java-stream-泛型
一、测试代码
public static void main(String[] args) { SelfList<Apple> appleList = new SelfList<>(); appleList.add(new Apple(1, "青色")); appleList.add(new Apple(2, "橙色")); appleList.add(new Apple(3, "红色")); appleList.add(new Apple(4, "绿色")); appleList.add(new Apple(5, "绿色")); appleList.add(new Apple(6, "紫色")); SelfList<Integer> greenAppleWightList = appleList.selfStream() .filter(item -> "绿色".equals(item.getColor())) .map(Apple::getWeight) .collect(SelfCollectors.toList()); System.out.println(greenAppleWightList);
}
二、涉及到的泛型
从后向前看
1,SelfCollectors.toList()
public final class SelfCollectors { public static <T> SelfCollector<T, ?> toList() { return new SelfCollectorImpl<>((Supplier<List<T>>) SelfList::new, List::add); } static class SelfCollectorImpl<T, A> implements SelfCollector<T, A> { private final Supplier<A> supplier; private final BiConsumer<A, T> accumulator; SelfCollectorImpl(Supplier<A> supplier, BiConsumer<A, T> accumulator) { this.supplier = supplier; this.accumulator = accumulator; } @Override public BiConsumer<A, T> accumulator() { return accumulator; } @Override public Supplier<A> supplier() { return supplier; } } }
