcerns对象中是否已经包含AbpAuditing字符串,如果已经包含那么就直接执行拦截的方法,然后就返回。这里需要特别注意的是在整个ABP系统中只有一个ApplicationService继承自IAvoidDuplicateCrossCuttingConcerns这个接口,所以在我们的系统中,只有继承自ApplicationService类的类中的方法被拦截器拦截时才会执行上面的过程。这个分析过程其实和之前的ValidationInterceptor中的分析过程是一致的,所以这里就不再赘述,直接拿出结果。
ABP中利用Asp.Net Core中的过滤器的特性其实也定义了一组Filter,这个可以看下面的代码。在Asp.Net Core中执行ConfigureServices的时候会执行AddAbp方法在这个方法中会执行对MvcOptions的一些操作。
//Configure MVC
services.Configure<MvcOptions>(mvcOptions =>
{
mvcOptions.AddAbp(services);
});
我们来看看这个mvcOptions的AddAbp方法。
internal static class AbpMvcOptionsExtensions
{
public static void AddAbp(this MvcOptions options, IServiceCollection services)
{
AddConventions(options, services);
AddFilters(options);
AddModelBinders(options);
}
private static void AddConventions(MvcOptions options, IServiceCollection services)
{
options.Conventions.Add(new AbpAppServiceConvention(services));
}
private static void AddFilters(MvcOptions options)
{
options.Filters.AddService(typeof(AbpAuthorizationFilter));
options.Filters.AddService(typeof(AbpAuditActionFilter));
options.Filters.AddService(typeof(AbpValidationActionFilter));
options.Filters.AddService(typeof(AbpUowActionFilter));
options.Filters.AddService(typeof(AbpExceptionFilter));
options.Filters.AddService(typeof(AbpResultFilter));
}
private static void AddModelBinders(MvcOptions options)
{
options.ModelBinderProviders.Insert(0, new AbpDateTimeModelBinderProvider());
}
}
在这个方法中,ABP系统默认添加了6中类型的Filter,这其中就包括AbpAuditActionFilter,在这个Filter中,我们来看看到底做了些什么?
public class AbpAuditActionFilter : IAsyncActionFilter, ITransientDependency
{
private readonly IAbpAspNetCoreConfiguration _configuration;
private readonly IAuditingHelper _auditingHelper;
public AbpAuditActionFilter(IAbpAspNetCoreConfiguration configuration, IAuditingHelper auditingHelper)
{
_configuration = configuration;
_auditingHelper = auditingHelper;
}
public async Task OnActionExecutionAsync(ActionExecutingContext context, ActionExecutionDelegate next)
{
if (!ShouldSaveAudit(context))
{
await next();
return;
}
using (AbpCrossCuttingConcerns.Applying(context.Controller, AbpCrossCuttingConcerns.Auditing))
{
var auditInfo = _auditingHelper.CreateAuditInfo(
context.ActionDescriptor.AsControllerActionDescriptor().ControllerTypeInfo.AsType(),
context.ActionDescriptor.AsControllerActionDescriptor().MethodInfo,
context.ActionArguments
);
var stopwatch = Stopwatch.StartNew();
try
{
var result = await next();
if (result.Exception != null && !result.ExceptionHandled)
{
auditInfo.Exception = result.Exception;
}
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
auditInfo.Exception = ex;
throw;
}
finally
{
stopwatch.Stop();
auditInfo.ExecutionDuration = Convert.ToInt32(stopwatch.Elapsed.TotalMilliseconds);
await _auditingHelper.SaveAsync(auditInfo);
}
}
}
private bool ShouldSaveAudit(ActionExecutingContext actionContext)
{
return _configuration.IsAuditingEnabled &&
actionContext.ActionDescriptor.IsControllerAction() &&
_auditingHelper.ShouldSaveAudit(actionContext.ActionDescriptor.GetMethodInfo(), true);
}
}
在继承自ApplicationService的类中的方法执行之前,首先会执行OnActionExecutionAsync方法,在这个方法中首先判断一些基础的条件,这些通常都是一些默认的设置,在判断完这些类型以后,就会执行下面的这些方法,在这个方法中会将默认的字符串AbpAuditing
| 名称 | 值 | 类型 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| ▶ | (obj as IAvoidDuplicateCrossCuttingConcerns) | {Castle.Proxies.SelfAppServiceroxy} | Abp.Application.Services.IAvoidDuplicateCrossCuttingConcerns {Castle.Proxies.SelfAppServiceProxy} |
写入到一个默认的List<string>类型中,这个具体过程可以参考上面的分析,在AbpCrossCuttingConcerns.Applying中第一个参数最为关键,那么这个context.Controller(也就是上图中obj对应的参数)到底指的是什么呢?这里我们执行一个继承自ApplicationService中的SelfAppService中的一个方法时,我们通过调试发现最终的类型是Castle.Proxies.SelfAppServiceProxy 类型,如果对这个还不太理解,可以这么理解其实就是我们自定义的SelfAppService这个继承自ApplicationService 类的类型。
再在后面就是通过构造函数注入的IAuditingHelper对象来创建一个auditInfo,这个创建的类是最关键的,ABP系统中有一个默认的IAuditingHelper的实现,我们来重点看看这个类中到底做了些什么?
