WPF中分享一个做四则数学运算的转换器
1 背景
在WPF开发过程中我们经常在进行绑定的过程中不可避免的使用四则运算,例如: x*30 + y/2,如果为每一种运算都单独写一个转换器那么代码中由于不同的需求便会有大量的转换器最终的效果就是代码中大量重复并且十分臃肿,我们知道在WPF中我们经常会用到MultiBinding来绑定多个变量并对这些变量进行运算,今天我就来介绍一个通过ConvertParameter中指定特定表达式的形式来写一个通用的数学转换器从而达到通用的效果。
2 代码展示
我们先来看看整个MathConverter的实现,后面我们再来就这这个代码逐一进行分析和讲解。
/// <summary>
/// Value converter that performs arithmetic calculations over its argument(s)
/// </summary>
/// <remarks>
/// MathConverter can act as a value converter, or as a multivalue converter (WPF only).
/// It is also a markup extension (WPF only) which allows to avoid declaring resources,
/// ConverterParameter must contain an arithmetic expression over converter arguments. Operations supported are +, -, * and /
/// Single argument of a value converter may referred as x, a, or {0}
/// Arguments of multi value converter may be referred as x,y,z,t (first-fourth argument), or a,b,c,d, or {0}, {1}, {2}, {3}, {4}, ...
/// The converter supports arithmetic expressions of arbitrary complexity, including nested subexpressions
/// </remarks>
public class MathConverter : IMultiValueConverter, IValueConverter
{
Dictionary<string, IExpression> _storedExpressions = new Dictionary<string, IExpression>();
public object Convert(object value, Type targetType, object parameter, CultureInfo culture)
{
return Convert(new object[] { value }, targetType, parameter, culture);
}
public object ConvertBack(object value, Type targetType, object parameter, CultureInfo culture)
{
throw new NotImplementedException();
}
public object Convert(object[] values, Type targetType, object parameter, CultureInfo culture)
{
try
{
decimal result = Parse(parameter.ToString()).Eval(values);
if (targetType == typeof(decimal)) return result;
if (targetType == typeof(string)) return result.ToString();
if (targetType == typeof(int)) return (int)result;
if (targetType == typeof(double)) return (double)result;
if (targetType == typeof(long)) return (long)result;
if (targetType == typeof(CornerRadius)) return new CornerRadius((double)result, (double)result, (double)result, (double)result);
if (targetType == typeof(Thickness)) return new Thickness((double)result, (double)result, (double)result, (double)result);
if (targetType == typeof(object)) return result;
throw new ArgumentException(String.Format("Unsupported target type {0}", targetType.FullName));
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
ProcessException(ex);
}
return DependencyProperty.UnsetValue;
}
public object[] ConvertBack(object value, Type[] targetTypes, object parameter, CultureInfo culture)
{
throw new NotImplementedException();
}
protected virtual void ProcessException(Exception ex)
{
Console.WriteLine(ex.Message);
}
private IExpression Parse(string s)
{
IExpression result = null;
if (!_storedExpressions.TryGetValue(s, out result))
{
result = new Parser().Parse(s);
_storedExpressions[s] = result;
}
return result;
}
interface IExpression
{
decimal Eval(object[] args);
}
class Constant : IExpression
{
private decimal _value;
public Constant(string text)
{
if (!decimal.TryParse(text, out _value))
{