假设SelfCollectorImpl已经定义好了,toList方法你会怎么写?
public static <T> SelfCollector<T, ?> toList() { return new SelfCollectorImpl<T, SelfList<T>>( // 参数1:Supplier类型 new Supplier<SelfList<T>>() { @Override public SelfList<T> get() { return new SelfList<T>(); } }, // 参数2:BiConsumer类型 new BiConsumer<SelfList<T>, T>() { @Override public void accept(SelfList<T> list, T t) { list.add(t); } } ); }
然后代码开发工具提示可以进行简化;
简化1,首先,由于传入的两个new 参数已经确定了SelfCollectorImpl类的泛型,如下图
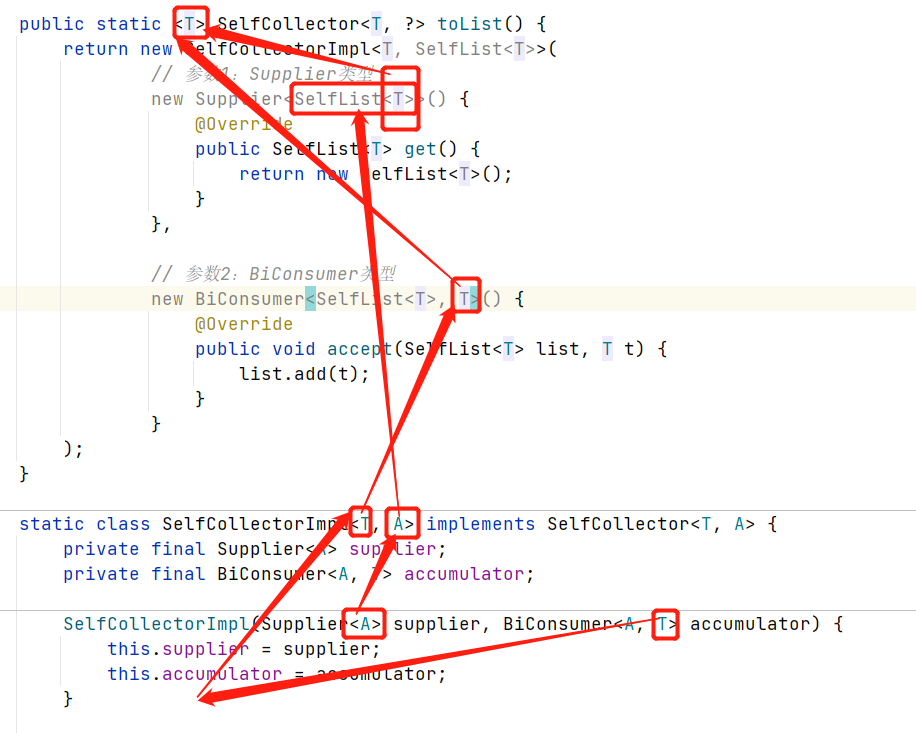
所以,可以简化为:
public static <T> SelfCollector<T, ?> toList() { return new SelfCollectorImpl<>( // 参数1:Supplier类型 new Supplier<SelfList<T>>() { @Override public SelfList<T> get() { return new SelfList<T>(); } }, // 参数2:BiConsumer类型 new BiConsumer<SelfList<T>, T>() { @Override public void accept(SelfList<T> list, T t) { list.add(t); } } ); }
简化2,简化为lambda表达式:
public static <T> SelfCollector<T, ?> toList() { return new SelfCollectorImpl<>( // 参数1:Supplier类型 () -> new SelfList<T>(), // 参数2:BiConsumer类型 (list, t) -> list.add(t) ); }
简化3,Replace lambda with method reference:
public static <T> SelfCollector<T, ?> toList() { return new SelfCollectorImpl<>( // 参数1:Supplier类型 (Supplier<SelfList<T>>) SelfList::new, // 参数2:BiConsumer类型 ArrayList::add ); }
