pytorch实现yolov3(3) 实现forward
之前的文章里https://www.cnblogs.com/sdu20112013/p/11099244.html实现了网络的各个layer.
本篇来实现网络的forward的过程.
定义网络
class Darknet(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, cfgfile):
super(Darknet, self).__init__()
self.blocks = parse_cfg(cfgfile)
self.net_info, self.module_list = create_modules(self.blocks)
实现网络的forward过程
forward函数继承自nn.Module
Convolutional and Upsample Layers
if module_type == "convolutional" or module_type == "upsample":
x = self.module_list[i](x)
Route Layer / Shortcut Layer
在上一篇里讲过了,route layer的输出是之前某一层或某两层在depth方向的连接.即
output[current_layer] = output[previous_layer]
或者
map1 = outputs[i + layers[0]]
map2 = outputs[i + layers[1]]
output[current layer]=torch.cat((map1, map2), 1)
所以route layer代码如下:
elif module_type == "route":
layers = module["layers"]
layers = [int(a) for a in layers]
if (layers[0]) > 0:
layers[0] = layers[0] - i
if len(layers) == 1:
x = outputs[i + (layers[0])]
else:
if (layers[1]) > 0:
layers[1] = layers[1] - i
map1 = outputs[i + layers[0]]
map2 = outputs[i + layers[1]]
x = torch.cat((map1, map2), 1)
shortcut layer的输出为前一层及前xx层(配置文件中配置)的输出之和
elif module_type == "shortcut":
from_ = int(module["from"])
x = outputs[i-1] + outputs[i+from_]
YOLO layer
yolo层的输出是一个n*n*depth的feature map矩阵.假设你想访问第(5,6)个cell的第2个boundingbox的话你需要map[5,6,(5+C):2*(5+C)]这样访问,这种形式操作起来有点麻烦,所以我们引入一个predict_transform函数来改变一下输出的形式.
简而言之我们希望把一个batch_size*grid_size*grid_size*(B*(5+C))的4-D矩阵转换为batch_size*(grid_size*grid_size*B)*(5+C)的矩阵.
2-D矩阵的每一行的排列如下:
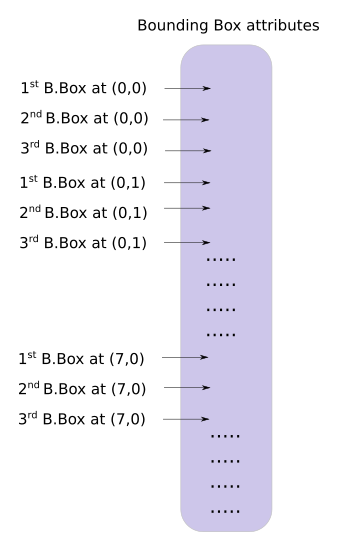
batch_size = prediction.size(0)
stride = inp_dim // prediction.size(2)
grid_size = inp_dim // stride
bbox_attrs = 5 + num_classes
num_anchors = len(anchors)
prediction = prediction.view(batch_size, bbox_attrs*num_anchors, grid_size*grid_size)
prediction = prediction.transpose(1,2).contiguous()
prediction = prediction.view(batch_size, grid_size*grid_size*num_anchors, bbox_attrs)
上述代码涉及到pytorch中view的用法,和numpy中resize类似.contiguous一般与transpose,permute,view搭配使用,维度变换后tensor在内存中不再是连续存储的,而view操作要求连续存储,所以需要contiguous.最终我们得到一个batch_size*(grid_size*grid_size*num_anchors)*bbox_attrs的矩阵.
接下来要对预测boundingbox的坐标.
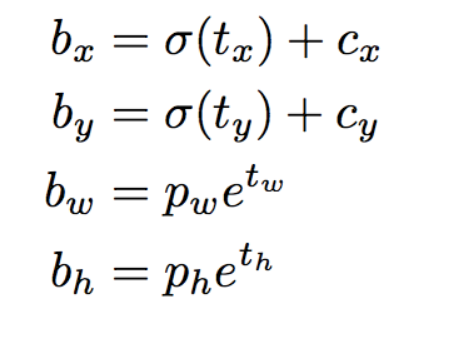
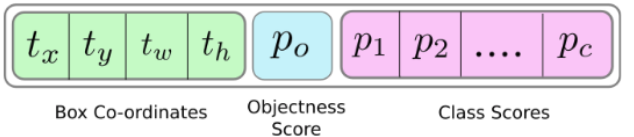
注意此时prediction[:,:,0],prediction[:,:,1],prediction[:,:,2],prediction[:,:,3]prediction[:,:,4]即相应的tx,ty,tw,th,obj score.
