WPF中自定义加载时带动画效果的Form和FormItem
背景
今天我们来谈一下我们自定义的一组WPF控件Form和FormItem,然后看一下如何自定义一组完整地组合WPF控件,在我们很多界面显示的时候我们需要同时显示文本、图片并且我们需要将这些按照特定的顺序整齐的排列在一起,这样的操作当然通过定义Grid和StackPanel然后组合在一起当然也是可以的,我们的这一组控件就是将这个过程组合到一个Form和FormItem中间去,从而达到这样的效果,我们首先来看看这组控件实现的效果。
一 动画效果
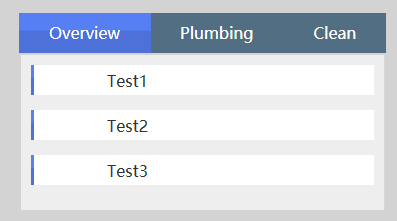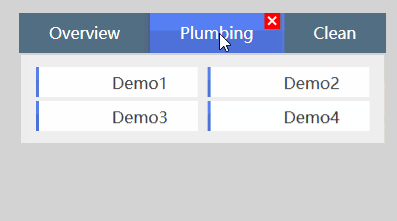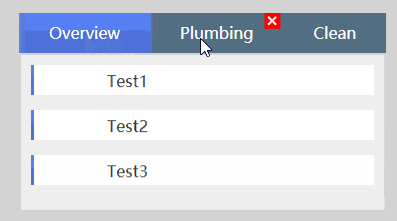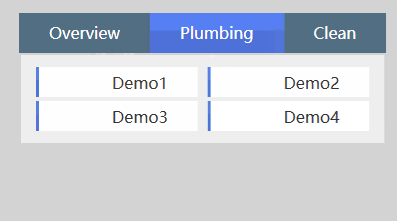
看了这个效果之后我们来看看怎么来使用Form和FormItem控件,后面再进一步分析这两个控件的一些细节信息。
<xui:TabControl Canvas.Left="356" Canvas.Top="220">
<xui:TabItem Header="Overview">
<xui:Form Margin="2" >
<xui:FormItem Content="Test1" Height="30"></xui:FormItem>
<xui:FormItem Content="Test2" Height="30"></xui:FormItem>
<xui:FormItem Content="Test3" Height="30"></xui:FormItem>
</xui:Form>
</xui:TabItem>
<xui:TabItem Header="Plumbing">
<xui:Form Margin="2" Columns="2" Rows="2">
<xui:FormItem Content="Demo1" Height="30" Margin="5 2"></xui:FormItem>
<xui:FormItem Content="Demo2" Height="30" Margin="5 2"></xui:FormItem>
<xui:FormItem Content="Demo3" Height="30" Margin="5 2"></xui:FormItem>
<xui:FormItem Content="Demo4" Height="30" Margin="5 2"></xui:FormItem>
</xui:Form>
</xui:TabItem>
<xui:TabItem Header="Clean">
<xui:TextBox Text="Test2" Width="220" Height=" 30" Margin="5"></xui:TextBox>
</xui:TabItem>
</xui:TabControl>
这个里面xui命名控件是我们的自定义控件库的命名空间,这个里面的TableControl也是一种特殊的自定义的TableControl,关于这个TableControl我们后面也会进一步分析。
二 自定义控件实现
按照上面的顺序我们先来分析Form控件,然后再分析FormItem控件的实现细节
2.1 Form
通过上面的代码我们发现Form是可以承载FormItem的,所以它是一个可以承载子控件的容器控件,这里Form是集成ItemsControl的,我们来看看具体的代码
public class Form : ItemsControl
{
static Form()
{
DefaultStyleKeyProperty.OverrideMetadata(typeof(Form), new FrameworkPropertyMetadata(typeof(Form)));
}
public double HeaderWidth
{
get { return (double)GetValue(HeaderWidthProperty); }
set { SetValue(HeaderWidthProperty, value); }
}
// Using a DependencyProperty as the backing store for HeaderWidth. This enables animation, styling, binding, etc...
public static readonly DependencyProperty HeaderWidthProperty =
DependencyProperty.Register("HeaderWidth", typeof(double), typeof(Form), new PropertyMetadata(70D));
public int Rows
{
get { return (int)GetValue(RowsProperty); }
set { SetValue(RowsProperty, value); }
}
// Using a DependencyProperty as the backing store for Rows. This enables animation, styling, binding, etc...
public static readonly DependencyProperty RowsProperty =
DependencyProperty.Register("Rows", typeof(int), typeof(Form), new PropertyMetadata(0));
public int Columns
{
get { return (int)GetValue(ColumnsProperty); }
set { SetValue(ColumnsProperty, value); }
}
// Using a DependencyProperty as the backing store for Columns. This enables animation, styling, binding, etc...