以上是通过Supplier先指定了SelfCollectorImpl的泛型A,A确定了,通过BiConsumer的定义,T也就确定了,如下图:
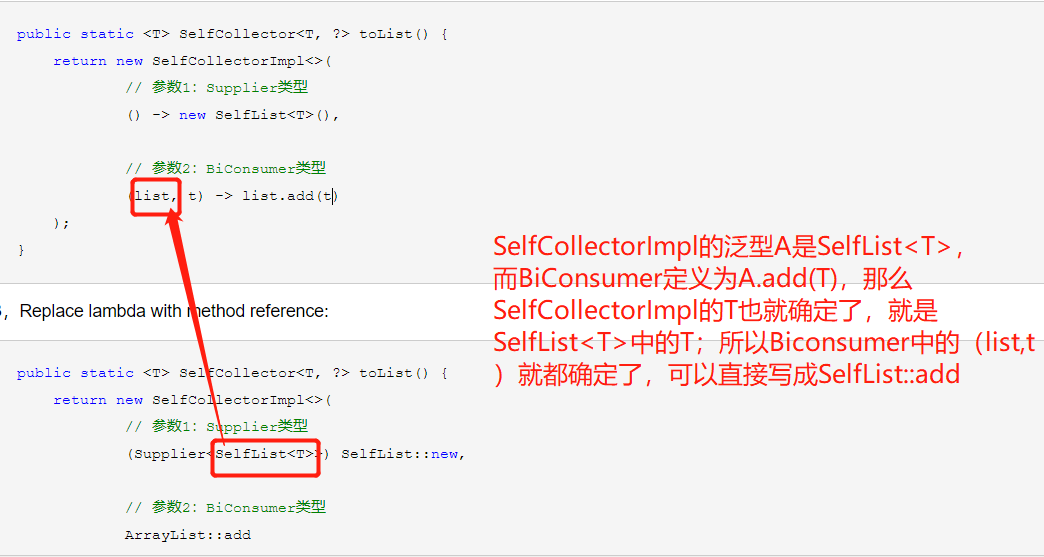
也可以改写成先通过BiConsumer来指定泛型:
public static <T> SelfCollector<T, ?> toList() { return new SelfCollectorImpl<>( // 参数1:Supplier类型 SelfList::new, // 参数2:BiConsumer类型 (BiConsumer<SelfList<T>, T>) SelfList::add ); }
再回溯一下原因:
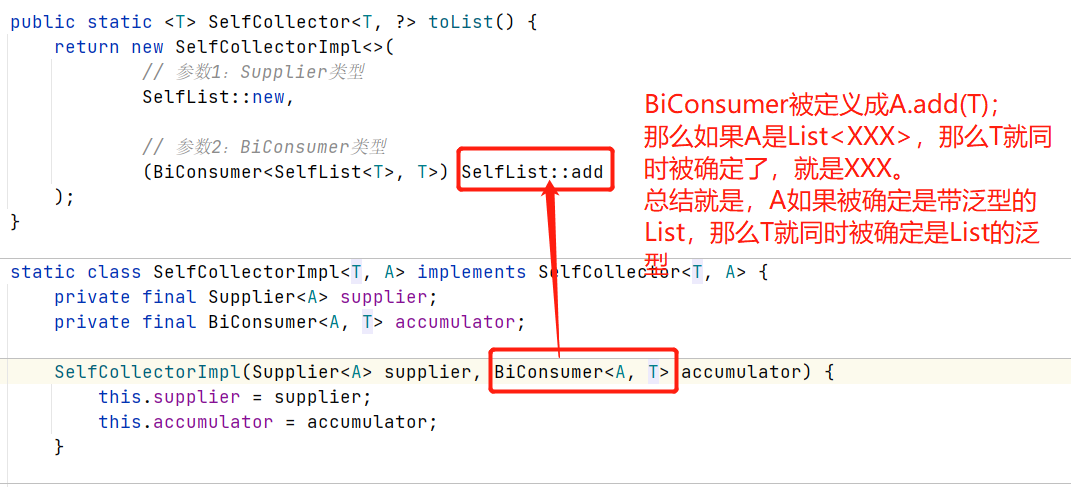
2,A是SelfList<T>,T是什么?看.collect
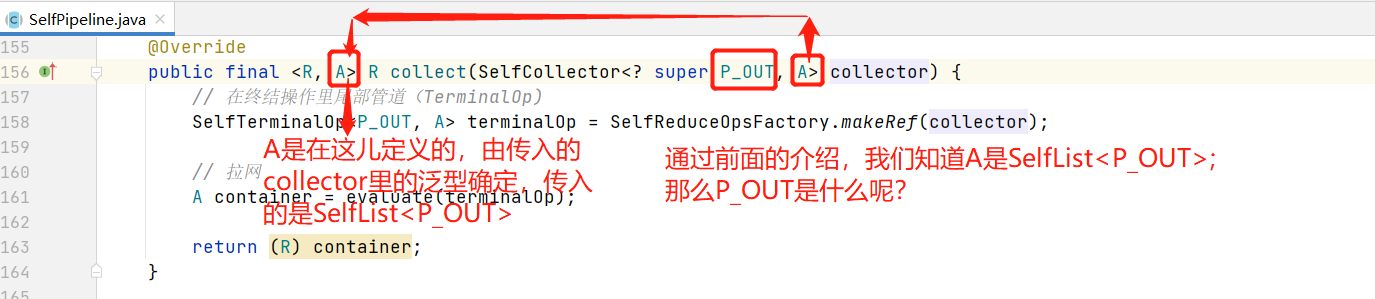
知道了P_OUT是什么,就知道答案了;
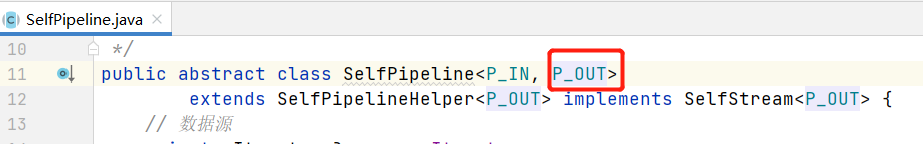
P_OUT是管道流的输出,看看管道流的输出是什么;
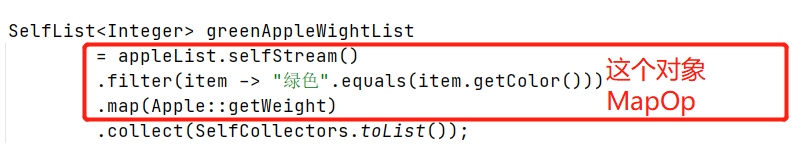
MapOp这个管道流对象调用了.collect方法,所以 P_OUT就是 MapOp的输出,看看MapOp的输出是什么?
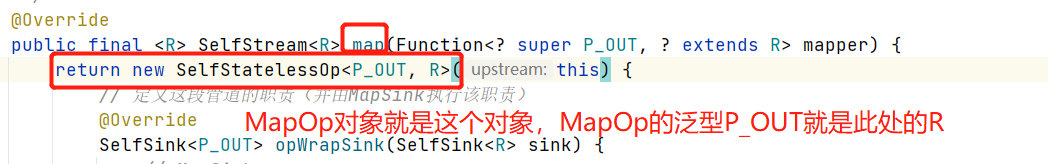

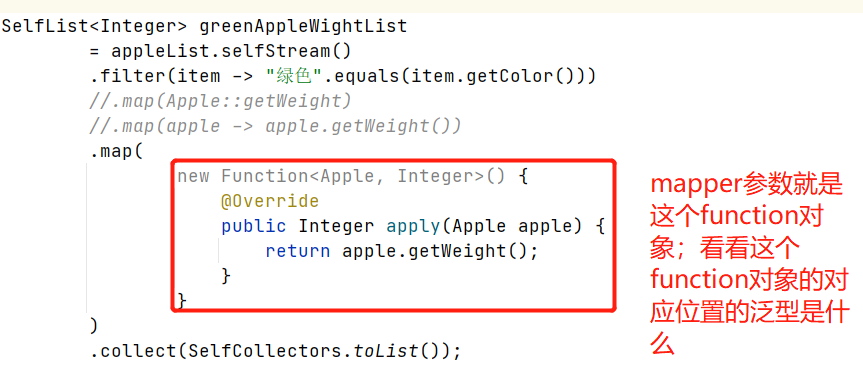
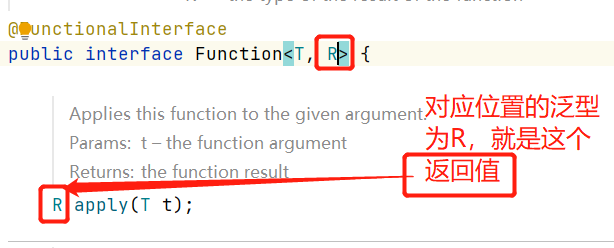
所以,MapOp的输出是个Integer,所以SelfList<T>的T是个Integer。
三、总结
类泛型、接口泛型都是在类名和接口名后定义,方法泛型在方法名前面定义;
泛型可以通过new的时候、方法参数的时候或者其他地方指定(赋予实际类型);
通过以上的java-stream的例子可以看出,泛型经常被传递,需要一路抽丝剥茧、顺藤摸瓜才能最终搞清楚泛型的具体实际类型;
四、遗留的问题
作出推测,泛型应该只在一个地方生效,如果要在其他地方生效,就需要传递;
而且对于编译器而言,应该是顺序向后传递的,这样编译的时候才能保证任何地方都能泛型擦除后,强转回来;


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号