public class AuditingHelper : IAuditingHelper, ITransientDependency
{
public ILogger Logger { get; set; }
public IAbpSession AbpSession { get; set; }
public IAuditingStore AuditingStore { get; set; }
private readonly IAuditInfoProvider _auditInfoProvider;
private readonly IAuditingConfiguration _configuration;
private readonly IUnitOfWorkManager _unitOfWorkManager;
private readonly IAuditSerializer _auditSerializer;
public AuditingHelper(
IAuditInfoProvider auditInfoProvider,
IAuditingConfiguration configuration,
IUnitOfWorkManager unitOfWorkManager,
IAuditSerializer auditSerializer)
{
_auditInfoProvider = auditInfoProvider;
_configuration = configuration;
_unitOfWorkManager = unitOfWorkManager;
_auditSerializer = auditSerializer;
AbpSession = NullAbpSession.Instance;
Logger = NullLogger.Instance;
AuditingStore = SimpleLogAuditingStore.Instance;
}
public bool ShouldSaveAudit(MethodInfo methodInfo, bool defaultValue = false)
{
if (!_configuration.IsEnabled)
{
return false;
}
if (!_configuration.IsEnabledForAnonymousUsers && (AbpSession?.UserId == null))
{
return false;
}
if (methodInfo == null)
{
return false;
}
if (!methodInfo.IsPublic)
{
return false;
}
if (methodInfo.IsDefined(typeof(AuditedAttribute), true))
{
return true;
}
if (methodInfo.IsDefined(typeof(DisableAuditingAttribute), true))
{
return false;
}
var classType = methodInfo.DeclaringType;
if (classType != null)
{
if (classType.GetTypeInfo().IsDefined(typeof(AuditedAttribute), true))
{
return true;
}
if (classType.GetTypeInfo().IsDefined(typeof(DisableAuditingAttribute), true))
{
return false;
}
if (_configuration.Selectors.Any(selector => selector.Predicate(classType)))
{
return true;
}
}
return defaultValue;
}
public AuditInfo CreateAuditInfo(Type type, MethodInfo method, object[] arguments)
{
return CreateAuditInfo(type, method, CreateArgumentsDictionary(method, arguments));
}
public AuditInfo CreateAuditInfo(Type type, MethodInfo method, IDictionary<string, object> arguments)
{
var auditInfo = new AuditInfo
{
TenantId = AbpSession.TenantId,
UserId = AbpSession.UserId,
ImpersonatorUserId = AbpSession.ImpersonatorUserId,
ImpersonatorTenantId = AbpSession.ImpersonatorTenantId,
ServiceName = type != null
? type.FullName
: "",
MethodName = method.Name,
Parameters = ConvertArgumentsToJson(arguments),
ExecutionTime = Clock.Now
};
try
{
_auditInfoProvider.Fill(auditInfo);
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
Logger.Warn(ex.ToString(), ex);
}
return auditInfo;
}
public void Save(AuditInfo auditInfo)
{
using (var uow = _unitOfWorkManager.Begin(TransactionScopeOption.Suppress))
{
AuditingStore.Save(auditInfo);
uow.Complete();
}
}
public async Task SaveAsync(AuditInfo auditInfo)
{
using (var uow = _unitOfWorkManager.Begin(TransactionScopeOption.Suppress))
{
await AuditingStore.SaveAsync(auditInfo);
await uow.CompleteAsync();
}
}
private string ConvertArgumentsToJson(IDictionary<string, object> arguments)
{
try
{
if (arguments.IsNullOrEmpty())
{
return "{}";
}
var dictionary = new Dictionary<string, object>();