throw new ArgumentException(String.Format("'{0}' is not a valid number", text));
}
}
public decimal Eval(object[] args)
{
return _value;
}
}
class Variable : IExpression
{
private int _index;
public Variable(string text)
{
if (!int.TryParse(text, out _index) || _index < 0)
{
throw new ArgumentException(String.Format("'{0}' is not a valid parameter index", text));
}
}
public Variable(int n)
{
_index = n;
}
public decimal Eval(object[] args)
{
if (_index >= args.Length)
{
throw new ArgumentException(String.Format("MathConverter: parameter index {0} is out of range. {1} parameter(s) supplied", _index, args.Length));
}
return System.Convert.ToDecimal(args[_index]);
}
}
class BinaryOperation : IExpression
{
private Func<decimal, decimal, decimal> _operation;
private IExpression _left;
private IExpression _right;
public BinaryOperation(char operation, IExpression left, IExpression right)
{
_left = left;
_right = right;
switch (operation)
{
case '+': _operation = (a, b) => (a + b); break;
case '-': _operation = (a, b) => (a - b); break;
case '*': _operation = (a, b) => (a * b); break;
case '/': _operation = (a, b) => (a / b); break;
default: throw new ArgumentException("Invalid operation " + operation);
}
}
public decimal Eval(object[] args)
{
return _operation(_left.Eval(args), _right.Eval(args));
}
}
class Negate : IExpression
{
private IExpression _param;
public Negate(IExpression param)
{
_param = param;
}
public decimal Eval(object[] args)
{
return -_param.Eval(args);
}
}
class Parser
{
private string text;
private int pos;
public IExpression Parse(string text)
{
try
{
pos = 0;
this.text = text;
var result = ParseExpression();
RequireEndOfText();
return result;
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
string msg =
String.Format("MathConverter: error parsing expression '{0}'. {1} at position {2}", text, ex.Message, pos);
throw new ArgumentException(msg, ex);
}
}
private IExpression ParseExpression()
{
IExpression left = ParseTerm();
while (true)
{
if (pos >= text.Length) return left;
var c = text[pos];
if (c == '+' || c == '-')
{
++pos;
IExpression right = ParseTerm();
left = new BinaryOperation(c, left, right);
}
else
{
return left;
}
}
}
private IExpression ParseTerm()
{
IExpression left = ParseFactor();
while (true)
{
if (pos >= text.Length) return left;
var c = text[pos];
if (c == '*' || c == '/')
{
++pos;
IExpression right = ParseFactor();
left = new BinaryOperation(c, left, right);
}
else
{
return left;
}
}
}
private IExpression ParseFactor()
{
SkipWhiteSpace();
if (pos >= text.Length) throw new ArgumentException("Unexpected end of text");
var c = text[pos];
if (c == '+')
{
++pos;
return ParseFactor();
}
if (c == '-')
{
++pos;
return new Negate(ParseFactor());
}
if (c == 'x' || c == 'a') return CreateVariable(0);
if (c == 'y' || c == 'b') return CreateVariable(1);
if (c == 'z' || c == 'c') return CreateVariable(2);
if (c == 't' || c == 'd') return CreateVariable(3);
if (c == '(')
{
++pos;
var expression = ParseExpression();
SkipWhiteSpace();
Require(')');
SkipWhiteSpace();
return expression;
}
if (c == '{')
{
++pos;