接下来是预测相对当前cell左上角的offset
#sigmoid转换为0-1范围内
#Sigmoid the centre_X, centre_Y. and object confidencce
prediction[:,:,0] = torch.sigmoid(prediction[:,:,0])
prediction[:,:,1] = torch.sigmoid(prediction[:,:,1])
prediction[:,:,4] = torch.sigmoid(prediction[:,:,4])
#Add the center offsets
grid = np.arange(grid_size)
a,b = np.meshgrid(grid, grid)
x_offset = torch.FloatTensor(a).view(-1,1)
y_offset = torch.FloatTensor(b).view(-1,1)
if CUDA:
x_offset = x_offset.cuda()
y_offset = y_offset.cuda()
x_y_offset = torch.cat((x_offset, y_offset), 1).repeat(1,num_anchors).view(-1,2).unsqueeze(0)
#prediction[:,:,:0],prediction[:,:,:1]修改为相对于当前cell偏移
prediction[:,:,:2] += x_y_offset
有关meshgrid用法效果如下:
import numpy as np
import torch
grid_size = 13
grid = np.arange(grid_size)
a,b = np.meshgrid(grid, grid)
print(a)
print(b)
x_offset = torch.FloatTensor(a).view(-1,1)
#print(x_offset)
y_offset = torch.FloatTensor(b).view(-1,1)
这段代码输出如下:

预测boundingbox的width,height.注意anchors的大小要转换为适配当前feature map的大小.配置文件中配置的是相对于模型输入的大小.
anchors = [(a[0]/stride, a[1]/stride) for a in anchors] #适配到feature map上的尺寸
#log space transform height and the width
anchors = torch.FloatTensor(anchors)
if CUDA:
anchors = anchors.cuda()
anchors = anchors.repeat(grid_size*grid_size, 1).unsqueeze(0)
prediction[:,:,2:4] = torch.exp(prediction[:,:,2:4])*anchors
##还原为原始图片上对应的坐标
prediction[:,:,:4] *= stride
预测class probability
prediction[:,:,5: 5 + num_classes] = torch.sigmoid((prediction[:,:, 5 : 5 + num_classes]))
predict_transform完整代码如下
#yolo经过不断地卷积得到的feature map size= batch_size*(B*(5+C))*grid_size*grid_size
def predict_transform(prediction, inp_dim, anchors, num_classes, CUDA = True):
if CUDA:
prediction = prediction.to(torch.device("cuda")) #使用gpu torch0.4不需要 torch1.0需要
batch_size = prediction.size(0)
stride = inp_dim // prediction.size(2)
grid_size = inp_dim // stride
bbox_attrs = 5 + num_classes
num_anchors = len(anchors)
print("prediction.shape=",prediction.shape)
print("batch_size=",batch_size)
print("inp_dim=",inp_dim)
#print("anchors=",anchors)
#print("num_classes=",num_classes)
print("grid_size=",grid_size)
print("bbox_attrs=",bbox_attrs)
prediction = prediction.view(batch_size, bbox_attrs*num_anchors, grid_size*grid_size)
prediction = prediction.transpose(1,2).contiguous()
prediction = prediction.view(batch_size, grid_size*grid_size*num_anchors, bbox_attrs)
#Sigmoid the centre_X, centre_Y. and object confidencce
prediction[:,:,0] = torch.sigmoid(prediction[:,:,0])
prediction[:,:,1] = torch.sigmoid(prediction[:,:,1])
prediction[:,:,4] = torch.sigmoid(prediction[:,:,4])
#Add the center offsets
grid = np.arange(grid_size).astype(np.float32)
a,b = np.meshgrid(grid, grid)
x_offset = torch.FloatTensor(a).view(-1,1)
y_offset = torch.FloatTensor(b).view(-1,1)
if CUDA:
x_offset = x_offset.cuda()
y_offset = y_offset.cuda()
x_y_offset = torch.cat((x_offset, y_offset), 1).repeat(1,num_anchors).view(-1,2).unsqueeze(0)
print(type(x_y_offset),type(prediction[:,:,:2]))
prediction[:,:,:2] += x_y_offset
anchors = [(a[0]/stride, a[1]/stride) for a in anchors] #适配到和feature map大小匹配
#log space transform height and the width
anchors = torch.FloatTensor(anchors)
if CUDA:
anchors = anchors.cuda()
anchors = anchors.repeat(grid_size*grid_size, 1).unsqueeze(0)
prediction[:,:,2:4] = torch.exp(prediction[:,:,2:4])*anchors
prediction[:,:,5: 5 + num_classes] = torch.sigmoid((prediction[:,:, 5 : 5 + num_classes]))
prediction[:,:,:4] *= stride #恢复到原始图片上的相应坐标,width,height等
return prediction
助手函数写好了,现在来继续实现Darknet类的forward方法
elif module_type == "yolo":
anchors = self.module_list[i][0].anchors
inp_dim = int(self.net_info["height"])
num_classes = int (module["classes"])
x = x.data
x = predict_transform(x, inp_dim, anchors, num_classes, CUDA)
if not write: #if no collector has been intialised.