foreach (var argument in arguments)
{
if (argument.Value != null && _configuration.IgnoredTypes.Any(t => t.IsInstanceOfType(argument.Value)))
{
dictionary[argument.Key] = null;
}
else
{
dictionary[argument.Key] = argument.Value;
}
}
return _auditSerializer.Serialize(dictionary);
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
Logger.Warn(ex.ToString(), ex);
return "{}";
}
}
private static Dictionary<string, object> CreateArgumentsDictionary(MethodInfo method, object[] arguments)
{
var parameters = method.GetParameters();
var dictionary = new Dictionary<string, object>();
for (var i = 0; i < parameters.Length; i++)
{
dictionary[parameters[i].Name] = arguments[i];
}
return dictionary;
}
}
在这个类中重点的就是CreateAuditInfo这个方法,这个方法会创建一个AuditInfo对象,然后往这个对象中填充一些系统的常见的一些信息,比如:TenantId、UserId、ServiceName等等一系类的常用对象,我们来看看AuditInfo这个对象包含哪些重要的东西吧?
public class AuditInfo
{
/// <summary>
/// TenantId.
/// </summary>
public int? TenantId { get; set; }
/// <summary>
/// UserId.
/// </summary>
public long? UserId { get; set; }
/// <summary>
/// ImpersonatorUserId.
/// </summary>
public long? ImpersonatorUserId { get; set; }
/// <summary>
/// ImpersonatorTenantId.
/// </summary>
public int? ImpersonatorTenantId { get; set; }
/// <summary>
/// Service (class/interface) name.
/// </summary>
public string ServiceName { get; set; }
/// <summary>
/// Executed method name.
/// </summary>
public string MethodName { get; set; }
/// <summary>
/// Calling parameters.
/// </summary>
public string Parameters { get; set; }
/// <summary>
/// Start time of the method execution.
/// </summary>
public DateTime ExecutionTime { get; set; }
/// <summary>
/// Total duration of the method call.
/// </summary>
public int ExecutionDuration { get; set; }
/// <summary>
/// IP address of the client.
/// </summary>
public string ClientIpAddress { get; set; }
/// <summary>
/// Name (generally computer name) of the client.
/// </summary>
public string ClientName { get; set; }
/// <summary>
/// Browser information if this method is called in a web request.
/// </summary>
public string BrowserInfo { get; set; }
/// <summary>
/// Optional custom data that can be filled and used.
/// </summary>
public string CustomData { get; set; }
/// <summary>
/// Exception object, if an exception occurred during execution of the method.
/// </summary>
public Exception Exception { get; set; }
public override string ToString()
{
var loggedUserId = UserId.HasValue
? "user " + UserId.Value
: "an anonymous user";
var exceptionOrSuccessMessage = Exception != null
? "exception: " + Exception.Message
: "succeed";
return $"AUDIT LOG: {ServiceName}.{MethodName} is executed by {loggedUserId} in {ExecutionDuration} ms from {ClientIpAddress} IP address with {exceptionOrSuccessMessage}.";
}
}
在创建完这个用来保存AuditingInfo的AuditInfo对象后,接下来的事情就比较明了了,就是创建一个StopWatch用于记录当前方法执行的时间,后面再用一个try、catch、finally来包装执行的方法,捕获错误,并将当前的Exception捕获并赋值给刚才创建的auditInfo中,完成这个步骤之后就是将整个AuditInfo进行保存从而方便我们对当前方法进行排错和优化效率的操作了。
在执行完最重要的步骤之后就是如何保存这些重要的信息了,我们来一起看看这个重要的步骤都做了些什么吧?