public static readonly DependencyProperty ColumnsProperty =
DependencyProperty.Register("Columns", typeof(int), typeof(Form), new PropertyMetadata(1));
}
然后我们再来看看Form的样式文件
<Style TargetType="local:Form">
<Setter Property="Padding" Value="10"></Setter>
<Setter Property="Template">
<Setter.Value>
<ControlTemplate TargetType="local:Form">
<ScrollViewer Background="#eee" HorizontalScrollBarVisibility="Disabled" VerticalScrollBarVisibility="Auto">
<UniformGrid Columns="{TemplateBinding Columns}" Rows="{TemplateBinding Rows}" IsItemsHost="True" Background="Transparent" VerticalAlignment="Top" Margin="{TemplateBinding Padding}"></UniformGrid>
</ScrollViewer>
</ControlTemplate>
</Setter.Value>
</Setter>
<Setter Property="ItemTemplate">
<Setter.Value>
<DataTemplate>
<ContentPresenter Content="{Binding}" Focusable="False"></ContentPresenter>
</DataTemplate>
</Setter.Value>
</Setter>
</Style>
这里我们使用UniformGrid作为内容承载容器,所以我们现在清楚了为什么需要定义Columns和Rows这两个依赖项属性了,这个UniformGrid是嵌套在ScrollerViewer中的,所以如果其子控件超出了一定范围,其子控件外面是会显示滚动条的。
2.2 FormItem
FormItem是从ListBoxItem继承而来,而ListBoxItem又是从ContentControl继承而来的,所以可以添加到任何具有Content属性的控件中去,常见的ListBoxItem可以放到ListBox中,也可以放到ItemsControl中去,ListBoxItem可以横向和TreeViewItem进行比较,只不过TreeViewItem是直接从HeaderedItemsControl继承过来的,然后再继承自ItemsControl。两者有很多的共同之处,可以做更多的横向比较,我们今天只是来讲ListBoxItem,首先看看我们使用的样式,这里贴出前端代码:
<Style TargetType="local:FormItem">
<Setter Property="Margin" Value="0 0 0 15"></Setter>
<Setter Property="Background" Value="#fff"></Setter>
<Setter Property="Height" Value="50"></Setter>
<Setter Property="HorizontalAlignment" Value="Stretch"></Setter>
<Setter Property="VerticalAlignment" Value="Stretch"></Setter>
<Setter Property="Padding" Value="6"></Setter>
<Setter Property="Foreground" Value="{StaticResource DarkColor}"></Setter>
<Setter Property="Template">
<Setter.Value>
<ControlTemplate TargetType="local:FormItem">
<Grid Background="{TemplateBinding Background}" Height="{TemplateBinding Height}">
<Grid.ColumnDefinitions>
<ColumnDefinition Width="{Binding HeaderWidth,RelativeSource={RelativeSource Mode=FindAncestor,AncestorType=local:Form}}"></ColumnDefinition>
<ColumnDefinition Width="*"></ColumnDefinition>
</Grid.ColumnDefinitions>
<Rectangle Width="3" HorizontalAlignment="Left" Fill="{StaticResource Highlight}"></Rectangle>
<StackPanel VerticalAlignment="Center" HorizontalAlignment="Left" Margin="13 0 0 0" Orientation="Horizontal">
<Image x:Name="Icon" Source="{TemplateBinding Icon}" Width="24" Height="24" Margin="0 0 10 0" VerticalAlignment="Center" HorizontalAlignment="Left"></Image>
<TextBlock Text="{TemplateBinding Title}" Foreground="{TemplateBinding Foreground}" VerticalAlignment="Center" HorizontalAlignment="Left"></TextBlock>
</StackPanel>
<ContentPresenter Margin="{TemplateBinding Padding}" Grid.Column="1" HorizontalAlignment="{TemplateBinding HorizontalAlignment}" VerticalAlignment="{TemplateBinding VerticalAlignment}"></ContentPresenter>
</Grid>
<ControlTemplate.Triggers>
<Trigger Property="Icon" Value="{x:Null}">
<Setter Property="Visibility" Value="Collapsed" TargetName="Icon"></Setter>
</Trigger>
</ControlTemplate.Triggers>
</ControlTemplate>
</Setter.Value>
</Setter>
</Style>
这里我们重写了ListBoxItem 的ControlTemplate,我们需要注意的一个地方就是我们使用了
<ContentPresenter Margin="{TemplateBinding Padding}" Grid.Column="1" HorizontalAlignment="{TemplateBinding HorizontalAlignment}" VerticalAlignment="{TemplateBinding VerticalAlignment}"></ContentPresenter>
来替代ListBoxItem的Content,我们需要始终记住,只有控件拥有Content属性才能使用ContentPresenter ,这个属性是用来呈现控件的Content。
另外一个需要重点介绍的就是FormItem这个类中的代码,这个控件在加载的时候所有的效果都是在后台中进行加载的,首先贴出相关的类的实现,然后再做进一步的分析。
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Windows;
using System.Windows.Controls;
using System.Windows.Media;
using System.Windows.Media.Animation;
namespace X.UI
{
public class FormItem : ListBoxItem
{
static FormItem()
{
DefaultStyleKeyProperty.OverrideMetadata(typeof(FormItem), new FrameworkPropertyMetadata(typeof(FormItem)));