detections = x
write = 1
else:
detections = torch.cat((detections, x), 1)
在没有写predict_transform之前,不同的feature map矩阵,比如13*13*N1,26*26*N2,52*52*N3是没法直接连接成一个tensor的,现在都变成了xx*(5+C)则可以了.
上面代码里的write flag主要是为了区别detections是否为空,为空则说明是第一个yolo layer做的预测,将yolo层的输出赋值给predictions,不为空则连接当前yolo layer的输出至detections.
测试
下载测试图片wget https://github.com/ayooshkathuria/pytorch-yolo-v3/raw/master/dog-cycle-car.png
def get_test_input():
img = cv2.imread("dog-cycle-car.png")
img = cv2.resize(img, (608,608)) #Resize to the input dimension
img_ = img[:,:,::-1].transpose((2,0,1)) # BGR -> RGB | H X W C -> C X H X W
img_ = img_[np.newaxis,:,:,:]/255.0 #Add a channel at 0 (for batch) | Normalise
img_ = torch.from_numpy(img_).float() #Convert to float
img_ = Variable(img_) # Convert to Variable
return img_
model = Darknet("cfg/yolov3.cfg")
inp = get_test_input()
pred = model(inp, torch.cuda.is_available())
print (pred)
cv2.imread()导入图片时是BGR通道顺序,并且是h*w*c,比如416*416*3这种格式,我们要转换为3*416*416这种格式.如果有
- RuntimeError: expected type torch.FloatTensor but got torch.cuda.FloatTensor
在predict_transform开头添加prediction = prediction.to(torch.device("cuda")) #使用gpu - RuntimeError: shape '[1, 255, 3025]' is invalid for input of size 689520
注意检查你的input的img的大小和你模型的输入大小是否匹配. 比如模型是608*608的
最终测试结果如下:
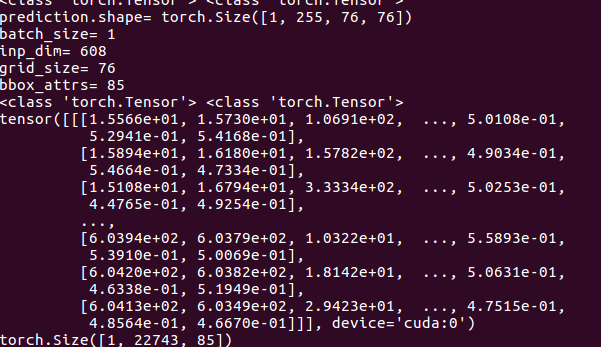
预测出22743个boundingbox,一共3种feature map,分别为19*19,38*38,76*76 每种尺度下预测出3个box,一共3*(19*19 + 38*38 + 76*76) = 22743个box.


【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· AI与.NET技术实操系列:向量存储与相似性搜索在 .NET 中的实现
· 基于Microsoft.Extensions.AI核心库实现RAG应用
· Linux系列:如何用heaptrack跟踪.NET程序的非托管内存泄露
· 开发者必知的日志记录最佳实践
· SQL Server 2025 AI相关能力初探
· winform 绘制太阳,地球,月球 运作规律
· 震惊!C++程序真的从main开始吗?99%的程序员都答错了
· 【硬核科普】Trae如何「偷看」你的代码?零基础破解AI编程运行原理
· AI与.NET技术实操系列(五):向量存储与相似性搜索在 .NET 中的实现
· 超详细:普通电脑也行Windows部署deepseek R1训练数据并当服务器共享给他人