public async Task SaveAsync(AuditInfo auditInfo)
{
using (var uow = _unitOfWorkManager.Begin(TransactionScopeOption.Suppress))
{
await AuditingStore.SaveAsync(auditInfo);
await uow.CompleteAsync();
}
}
在这个函数里面,执行一个AuditingStore的SaveAsync的方法,这是一个异步方法,用来对最终的信息进行保存。ABP中默认是采用日志的方式来将当前的auditInfo转化为字符串然后保存到日志文件中的,当然我们也可以将当前的信息保存到数据库中的,这样我们就能够查看更多的系统运行状态的信息了,下面是一张具体的截图我们来看看。
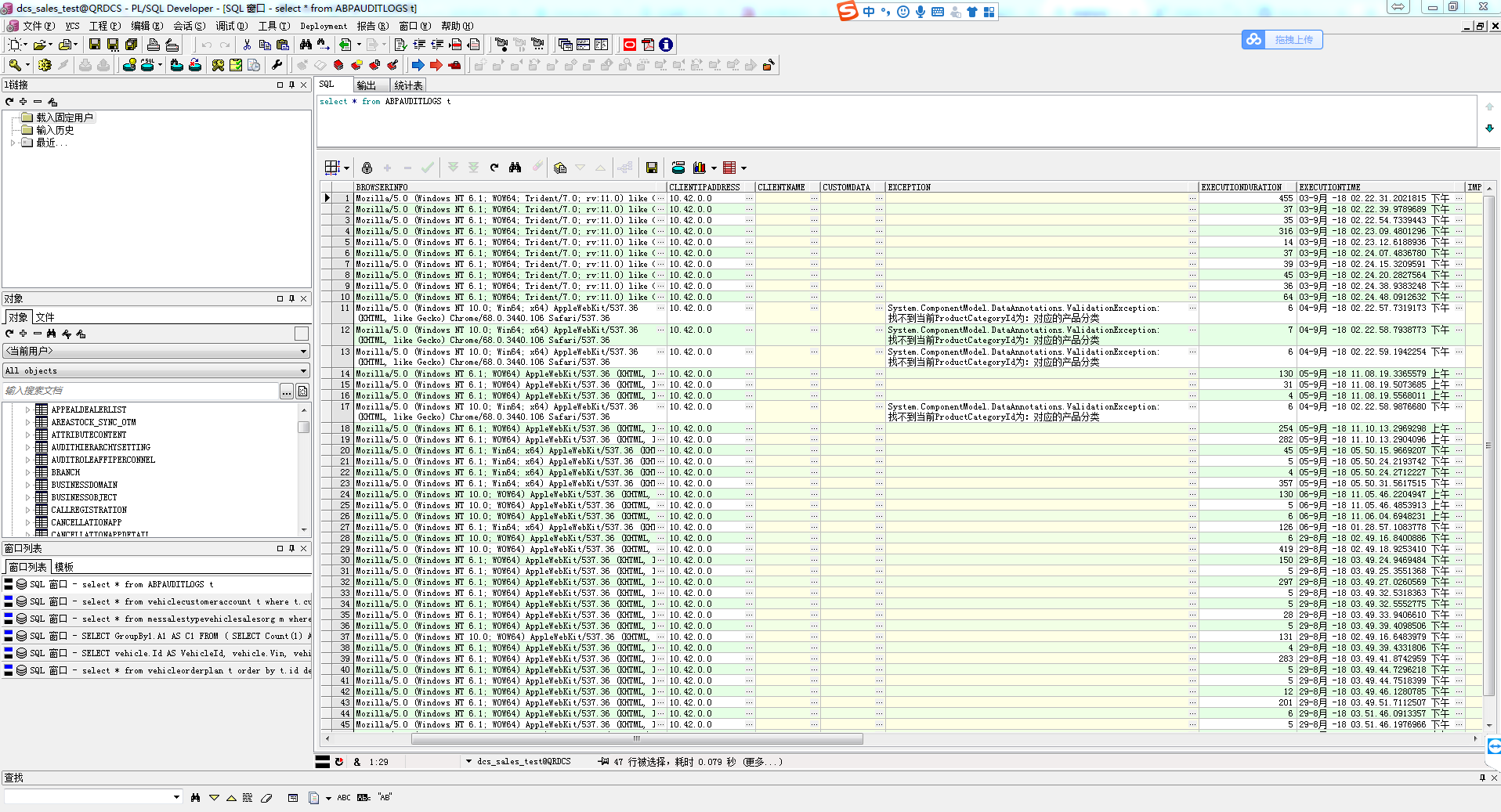
最后,点击这里返回整个ABP系列的主目录。