}
public FormItem()
{
System.Windows.Media.TranslateTransform transform = EnsureRenderTransform<System.Windows.Media.TranslateTransform>(this);
transform.X = transform.Y = 100;
Opacity = 0;
IsVisibleChanged += FormItem_IsVisibleChanged;
}
void FormItem_IsVisibleChanged(object sender, DependencyPropertyChangedEventArgs e)
{
if (this.Parent is Form)
{
if (!IsVisible)
{
int index = (this.Parent as Form).Items.IndexOf(this);
System.Windows.Media.TranslateTransform transform = EnsureRenderTransform<System.Windows.Media.TranslateTransform>(this);
DoubleAnimation da = new DoubleAnimation()
{
From = 0,
To = 100,
EasingFunction = new CircleEase { EasingMode = EasingMode.EaseOut }
};
transform.BeginAnimation(System.Windows.Media.TranslateTransform.XProperty, da);
transform.BeginAnimation(System.Windows.Media.TranslateTransform.YProperty, da);
DoubleAnimation daopacity = new DoubleAnimation
{
From = 1,
To = 0,
};
this.BeginAnimation(UIElement.OpacityProperty, daopacity);
}
else
{
int index = (this.Parent as Form).Items.IndexOf(this);
System.Windows.Media.TranslateTransform transform = EnsureRenderTransform<System.Windows.Media.TranslateTransform>(this);
DoubleAnimation da = new DoubleAnimation()
{
From = 100,
To = 0,
BeginTime = TimeSpan.FromMilliseconds(100 * (index + 1)),
Duration = TimeSpan.FromMilliseconds(666),
EasingFunction = new CircleEase { EasingMode = EasingMode.EaseOut }
};
transform.BeginAnimation(System.Windows.Media.TranslateTransform.XProperty, da);
transform.BeginAnimation(System.Windows.Media.TranslateTransform.YProperty, da);
DoubleAnimation daopacity = new DoubleAnimation
{
From = 0,
To = 1,
BeginTime = TimeSpan.FromMilliseconds(100 * (index + 1)),
Duration = TimeSpan.FromMilliseconds(666),
EasingFunction = new CircleEase { EasingMode = EasingMode.EaseOut }
};
this.BeginAnimation(UIElement.OpacityProperty, daopacity);
}
}
}
private T EnsureRenderTransform<T>(UIElement uiTarget)
where T : Transform
{
if (uiTarget.RenderTransform is T)
return uiTarget.RenderTransform as T;
else
{
T instance = typeof(T).Assembly.CreateInstance(typeof(T).FullName) as T;
uiTarget.RenderTransform = instance;
return instance;
}
}
public string Title
{
get { return (string)GetValue(TitleProperty); }
set { SetValue(TitleProperty, value); }
}
// Using a DependencyProperty as the backing store for Title. This enables animation, styling, binding, etc...
public static readonly DependencyProperty TitleProperty =
DependencyProperty.Register("Title", typeof(string), typeof(FormItem), new PropertyMetadata(""));
public ImageSource Icon
{
get { return (ImageSource)GetValue(IconProperty); }
set { SetValue(IconProperty, value); }
}
// Using a DependencyProperty as the backing store for Icon. This enables animation, styling, binding, etc...
public static readonly DependencyProperty IconProperty =
DependencyProperty.Register("Icon", typeof(ImageSource), typeof(FormItem), new PropertyMetadata(null));
}
}
这里在FormItem的构造函数中,添加了一个IsVisibleChanged事件,这个事件会在加载当前控件的时候发生,另外当当前控件的属性值发生变化的时候会触发该效果。其实效果就是同时在X和Y方向做一个平移的效果,这个也是一个常用的效果。
我们重点讨论的是下面的这段代码:
private T EnsureRenderTransform<T>(UIElement uiTarget)
where T : Transform
{
if (uiTarget.RenderTransform is T)
return uiTarget.RenderTransform as T;
else
{
T instance = typeof(T).Assembly.CreateInstance(typeof(T).FullName) as T;
uiTarget.RenderTransform = instance;
return instance;
}
}
这里我们创建TranslateTransform的时候是使用的System.Windows.Media.TranslateTransform transform = EnsureRenderTransform<System.Windows.Media.TranslateTransform>(this);这个方法,而不是每次都new一个对象,每次new一个对象的效率是很低的,而且会占据内存,我们如果已经创建过当前对象完全可以重复利用,这里我们使用了带泛型参数的函数来实现当前效果,typeof(T).Assembly.CreateInstance(typeof(T).FullName) as T,核心是通过程序集来创建对象,这种方式我们也是经常会使用的,比如我们可以通过获取应用程序级别的程序集来通过Activator.CreateInstance来创建窗体等一系列的对象,这种通过反射的机制来扩展的方法是我们需要特别留意的,另外写代码的时候必须注重代码的质量和效率,而不仅仅是实现了某一个功能,这个在以后的开发过程中再一点点去积累去吸收。


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号