var end = text.IndexOf('}', pos);
if (end < 0) { --pos; throw new ArgumentException("Unmatched '{'"); }
if (end == pos) { throw new ArgumentException("Missing parameter index after '{'"); }
var result = new Variable(text.Substring(pos, end - pos).Trim());
pos = end + 1;
SkipWhiteSpace();
return result;
}
const string decimalRegEx = @"(\d+\.?\d*|\d*\.?\d+)";
var match = Regex.Match(text.Substring(pos), decimalRegEx);
if (match.Success)
{
pos += match.Length;
SkipWhiteSpace();
return new Constant(match.Value);
}
else
{
throw new ArgumentException(String.Format("Unexpeted character '{0}'", c));
}
}
private IExpression CreateVariable(int n)
{
++pos;
SkipWhiteSpace();
return new Variable(n);
}
private void SkipWhiteSpace()
{
while (pos < text.Length && Char.IsWhiteSpace((text[pos]))) ++pos;
}
private void Require(char c)
{
if (pos >= text.Length || text[pos] != c)
{
throw new ArgumentException("Expected '" + c + "'");
}
++pos;
}
private void RequireEndOfText()
{
if (pos != text.Length)
{
throw new ArgumentException("Unexpected character '" + text[pos] + "'");
}
}
}
}
3 代码分析
3.1 IExpression
首先我们发现在Convert方法中调用了一个私有的Parse方法用于将外部传入的ConverterParameter转化为一个IExpression的接口,我们这里首先来看看这个接口的定义:
interface IExpression
{
decimal Eval(object[] args);
}
我们再来看看这个接口的实现:
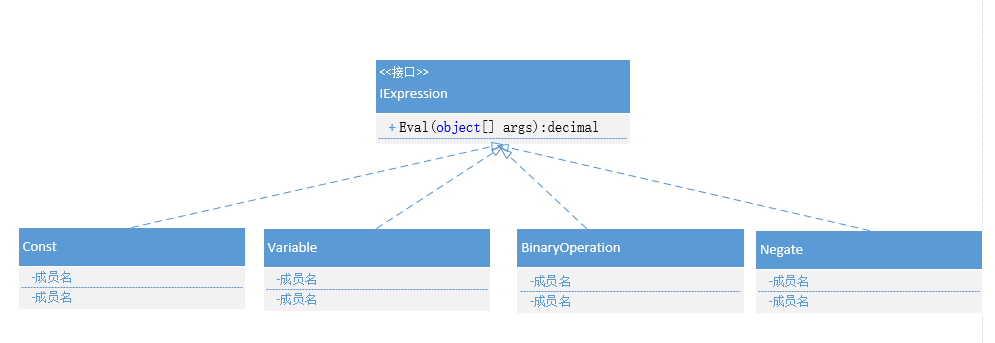
通过这张图我们知道了我们总共定义了四种类型的Expression,用于将数据源中的数据转化成一个decimal类型的数据,这里比较特殊的一类是BinaryOperation类型的定义,这个是转换加减乘除操作的关键,它内部实现的时候能够识别外部传入的操作符,并对左右两个Expression进行四则运算。
3.2 支持的表达式类型
当然我们的转换器中不可能包罗万象,现在的代码中仅仅支持下面的几种使用类型,使用时需要特别注意。
- 42.8
- a+b*c
- a+1 或者 x+1 或者 {0}+1
- (x-1)/(x+1)
- -x*(x+9.5)
3.3 Parser类重点概念理解
我们发现这里面的核心内容都是在一个Parser的内部类中完成的,Parser是一个经典的递归下降解析器。 它使用了一个简单的算术表达式语法,它的变体可以在几乎每一本关于编译器的书中找到,如果你对编译器十分了解的话对这个肯定是十分了解的,在理解这部分代码之前我们先来了解一下Parser中使用的一些基础概念
- Expression(表达式)= Expression + Term
- Expression(表达式= Experssion - Term
- Term (术语)= Term * Factor
- Term (术语)= Term / Factor
- Factor(要素)= constant(常量)
- Factor(要素)= variable(变量)
- Factor(要素)= -Factor
- Factor(要素)= +Factor
- Factor(要素)= (Expression)
有了上面的讲述,你对里面的重点方法ParseExpression()、ParseTerm()、ParseFactor()、以及为什么需要这样进行定义,以及如何一层层向下调用有了更加深入的理解,我们在解析表达式的时候,我们把+或者-之间的部分当做一个Term来处理,然后再解析这个Term中的Factor,这里需要注意的是我们在解析*或者/运算的时候,会将左右两侧的部分最终解析成一个BinaryOperation的结构,另外在解析Factor的时候如果我们遇到了()这种类型的结构时我们会将整个结构又重新当做一个表达式从头开始进行解析,这个需要特别注意。
4 使用范例
上面说了这么多,回归到本质我们需要知道怎么使用这个MathConverter,通过下面的例子相信你会有一个清晰的使用方式。
4.1 简单用法
<RotateTransform Angle="{Binding Text, ElementName=Seconds,
Converter={ikriv:MathConverter}, ConverterParameter=x*6}" />
4.2 进阶用法
<!-- WPF -->
<!-- small hand (hours) -->
<Line X1="0" Y1="0" X2="0" Y2="-35"
Stroke="Black" StrokeThickness="4">
<Line.RenderTransform>
<RotateTransform>
<RotateTransform.Angle>
<MultiBinding Converter="{ikriv:MathConverter}"
ConverterParameter="x*30 + y/2">
<Binding Path="Text" ElementName="Hours" />
<Binding Path="Text" ElementName="Minutes" />
</MultiBinding>
</RotateTransform.Angle>
</RotateTransform>
</Line.RenderTransform>
</Line>
这里的核心是我们通过ConverterParameter="x*30 + y/2"来定义我们的使用表达式,这个表达式的定义就需要根据我们的需要来进行自定义了,当然这些自定义的规则需要匹配我们代码中的要求,比如使用x,y,z,t或者a,b,c,d来进行定义,如果有更多的参数使用{0}、{1}、{2}......这种方式来进行定义...



